three-geo
v1.4.5
Published
3D geographic visualization library
Downloads
169
Readme
three-geo
three-geo is a three.js based geographic visualization library. Using three-geo, we can easily build satellite-textured 3D terrain models in near real-time by simply specifying GPS coordinates anywhere on the globe. The geometry of the terrain is based on the RGB-encoded DEM (Digital Elevation Model) provided by the Mapbox Maps API.
The terrain is represented by standard THREE.Mesh objects. This makes it easy for us to access underlying geometry/texture array and perform original GIS (Geographic Information System) experiments in JavaScript. (See Usage for how to programatically obtain those mesh objects).
Credits: this library has been made possible thanks to
- geo-related libraries (mapbox, Turfjs) and the Mapbox Maps API.
- peterqliu for informative 3D terrain-related articles and implementation.
Demo
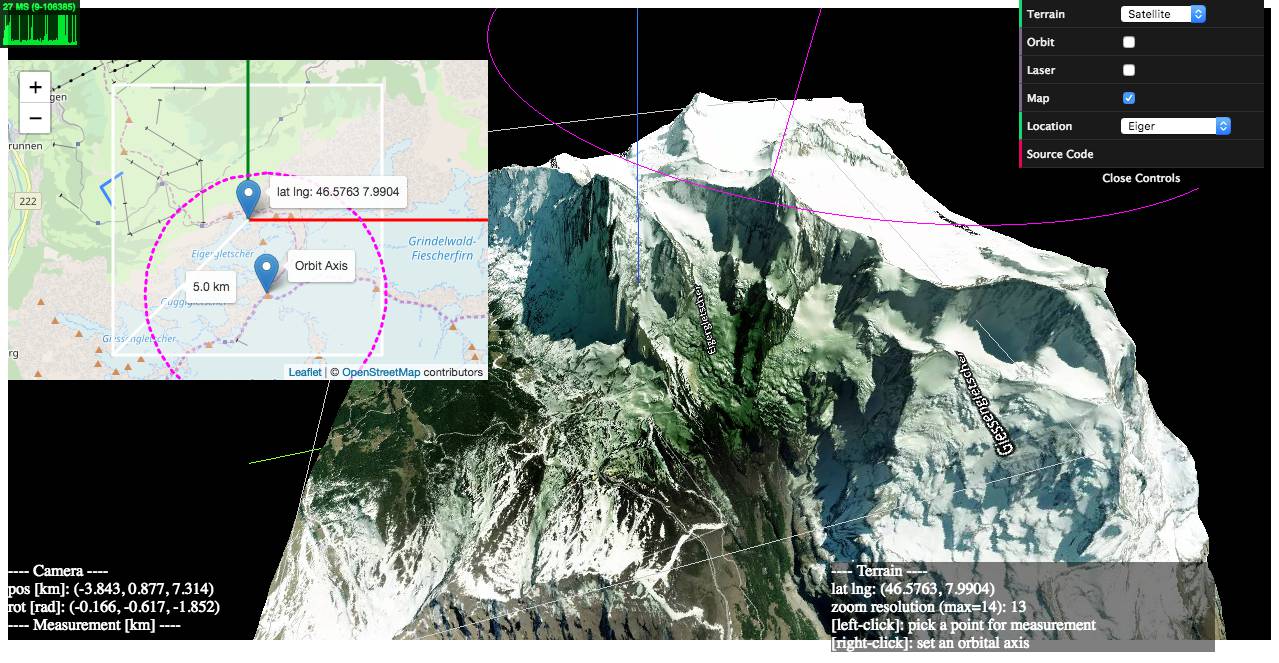
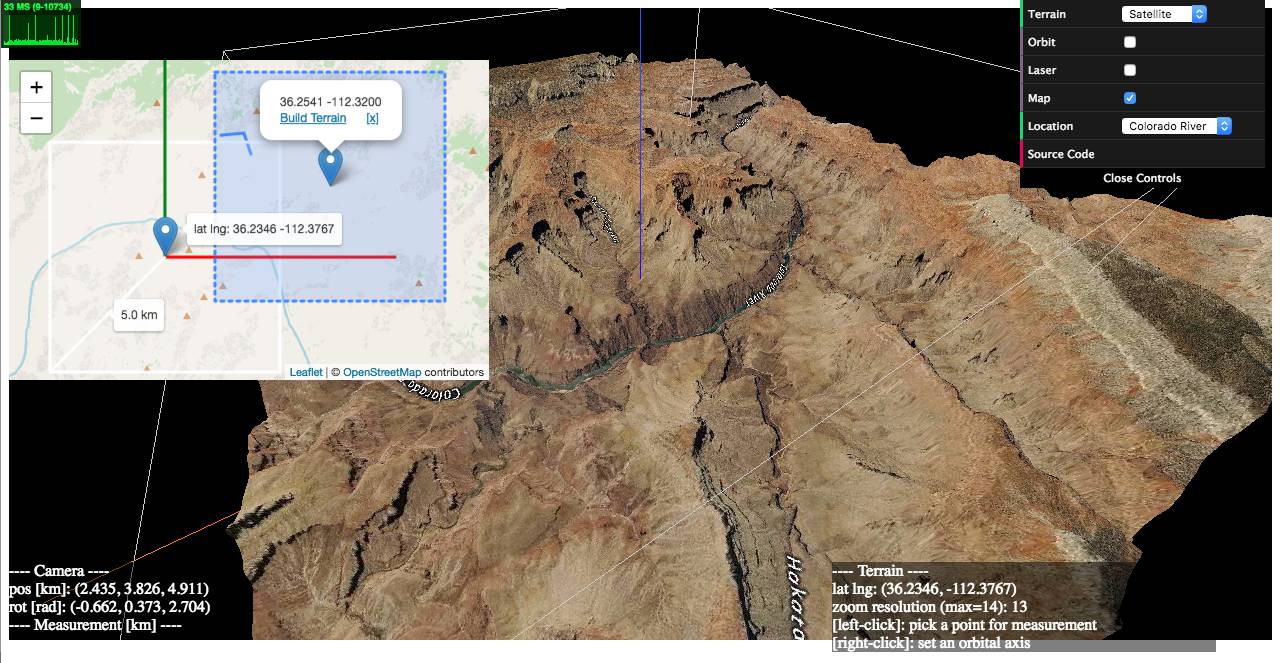
1) examples/geo-viewer (live | source code)
This demo app includes features such as
- on-demand 3D terrain building (by a mouse click on the Leaflet map),
- real-time camera projection onto Leaflet (with oritentaion and HFoV indication),
- terrain interaction with a VR-like laser beam,
