swaggerql
v0.4.0
Published
Easily and simply convert SQL database into a REST API with Swagger documentation
Downloads
20
Maintainers
Readme
SwaggerQL
Swagger + SQL = Simple reference microservice with transparent documentation and no coding.
All you need to do is create a Swagger file and specify SQL queries in the description.
When you should use it:
- you need an internal microservice with simple queries to an existing database
- you quickly need a prototype of a reference service
- you need to test data in the database
- you need a stub application with database access to test the deployment scripts
Getting Started
Install the appropriate database module before using the SwaggerQL:
pgfor PostgreSQL and Amazon Redshiftmysql2for MySQLmysqlfor MariaDB or MySQLsqlite3for SQLite3mssqlfor MSSQLoracledband Oracle instant-client for Oracle
npm install swaggerql
npm install pgCreate config/local.yaml
client: pg
connection:
host: 127.0.0.1
user: your_database_user
password: your_database_password
database: myapp_testRun SwaggerQL
$(npm bin)/swaggerqlAnd try http://0.0.0.0:8000
npm install swaggerql
npm install oracledbInstall Oracle instant-client
Create config/local.yaml
client: oracledb
connection:
user: your_database_user
password: your_database_password
connectString: (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=127.0.0.1)(PORT=1521)))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=MY_SID)))
pool:
min: 0
max: 3Run SwaggerQL
$(npm bin)/swaggerqlAnd try http://0.0.0.0:8000
More examples in the repository.
Configuration
Connect to DB
The knex library is used to connect to various databases. The most common configuration file format is:
client: <driver>
connection:
host: 127.0.0.1
user: your_database_user
password: your_database_password
database: myapp_testMore examples of connection configurations in Knex documentation
See node-config documentation for information about naming, load order and format of configuration files.
REST API
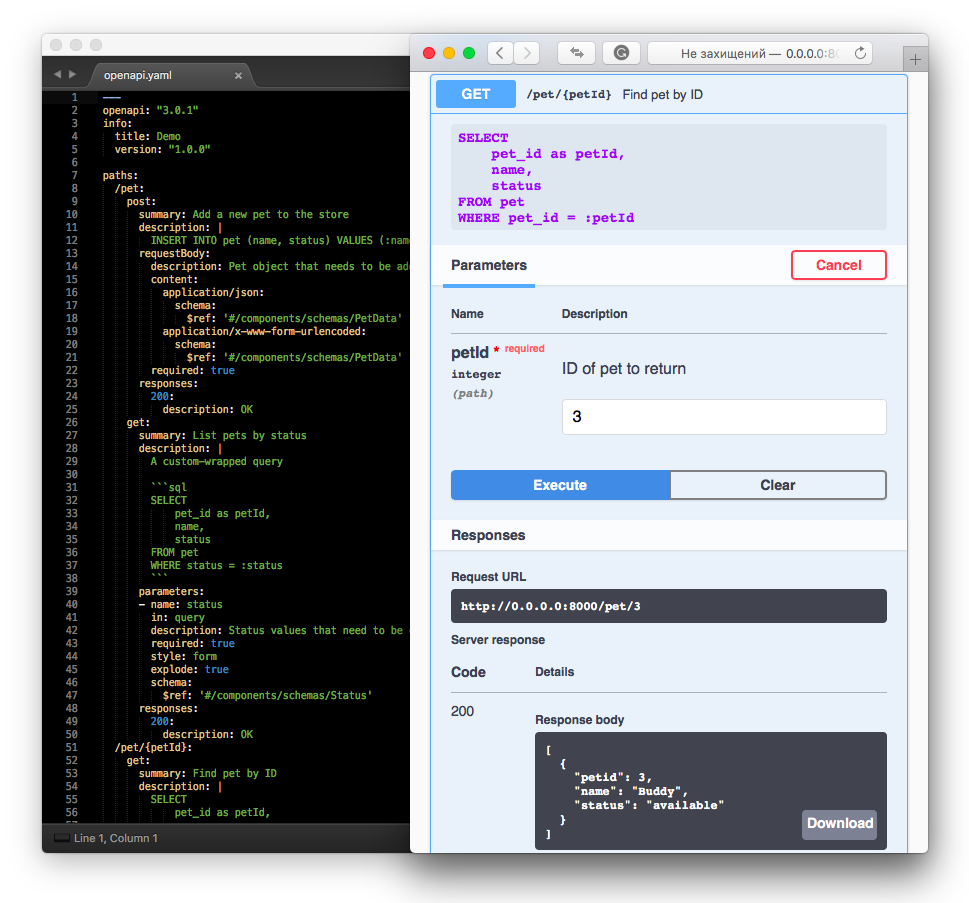
Build APIs by describing them in OpenAPI document specification and importing them via YAML or JSON to construct your own REST API.
The only difference is that a SQL query is inserted into the description field.
paths:
/two:
get:
summary: One plus one equals two
description: |
SELECT 1 + 1
responses:
200:
description: OKThe description can use Markdown with a specified SQL query:
description: |
Add one to one
```sql
SELECT 1 + 1
```Query Parameter Binding
You can pass parameters to SQL query from path, query, form parameters described in Swagger file.
Use named bindings, such as :name are interpreted as values and :name: interpreted as identifiers.
paths:
/increment:
get:
summary: Increment of N per one
description: |
SELECT 1 + :n
parameters:
- name: n
in: query
description: Number
required: true
style: form
explode: true
schema:
type: integer
responses:
200:
description: OKExecution options
Query expression can be handled as a transaction if the client sends X-Transaction header.
Sometimes there's need to release cursors in the database.
paths:
/compute:
get:
summary: Adding the results of a calculation
description: |
insert into table
select function()
parameters:
- name: X-Transaction
in: header
description: Run Query in transaction wrapper
schema:
type: boolean
default: trueCLI
Configuration options can be overridden via command-line arguments or environment variables. Priorities are the following:
- A command-line option has the highest priority. It overrides the environment variable and config file value.
- An environment variable has second priority. It overrides the config file value.
- A config file value has the lowest priority.
- If there isn't a command-line option, environment variable or config file option specified, the default is used.
Run $(npm bin)/swaggerql --help for more information.
Usage: swaggerql [options]
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
-i, --input-spec <path> path to specification file (default: "openapi.yaml")
-p, --port <number> http port to start server (default: 8000)
-d, --client <name> name of client SQL driver
-c, --connection <dsn|json> connection options to the appropriate database client
-l, --log-level <level> logging level: debug, info, warn, error (default: "info")
-h, --help output usage informationEnvironment variables:
SWAGGERQL_INPUT_SPEC— path to specification fileSWAGGERQL_PORT— http port to start serverSWAGGERQL_CLIENT— name of client SQL driverSWAGGERQL_CONNECTION— connection options to the appropriate database clientSWAGGERQL_LOG_LEVEL— logging level
Docker
docker run -it --rm -p 8000:8000 \
-v $(pwd)/config/local.yaml:/app/config/production.yaml \
-v $(pwd)/openapi.yaml:/app/openapi.yaml \
swaggerql/swaggerql-mysqlAvailable Docker containers:





