vue-async-cache
v1.1.0
Published
`vue-async-cache` is a library to cache asynchrone function call between different component. It was initially build to improve cache of api call with VueJs. This library can be especially useful to cache some fetch query, for example using axios. The con
Downloads
5
Readme
vue-async-cache
vue-async-cache is a library to cache asynchrone function call between different component.
It was initially build to improve cache of api call with VueJs. This library can be especially useful to cache some fetch query, for example using axios. The concept was inspired from Apollo cache, even if it is far from being comparable.
The library take care to save the response of the async function and share it between components using context api. It will also avoid unnecessary call made simultaneously to the same async function. It will identify the cache id base on the name of the function and the parameters passed. So if you call multiple times the same function with different parameters, it will not use the same cache. Example:
api is an async function
export api = async (param1, param2) => ... call(api, '/counter');
call(api, '/timer');This 2 call to api function will have different cache because they don't share the same parameters.
call(api, '/counter');
call(api, '/counter');This 2 call to api function will have the same cache and api will be called only once.
Example
See full example at here.
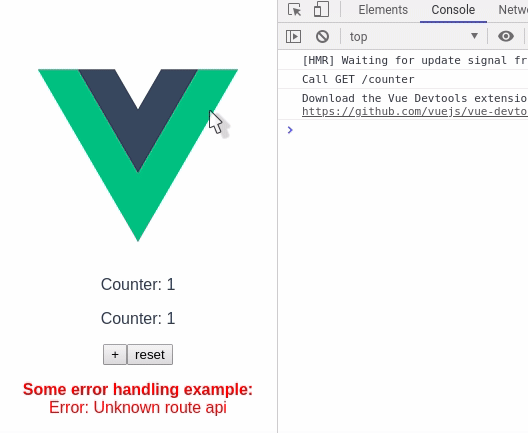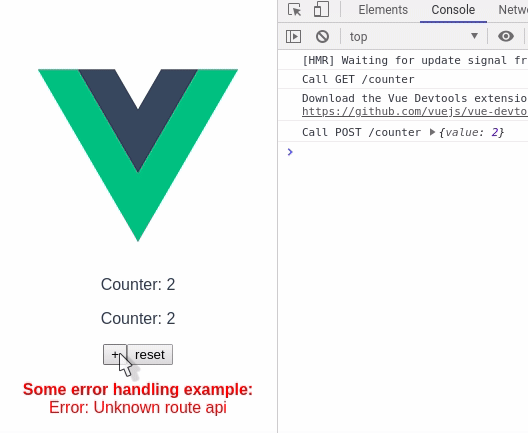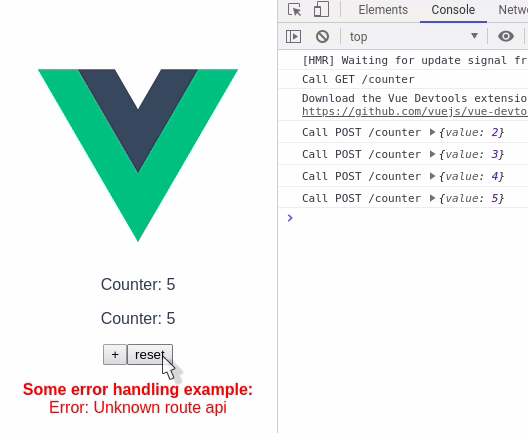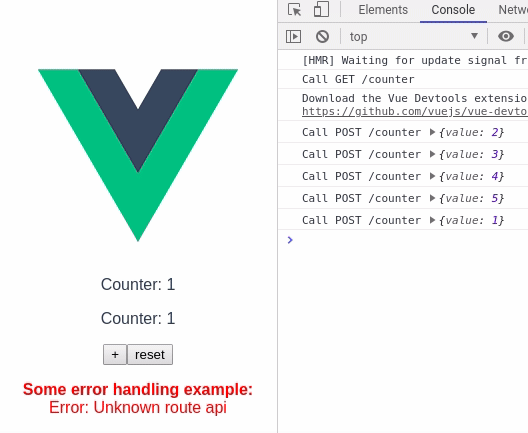
Counter.vue
<template>
<div class="counter">
<p>Counter: {{count}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
Component,
Vue,
} from "vue-property-decorator";
import { api } from "../mockapi";
import { useAsyncCacheWatch } from "vue-async-cache";
@Component
export default class Counter extends Vue {
private cacheWatch = useAsyncCacheWatch(api, "/counter");
get count() {
return this.cacheWatch.getResponse();
}
async mounted() {
this.cacheWatch.call();
}
}
</script>app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<Counter />
<Counter />
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { Component, Vue, Provide } from "vue-property-decorator";
import Counter from "./components/Counter.vue";
@Component({
components: {
Counter,
}
})
export default class App extends Vue {}
</script>In this example, without cache there would have been 2 calls to the api, but using vue-async-cache there is only 1 call. The library will take care to populate the response to all the components.
