vue-choropleth
v0.3.1
Published
Choropleth Map for Vue.js
Downloads
399
Maintainers
Readme
vue-choropleth
Vue components to display a choropleth map given a certain GeoJSON and another datasource to show information from. Using Vue2Leaflet
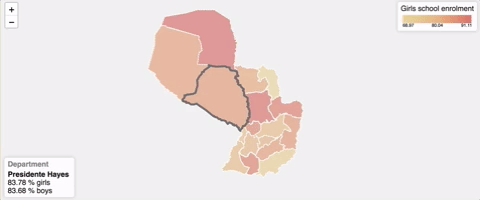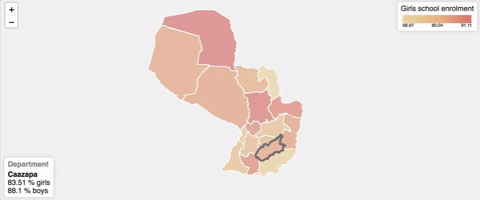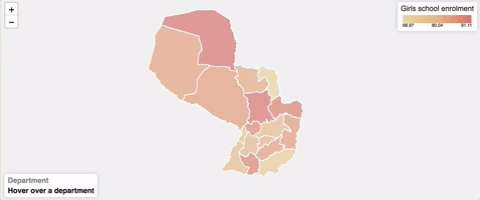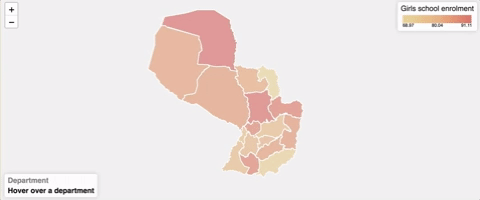
How to use
For a complete example using a single-file component, check the code in the example.
For a complete example using script tags check this codepen
Make sure you have Vue2Leaflet installed and add the l-map component along with the next vue-choropleth components:
import {LMap} from 'vue2-leaflet';
import { InfoControl, ReferenceChart, ChoroplethLayer } from 'vue-choropleth'
// Register these components in the components
export default {
name: "app",
components: {
LMap,
'l-info-control': InfoControl,
'l-reference-chart': ReferenceChart,
'l-choropleth-layer': ChoroplethLayer
},
// .......your component code.........Make sure the leaflet.css is included, either via a HTML link tag or in your vue component style
@import "~leaflet/dist/leaflet.css";On the template:
<l-map
:center="[-23.752961, -57.854357]"
:zoom="6"
style="height: 500px;"
:options="mapOptions">
<l-choropleth-layer
:data="pyDepartmentsData"
titleKey="department_name"
idKey="department_id"
:value="value"
:extraValues="extraValues"
geojsonIdKey="dpto"
:geojson="paraguayGeojson"
:colorScale="colorScale">
<template slot-scope="props">
<l-info-control
:item="props.currentItem"
:unit="props.unit"
title="Department"
placeholder="Hover over a department"/>
<l-reference-chart
title="Girls school enrolment"
:colorScale="colorScale"
:min="props.min"
:max="props.max"
position="topright"/>
</template>
</l-choropleth-layer>
</l-map>l-choropleth-layer Props
- geojson: The GeoJSON object to use
- data: Data object with the information to show on the map
- titleKey: Property of the data object to show when you hover over a certain region of your map (e.g. state_name)
- geojsonIdKey: Property under the properties array of the GeoJSON that serves as identifier of each region of the map.
- idKey: Property of the data object that matches the geojsonIdKey value.
- value: JS object with two properties, key: that maps to the data property that contains the value domain set (e.g. amount) and metric: that maps to the data property that describes the unit that you're working on (e.g.
"% of students") - extraValues: Array of value objects that show additional information of a certain region of the map.
- colorScale: Array of hex color codes to fill each region of the map with. At the minimum you need to specify two colors, the one to use with the lowest values and another one to use with the highest values. (e.g.
["e7d090", "de7062"]) Thel-choropleth-layercomponent pass the this information through its default slot: - currentItem: Current item on focus
- unit: metric associated with the value
- min: The lowest value on the domain set
- max: The highest value on the domain set
- strokeColor: String with the color to use for each of the polygons' stroke color (in hex format). (e.g.:
"e7d090"). If a value is not specifiedfffis used. - currentStrokeColor: String with the color to use for the stroke of the currently polygon that the user is hovering over. (e.g.:
"e7d090"). If a value is not specified666is used. - strokeWidth: Number with the width of the stroke for each polygon. (default:
2). - currentStrokeWidth: Number with the width of the stroke for the currently hovered polygon. (default:
5).
As seen on the example, usually you'll pass these values to the l-info-control and l-reference-chart components.
l-info-control props
This is the current item information view.
- item: Item to show information about
- unit: Metric to use while displaying information
- title: Description about what each item of the map is (e.g.
"State") - placeholder: Placeholder text to show when no element is currently selected
- position: Where to render the component. With values allowed here (default:
"bottomleft")
l-reference-chart props
- title: Short description to show as reference of the information described by the map (e.g.
"Population density") - colorScale: Same prop as used on
l-choropleth-layercomponent - min: The lowest value represented on the visualization
- max: The highest value represented on the visualization
- position: Where to render the component. With values allowed here (default:
"topright")
How to install
NPM
$ npm install vue-choropleth --saveyarn
$ yarn add vue-choroplethLive Demo
Example available here.
Build Setup
# Once you have cloned this repo, install dependencies
$ npm install
# build for development and production with minification
$ npm run build
Run demo locally
# Run demo at localhost:8080
$ npm link
$ cd examples/node-example
$ npm link vue-choropleth
$ npm install
# serve with hot reload at localhost:8080
$ npm run devGo to http://localhost:8080/ to see the demo
NOTE: If you make changes to the library you should run 'npm run build' again in the root folder. The dev server should detect modification and reload the demo
Web example
You'll also find an example using <script> tags included under examples/browser-example
Authors
Guillermo Peralta Scura
Thanks to the works of Mickaël Bouchaud with Vue2Leaflet