- measuring Euclidean distances between terrain points,
- auto camera orbiting around the custom z-axis.
Live:
https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/geo-viewer/io/index.html?lat=46.5763&lng=7.9904
https://w3reality.github.io/three-geo/examples/geo-viewer/io/index.html?lat=36.2058&lng=-112.4413
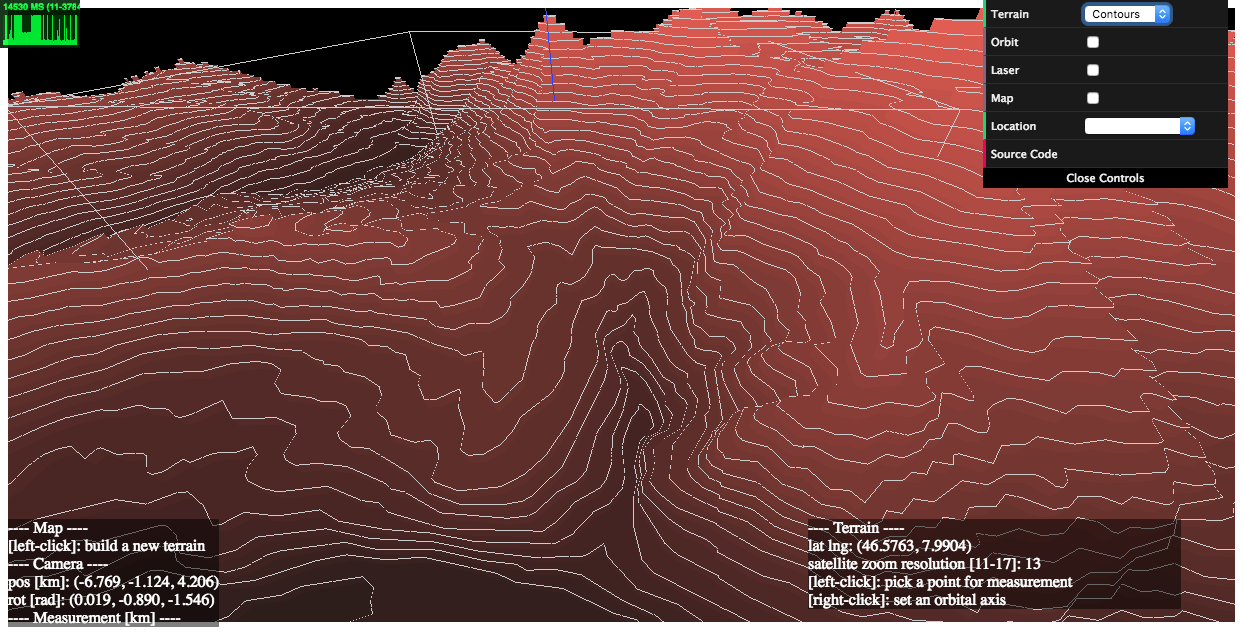
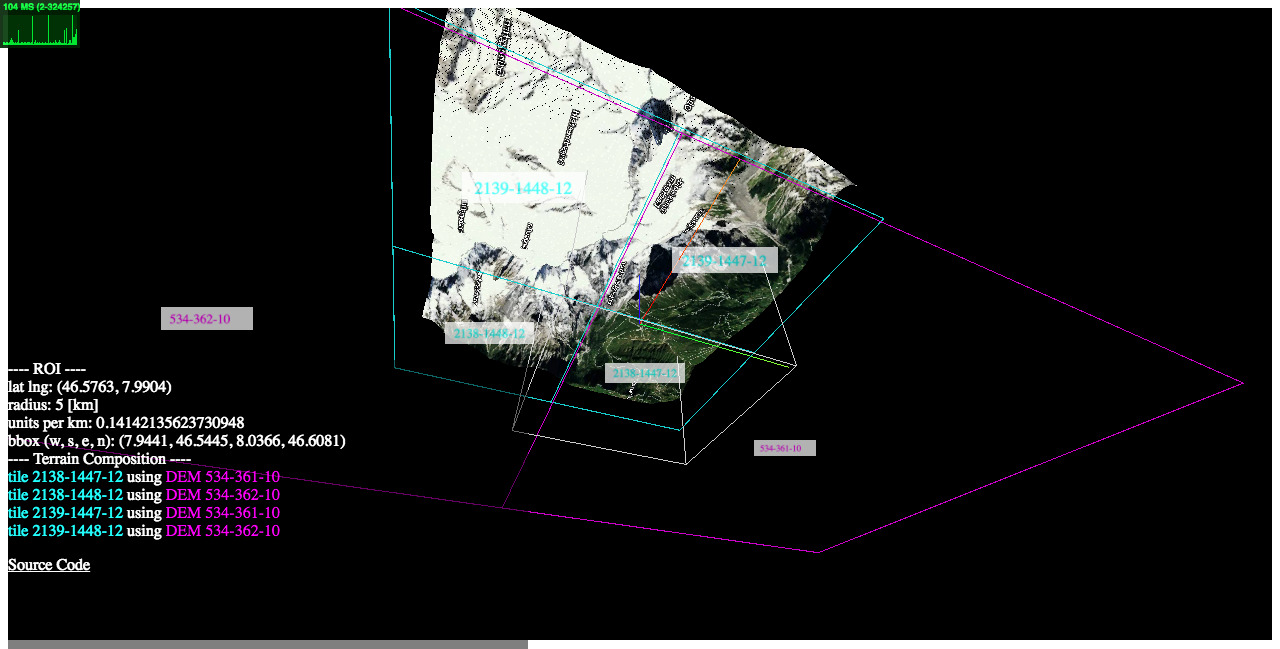
2) examples/heightmaps (live | source code)
This demo illustrates the relationship between a reconstructed 3D terrain and its underlying satellite/DEM tiles.
3) examples/flat (live | source code)
How to get a flattened view of the terrain by post-editing the underlying geometry.
