xyz-cli
v0.4.2
Published
Command line tool dor node xyz
Downloads
3,623
Readme
xyz-cli
Command line Interface for node-xyz
Usage
xyz-cli can be installed using
$ npm install -g xyz-cliThe cli app is xyz and should be available in your command line environment.
Commands
dev
This command is the most useful one in xyz-cli. It runs a set of xyz-core instances according to a config file.
xyz dev [options] [xyzCommandLineArgs...]where options can be:
| option (short and long form) | default value | Description |
| :------------- | :------------- | :----------|
| -c --config| ./xyzrc.json | the config file to use when running microservices. More information is given below |
| -e --errlog | false | will print the logs of each service in the init phase to terminal, even of stdout is set to false in the config file. |
| -x --xyzadmin | false | will create a new xyz-core instance inside the cli process. More information given below |
| -d --delay | 500 | the delay between spawning new processes in milliseconds. |
xyzCommandLineArgs can be an optional set of parameters passed to the xyz-core instance created inside the cli process. Hence, this works only when -x is activated. They act exactly like passing --xyz- prefixed arguments to a single process. The main difference is that in this case -- MUST be omitted.
Example:
xyz dev -x -c ./xyzrc.json xyz-name my-cli-node xyz-transport.0.port 8000
In this case, aside from whatever that is inside the config file, a new xyz-core instance will be creted with name my-cli-node and on port 8000
The Config File
The config file should be json file with the following format:
{
"nodes": [
{
"path": "path/to/my/file.js",
"instance": 2,
"port": 5000,
"increment": 100,
"stdio": "console",
"params": ""
},
...
]
}Where the keys cna be:
| Key name | Description |
| :------------- | :------------- |
| path | path to the .js file relative to where xyz command is running |
| instance | The number of instances to create |
| port | starting port for this set of instances. xyz-cli will automatically override the port given in selfConf. |
| increment | increment value in port when instance is more than one |
| stdio | destination of the node's output. can be console or file. if file is selected, the node's output will be written to a file with appropriate name in a new folder named log relative to where the .js file is.|
| params | values passed to the process as process.argv. can be anything with --xyz prefix similar to how a single ndoe's configuration can be overwritten with command line arguments.|
| env | environemtns variables passed to the process.|
As an example, the above code will generate two file.js nodes, one in port 5000 and the other in 5100.
xyz-cli will only override the port of the first server. The rest should be handled by the developer.
