vue-form-base
v0.0.4
Published
Form-Generator: a Vue 2.0 component, reactive Result using Vuex, responsive Display
Downloads
33
Maintainers
Readme
Vue-Form-Base
Vue-Form-Base is a Vue 2.0 Component and Form-Generator for editing plain or deep nested Javascript objects getting a reactive Result.
You have to create a lot of different forms? Vue-Form-Base can simplify your job by creating forms from JS-Objects.
Select from different HTML5 Input-types like Text, Password, Checkboxes, Radios, Select, Multiselect, Color, Files or a lot of other fields. Apart from 'select' or multiselect' the Browser specific implementation of Input-Types is used. Some Informations to HTML5 input-types here
We use the Materialize CSS framework for styling. Input Fields have a clear, minimalistic design, but don't worry you can change your style with CSS in a lot of ways. For more details see section Style with CSS
Add global Validation to the form or validate only a single field. Use inline validation or write a new function for individuell validation.
Make complex data editable by mapping your incoming and outgoing data: i.e. change dateformats, trim strings or join/split arrays for editing in a textfield.
And finally get a full reactive Result by using Vuex.
Installation
npm install vue-form-base --saveUsing single-file components with a .vue extension,
import Formbase.vue File from your path
import FormBase from 'vue-form-base'; then register in
export default {
...
components:{
FormBase
}
}and use it in template
<template>
<form-base :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="datastate" />
</template>Minimalistic Example
If your data-state-name property has the value datastate,
then you must additionally define datastate in Vuex State.
State:{
datastate:null,
...
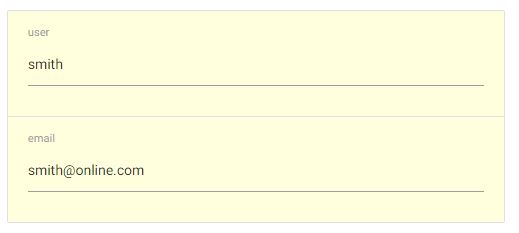
}Now use existing Data Object
data:{
name: 'smith',
email:'[email protected]'
}define the following minimalistic Schema
schema:{
name: {type:'text'},
email: {type:'email'}
}and get this full editable Form
Edit using different Input-Types
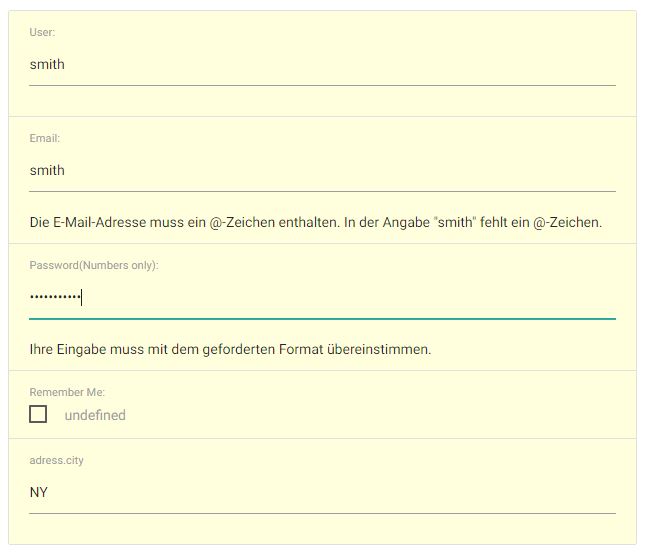
A more realistic Example.
Your Data to edit:
data:{
name: 'smith',
email:'smith',
password: '12345ABCDEF',
remember: 'undefined',
adress:{
city:'NY',
}
},Create a Schema Object:
schema:{
user: {type:'text', label:'User:', placeholder:'User...',
mapSet: (val, obj, data, schema) => {
// type 'hide' to hide dependent item password
schema.password.hidden = val === 'hide';
return val;
}
},
email: {type:'email',label:'Email:', validate:true },
password: {type:'password', label:'Password(Numbers only):', pattern:'[0-9]*', validate: msg => console.log(msg) },
remember: {type:'checkbox', label:'Remember Me:', true:'Yes', false:'No' },
adress:{
city:{ type:'text', mapSet: v => v && v.toUpperCase() }
}
}IMPORTANT:
Properties from Data-Object, which doesn't exist in Schema-Object, are ignored.
Reactive Result (Vuex)
Model Data und describing Schema flow as prop into the Vue-Form-Base. On the concept of one-way data flow you get reactive access to your modified data via Vuex Store $store.state.datastate . Installed Vuex is mandatory, details about Vuex you can find here Vuex-Introduction
<form-base :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="datastate" />If you need to dynamically modify the internal Schema (for example if you want to change dynamically schema.hidden to show/hide one item depending from the input of another item) you can have reactive access to the modified Schema via Vuex Store $store.state.schemastate.
Inside a single component .vue file you can use your component like this
<template>
<form-base
:data="data"
:schema="schema"
data-state-name="datastate"
schema-state-name="schemastate"
>
</form-base>
</template>Get Access to the reactive Result using Vuex State anywhere in your Project.
this.$store.state.datastateIMPORTANT:
'Data' and 'Schema' passed as Prop becomes not mutated.
Two Forms can be reactiv Linked by using the same state property
<form-base :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="dataCommon" />
<form-base :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="dataCommon" />and if you need different CSS
<form-base id="form1" :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="dataCommon" />
<form-base id="form2" :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="dataCommon" />Reset modified Data and modified Schema use following code inside the parent single component .vue file
If you need to change the Schema-Object dynamically, like in this case hiding another item
schema:{
...
user: {
type:'text',
mapSet: (val, obj, data, schema) => { schema.password.hidden = val === 'hide'; return val }
},
password: {
...