update cache
vue-async-cache provide as well different way to interact with the cache:
<template>
<div class="hello">
<button @click="increment()">+</button>
<button @click="reset()">reset</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
Component,
Vue,
} from "vue-property-decorator";
import { api } from "../mockapi";
import { asyncCache, useAsyncCacheWatch } from "vue-async-cache";
@Component
export default class SetCounter extends Vue {
private cacheWatch = useAsyncCacheWatch(api, "/counter");
private cacheState!: any;
async increment() {
const count = this.cacheWatch.cache();
const response = await api('/counter', 'POST', { value: count + 1 });
await this.cacheWatch.update(response);
}
async reset() {
const response = await api('/counter', 'POST', { value: 1 });
await this.cacheWatch.update(response);
}
get response() {
return this.cacheWatch.getResponse();
}
}
</script>How to use it
vue-async-cache is using the store pattern to share the state between component. So the only thing you have to do is to import the store in the component:
import { asyncCache } from "vue-async-cache";asyncCache
asyncCache store provide methods and properties to interact with the cache: call, update, cache and responses.
asyncCache.call is a method that allow to cache the original function call. The first given parameter to call is the function you want to cache. The next parameters are the parameters you would have providen to the function you want to cache. call will return the id of the corresponding response in the cache.
async asyncCache.call(fn: (...args: any) => Promise<any>, ...args: any) => Promise<string>eg.:
await asyncCache.call(getItems);
const id = await asyncCache.call(getItem, 'id-20', { withComment: true });Note: in most of the case it is not necessary to use
calland instead prefer usingloadfromuseAsyncCacheWatchthat will take care to observe changes on the response.
asyncCache.cache is a asyncCache to access the cache. It work the same way as the call method, but it will retrieve the response from the cache, instead to call the async function.
update is a asyncCache that allow to update the cache without to make a call to the server. The first parameter is the new response you want to set. The second parameter is the cached function. The next parameter are the parameters you would have providen to the cached function.
eg.:
await asyncCache.update([
{id:'id-1', title: 'hello'},
{id:'id-2', title: 'hello2'},
], getItems);
await asyncCache.update({
id:'id-1',
title: 'hello',
content: 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, ac augue malesuada, tellus amet',
comments: [],
}, getItem, 'id-20', { withComment: true });asyncCache.responses property is the actual cache representing all the asynchrone call, error and response. To access the cache prefer using the cache function instead.
useAsyncCacheWatch
useAsyncCacheWatch helper is used for watching a specific response, allowing to automatically update the state of a component. This helper return the same attributes as asyncCache plus 3 extra attributes, getResponse and getError.
To use useAsyncCacheWatch, you need to provide some parameters, the first given parameter is the function you want to cache. The next parameters are the parameters you would have providen to the function you want to cache. It is actually exactly the same parameters as for asyncCache.call method.
import { useAsyncCacheWatch } from "vue-async-cache";
@Component
export default class Counter extends Vue {
private cacheWatch = useAsyncCacheWatch(api, "/counter");
get count() {
return this.cacheWatch.getResponse();
}
async mounted() {
this.cacheWatch.call();
}
}call does the same as asyncCache.call but you don't need to provide anymore the parameters.
cache does the same as asyncCache.cache but you don't need to provide anymore the parameters.
update does the same as asyncCache.update but you need to provide only the first parameter.
getResponse retrieve the response received after the function has been called.
getError retrieve the error received if the function called failed.