If you set
stdiotoconsole, everything will be printed to just one terminal. This might get messy and using the rest of the commands is near to impossible.
for the rest of this document we will use the two files in exampels folder of this repository as an example. The config file is:
{
"nodes": [
{
"path": "string.ms.js",
"instance": 3,
"port": 5000,
"increment": 100,
"stdio": "file",
"params": "--xyz-logLevel verbose --xyz-seed 127.0.0.1:4000"
},
{
"path": "math.ms.js",
"instance": 1,
"port": 4000,
"stdio": "file",
"params": "--xyz-logLevel verbose --xyz-name math.ms.master"
},
{
"path": "math.ms.js",
"instance": 1,
"port": 6000,
"stdio": "file",
"env": "foo bar"
"params": "--xyz-logLevel verbose --xyz-seed 127.0.0.1:4000 --xyz-name math.ms.slave"
}
]
}ls
After a successful dev command, it will list all running nodes. For the previous example it will print:
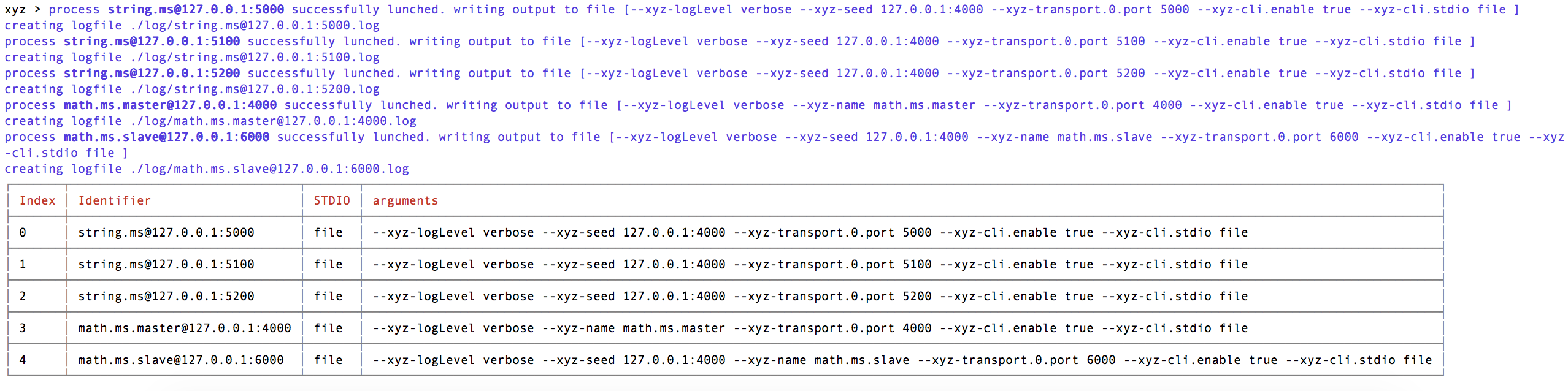
top
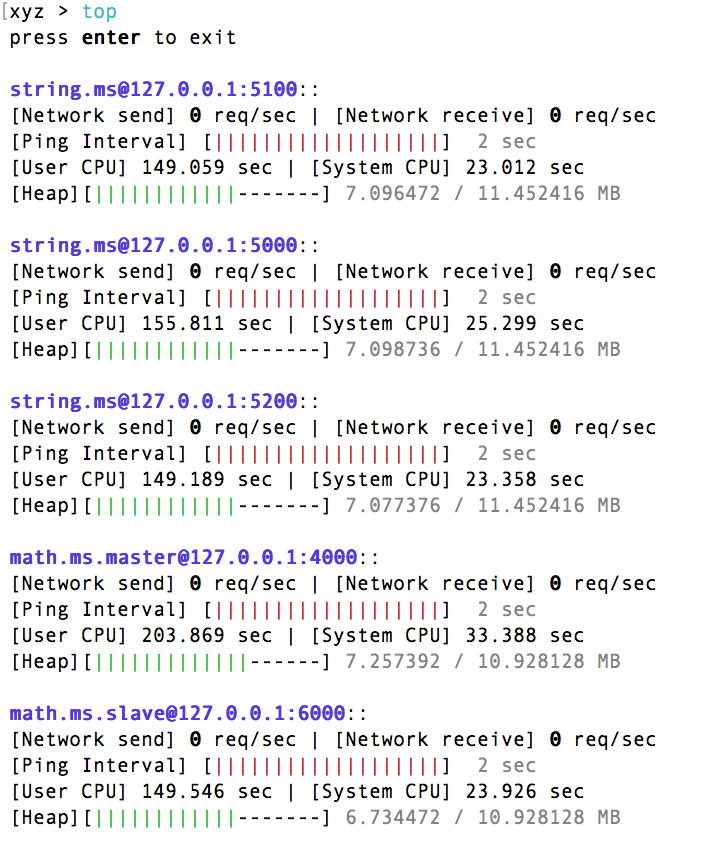
Will print the live updates of the nodes usage. Example:
inspect
<identifier>
will print all of the information that were printed using console.log in the main program. Example:
Identifier can be the index or identifier mentioned in the ls command. As an example, both inspect 0 and inspect [email protected]:5000 are valid.
All of the commands that accept an
<identifier>as argument have the same rule as above.
inspectJSON
<identifier>
Will return all of the information in inspect
inspectSelf
Will inspect the cli's node. Will work only when -x is active.
log
<identifier>
Will start logging the output of a specific microservice to the terminal. It is useful only when stdio in the config file is set to file.
kill
<identifier>
Kills a specific node.
restart
<identifier>
Will restart a specific node. useful while development.
duplicate
<identifier>
Will duplicate a specific node. This will create an Identical node with the same configurations, except the port. it will automatically increment the port of the source node util it finds an empty port for the new node (This might cause some problems if each node is having multiple servers)
msg
<identifier> <servicePath> [payload]
Will send a message to <indentifier> using <servicePath> with an optional payload [payload]. This will only work when you run services with -x and all nodes use the default ping as their service discovery mechanism.
The admin node (dev -x)
This option can be enabled to create a xyz-core instance inside the cli. This node will automatically expose some services so that other cli nodes (or basically any other client) can use them:
Services:
anonymousFN @ /node/get
anonymousFN @ /node/create
anonymousFN @ /node/restart
anonymousFN @ /node/kill
anonymousFN @ /node/duplicate
anonymousFN @ /node/inspect
anonymousFN @ /node/inspectJSON