4) examples/projection (live | source code)
How to register a new 3D object on top of the terrain based on its geographic location [latitude, longitude, elevation].
Setup
Installation
$ npm i three-geoLoading
Script tag: use ThreeGeo after
<script src="dist/three-geo.min.js"></script>ES6:
import ThreeGeo from 'dist/three-geo.esm.js';Usage
Here is an example of how to build a geographic terrain located at GPS coordinates (46.5763, 7.9904) in a 5 km radius circle. The terrain's satellite zoom resolution is set to 12. (The highest zoom value supported is 17.)
For standalone tests, use examples/simple-viewer (source code).
For use with NodeJS, do enable this isNode option as well.
const tgeo = new ThreeGeo({
tokenMapbox: '********', // <---- set your Mapbox API token here
});
const terrain = await tgeo.getTerrainRgb(
[46.5763, 7.9904], // [lat, lng]
5.0, // radius of bounding circle (km)
12); // zoom resolution
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.add(terrain);
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ canvas });
renderer.render(scene, camera);Who is using three-geo?
- jet-wasp - Three-geo as A-Frame component (source code)
- locus-pocus - A webapp to visualise your area using three-geo
API
In this section, we list three-geo's public API methods, where origin, radius, and zoom are parameters common to them:
originArray<number> Center of the terrain represented as GPS coordinates[latitude, longitude].radiusnumber Radius of the circle that fits the terrain.zoomnumber (integer) Satellite zoom resolution of the tiles in the terrain. Select from {11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17}, where 17 is the highest value supported. For a fixed radius, higher zoom resolution results in more tileset API calls.
ThreeGeo
constructor(opts={})Create a ThreeGeo instance with parameters.
opts.tokenMapbox="" string Mapbox API token. This must be provided.opts.unitsSide=1.0 number The side length of the square that fits the terrain in WebGL space.opts.isNode=false boolean To use three-geo with NodeJS, you must explicitly set this option totrue. [ Added in v1.4.5 ]
async getTerrainRgb(origin, radius, zoom)[ Added in v1.4 ]Return a THREE.Group object that represents a 3D surface of the terrain.
The group object contains an Array<THREE.Mesh> as
.children. Each mesh corresponds to a partial geometry of the terrain textured with satellite images.async getTerrainVector(origin, radius, zoom)[ Added in v1.4 ]Return a THREE.Group object that represents a 3D contour map of the terrain.
The group object contains an Array<THREE.Object3D> as
.children. Each child object is either an extruded THREE.Mesh with.nameattribute prefixed bydem-vec-shade-<ele>-, or a THREE.Line with.nameprefixed bydem-vec-line-<ele>-(<ele>is the height of each contour in meters).getProjection(origin, radius, unitsSide=1.0)[ Example ]Return an object
{ proj, projInv, bbox, unitsPerMeter }that includes transformation-related functions and parameters, whereproj(latlng)is a function that maps geo coordinateslatlng(an array[lat, lng]) to WebGL coordinates[x, y].projInv(x, y)is a function that maps WebGL coordinates[x, y]to geo coordinates[lat, lng].bboxis an array[w, s, e, n]that represents the computed bounding box of the terrain, wherew(West) ande(East) are longitudinal limits; ands(South) andn(North) are latitudinal limits.unitsPerMeteris the length in WebGL-space per meter.
getTerrain(origin, radius, zoom, callbacks={})callbacks.onRgbDemfunction (meshes) {} Implement this to request the geometry of the terrain. Called when the entire terrain's geometry is obtained.meshesArray<THREE.Mesh> All the meshes belonging to the terrain.
callbacks.onSatelliteMatfunction (mesh) {} Implement this to request the satellite textures of the terrain. Called when the satellite texture of each mesh belonging to the terrain is obtained.meshTHREE.Mesh One of the meshes that's part of the terrain.
callbacks.onVectorDemfunction (objs) {} Implement this to request the contour map of the terrain. Called when the contour map of the terrain is obtained.objsArray<THREE.Object3D> Extruded meshes (THREE.Mesh objects with.nameattribute prefixed bydem-vec-shade-<ele>-) and lines (THREE.Line objects with.nameattribute prefixed bydem-vec-line-<ele>-), where<ele>is the height of each contour in meters.
Build
$ npm i
$ npm run build