}
}then you need datastate and schemastate to restore like in this case
...
methods:{
reset(){
this.$store.state.datastate= cloneDeep(this.data);
this.$store.state.schemastate= cloneDeep(this.schema)
},
...
},
...In common use cases without modified Schema Reset can be shortened
<template>
<form-base :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="datastate" />
</template>
<script>
import { cloneDeep } from 'lodash'
export default {
...
methods:{
reset(){
this.$store.state.datastate= cloneDeep(this.data);
},
...
},
...
</script>Schema
<form-base :schema="schema" ... />Schema is an object, which defines and controls the behavior of your form. Each Key in your schema-object must reflect a key in the data-object.
schema:{
user: { type:'text'}, // minimalistic definition of input-type
}
// more
validate = val => console.log(val);
mapSet = val => val + '!'
schema:{
user: {
type:'text',
label:'User:',
pattern:'([A-Z]*)',
css:'blue',
validate, // is the same as - validate:validate,
mapSet, // is the same as - mapSet:mapSet,
order:1
},
...
}In common use cases the the value will be another object with several properties, to get different control over the behaviour of your input-field.
Properties in Schema
schema:{
order: number, // controls order of displaying
type: string, // 'text', 'password', 'email', ...
label: string, // title of item
placeholder: string, // placeholder set null to hide
true: string, // text if checkbox is checked
false: string, // text if checkbox is unchecked
accept: string, // type:'file' - limit files audio/*, image/*, .pdf
title: string, // define your own validation message
error: string, // preset/set inline error msg
css: string, // inject one or more classnames at item level
// Use 12 column grid system from materializecss.com/grid.html for displaying items
// for example a 12 column grid with 3 items in one row would look like:
// schema:{ item1:{ css:'col s4'}, item2:{ css:'col s4'}, item3:{ css:'next-row col s4'} }
pattern: string, // regex to control input
min: number, // limit number or range
max: number, // limit number or range
step: number,
maxlength: number, // max length of type text, password, email
multiple: bool, // type:'file' select one or more files
required: bool, // need an input value
disabled: bool, // disable input field
readonly: bool,
hidden: bool, // hide item - set from another item
options: array, // used with type: radio, list, text, select, mselect
mapGet: function, function( val, obj, state, schema ) {... return val}
mapSet: function, function( val, obj, state, schema ) {... return val} }
validate: true // use inline error message
validate: function, function( msg, obj, state, schema, validity ) {...}
noValidate: function, function( value, obj, state, schema ) {...}
}
Real-Life Example
...
schema:{
user: { type:'text', label:'Fullname:', placeholder:'Name...', css:'col s6'},
email: {type:'email', validate:true, mapSet: v => v && v.toUpperCase(), css:'next-row col s6' },
singleRole:{ type:'select', options:['Admin','Guest','User'] },
}
...Style with CSS
Customize your vue-form-base component using the following CSS-Classnames
IMPORTANT:
Don't use<style scoped>in parents component, because scoped definitions are inside the child component not accessable
Form-ID
#form-base is the default form-id. If you need different CSS for two or more forms in the same parent component, then change default value by setting a different id for each component and use this new id
/* default */
<form-base ... />
#form-base .collection {...}
/* individualize it */
<form-base id="my-custom-id" ... />
#my-custom-id .collection {...} General - Classnames
#form-base .collection {...} // style container for all items
#form-base .item {...} // each key is represented, by an item
#form-base .error {...} // style inline-error messages
Validate with Pseudoselectors
#form-base .item input:invalid { background-color: #fdd; }
#form-base .item input:valid { background-color: #dfd; }
#form-base .item input:focus { background-color: #ffd; } Type - Classnames
Style all items of a specific type, then use type-classnames. They start with a type ie. password appending -type. Then you have a classname password-type
#form-base .text-type {...} or #form-base .item.text-type {...}You can use most of HTML5 input-types like <input type="password" />. Some Informations to HTML5 input-types
/*
Available Types:
text, password, email, select, multiselect, list, file, radio,
checkbox, number, range, url, date, time, week, month
use class by appending -type -> .text-type
*/
#form-base .text-type { font-weight:500 }
#form-base .item.select-type {...}
#form-base .item.multiselect-type {...}
#form-base .item.checkbox-type {...}
Make validate CSS for multiselect type
If you want to style select or multiselect types you have append select after the classname
#form-base .item.multiselect-item select { height:6rem }Key - Classnames
Here you get direct access to each key in your Data-Object. If you want access deep nested keys youst must use a hyphen
data{ user:{ adress:{ city:'',... } ... } ... }access deep nested key 'city' with CSS
#form-base .item.user-adress-city-key {...} Example
a) Use Example with vue-webapp template, checkout example directory in this repo and follow the readme.
b)
Here is a working Vue-File, you can integrate this in your vue-project. Lodash and Vuex must be installed. In initial Vuex state definition state.datastate must exist
<style>
#form-base .error { color:red}
#form-base .item input:invalid{ background-color: #fdd; }
</style>
<template>
{{$store.state.datastate}}
<form-base :data="data" :schema="schema" data-state-name="datastate" />
</template>
import FormBase from './FormBase.vue';
export default {
data () {
return {
data:{
user: 'smith',
pw: 'secret'
},
schema:{
user: {
type:'text',
label:'User:',
placeholder:'User...'
},
pw: {
type:'password',
pattern:'^.{6,}',
lable:'Password:',
title: 'Password must have minimal 6 Chars',
required:true,
validate:true
}
}
}
},
components:{
FormBase
}
}
Features
- vue-component
- edit plain or deep nested objects
- support most of input types
- full reactive result
- configurable via Schema Defintion
- configurable Style based on Materialize CSS
Dependencies
Vue 2.0
Vuex
Lodash
Materialize CSSs