wgsl-debug
v0.0.1
Published
Typescript library providing print-like function to WGSL shader
Downloads
7
Readme
Typescript library providing print-like function to WGSL shader
|  |
|:--:|
| Go to example - View code |
|
|:--:|
| Go to example - View code |
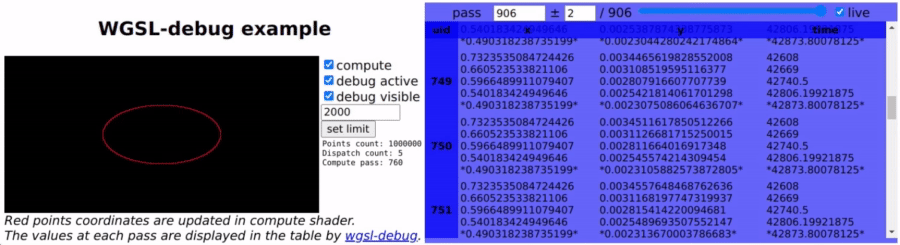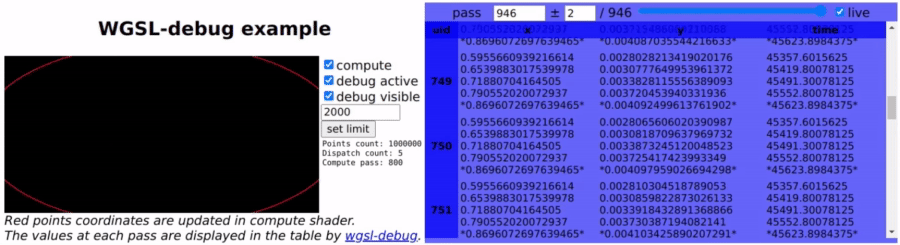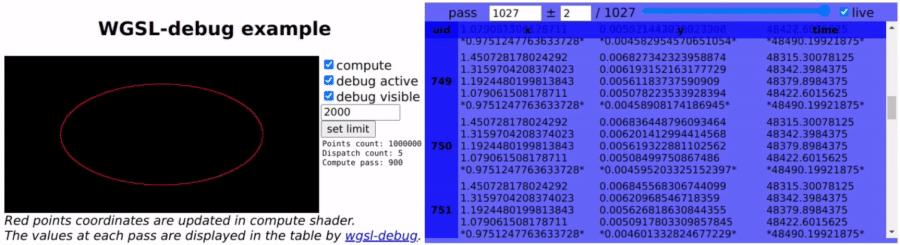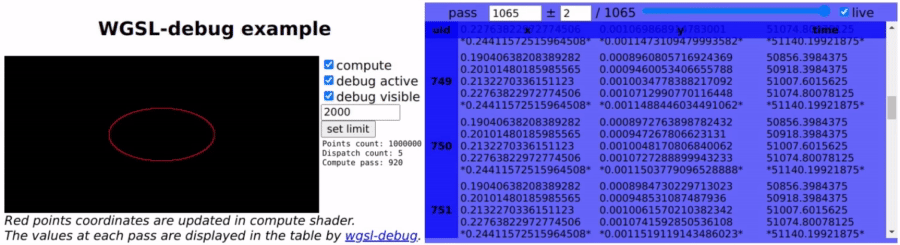
wgsl-debug provides print-like function for WebGPU WGSL shaders to print numbers through javascript console or user callback.
wgsl-debug-table provides a component to easily display the debugging data into dynamically updated HTML table.
Internaly it works by copying the debug data from GPU to a buffer, mapped and copied at each pass back to CPU to extract the data.
Debugged variables can be u32, i32 or f32 using the following functions:
dbg_u32(val: u32);
dbg_i32(val: i32);
dbg_f32(val: f32);Debugged variables can be numbered and named using 'marks', for better readability using the following functions.
dbg_u32m(mark: i32, val: u32); // variable name
dbg_i32m(mark: i32, val: i32); // variable name
dbg_f32m(mark: i32, val: f32); // variable nameThe comment on the debug call line will be used as the variable name.
Build
- wgsl-debug:
npm install
npm run build- wgsl-debug-table:
cd wgsl-debug-table/
npm install
npm run buildUsage: display debug values in HTML table
You can use example/main.ts to get started:
cd example/
npm install
npm run build
npm run previewdebugging setup in CPU javascript code
// import wgsl-debug and wgsl-debug-table
import { WGSL_debug } from 'wgsl-debug'
import { WGSL_debug_table } from 'wgsl-debug-table'
// create and setup the WGSL_debug object
const debug = WGSL_debug(1); // debugging buffers will use bindgroup 1
// set the output to be displayed in an HTML table
// debug_div_id is the HTML id of a div where you want the debug data to be displayed
const debug_table = WGSL_debug_table("debug_div_id");
debug.set_output(debug_table);
// add wgsl-debug functions to your shader
// shader_src is a string containing your shader code
// 'true' means the debugging is active
shader_src = debug.add_shader(shader_src, true);
// setup debugging for 1000 invocations per pass
debug.setup(device, 1000);
// add the debug buffer bind group
debug.create_bindgroup(pipeline);
// in each render/compute loop:
// set the debug bindgroup
debug.set_bindgroup(pass);
// collect debug data from the shader
debug.fetch(cmd_encoder);
// HTML table will be updated with the values of shader dbg_*() calls from the current pass
await debug.process();debug calls in GPU shader code
// call dbg_init
// 'invocation_index' is a u32 that must be unique within a pass
// it can be calculated for example from @builtin(global_invocation_id)
dbg_init(invocation_index);
// call the needed debugging functions
// 'my_spurious_var' is the variable we want the value to be printed
dbg_u32(my_spurious_var);
dbg_i32(my_spurious_var_i);
dbg_f32(my_spurious_var_f);
// call debug with a 'mark'
// '0' is an arbitrary mark number
// the comment 'spurious var' will be associated with mark '0' and printed in the html table
dbg_u32m(my_spurious_var, 0); // spurious var
dbg_i32m(my_spurious_var_i, 1); // spurious var i
dbg_f32m(my_spurious_var_f, 2); // spurious var fUsage: print debug values in the javascript console
Changes for the javascript code:
// only import wgsl-debug
// no call to debug.set_output()
// the values of shader dbg_*() calls from the current pass will be printed to javascript console
await debug.post()Usage: javascript callback function containing debug values
Changes for the javascript code:
// only import wgsl-debug
// no call to debug.set_output()
// cb_func gets called with an array of the values from the shader dbg_*() calls of the current pass
await debug.post(cb_func)