styled-error
v0.1.0
Published
Cleaner Nodejs errors
Downloads
2
Maintainers
Readme
styled-error :nail_care:
Ever wondered if your CLI needed less clutter and more CSS? Somebody else did and made something in CoffeeScript for it. This is the TypeScript edition. Case in point:
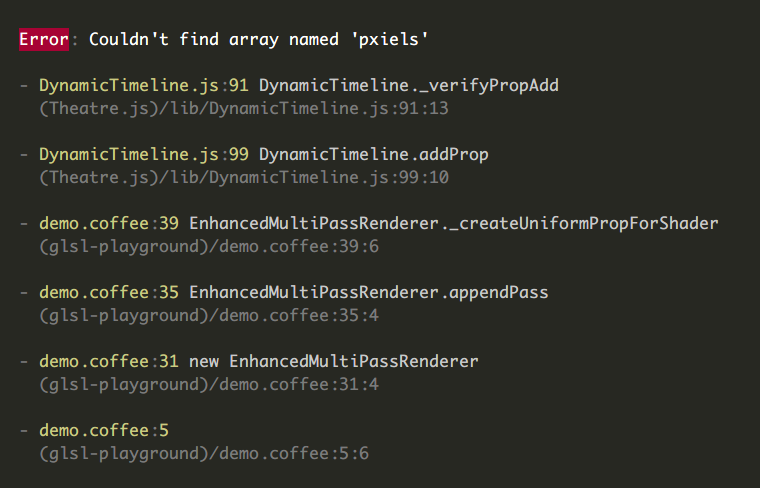
... which is more readable compared to node's unformatted errors:
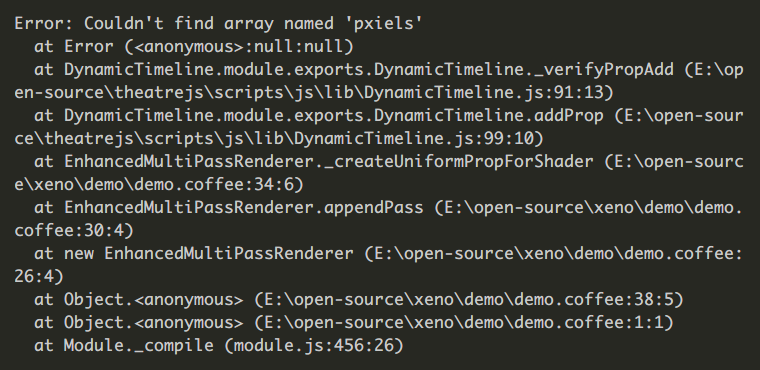
Installation
Install with pnpm:
$ pnpm add styled-errorUsage and Examples
To see an error rendered with colors, you can do this:
const StyledError = require('styled-error')
const se = new StyledError()
const renderedError = se.render(new Error('Some error message'))
console.log(renderedError)Of course, you can render caught exceptions too:
try {
doSomethingThatThrowsAnError()
} catch (error) {
console.log(se.render(error))
}But if you want styled-error to render all errors, there is a shortcut for it:
require('styled-error').start()... which is essentially equal to:
var StyledError = require('styled-error')
// instantiate StyledError, which can then be used to render error objects
var se = new StyledError()
se.start()You can also preload styled-error into your code using node's --require argument:
$ node --require styled-error/start your-module.jsHow it Works
StyledError turns error objects into something similar to an html document, and then uses RenderKid to render the document using simple html/css-like commands. This allows StyledError to be themed using simple css-like declarations.
Theming
StyledError's default theme is a bunch of simple css-like rules. Here is the source of the default theme.
Since the default theme is all css, you can customize it to fit your taste. Let's do a minimal one:
// the start() shortcut returns an instance of StyledError ...
se = require('styled-error').start()
// ... which we can then use to customize like this:
se.appendStyle({
// this is a simple selector to the element that says 'Error'
'styled-error > header > title > kind': {
// which we can hide:
display: 'none',
},
// the 'colon' after 'Error':
'styled-error > header > colon': {
// we hide that too:
display: 'none',
},
// our error message
'styled-error > header > message': {
// let's change its color:
color: 'bright-white',
// we can use black, red, green, yellow, blue, magenta, cyan, white,
// grey, bright-red, bright-green, bright-yellow, bright-blue,
// bright-magenta, bright-cyan, and bright-white
// we can also change the background color:
background: 'cyan',
// it understands paddings too!
padding: '0 1', // top/bottom left/right
},
// each trace item ...
'styled-error > trace > item': {
// ... can have a margin ...
marginLeft: 2,
// ... and a bullet character!
bullet: '"<grey>o</grey>"',
// Notes on bullets:
//
// The string inside the quotation mark gets used as the character
// to show for the bullet point.
//
// You can set its color/background color using tags.
//
// This example sets the background color to white, and the text color
// to cyan, the character will be a hyphen with a space character
// on each side:
// example: '"<bg-white><cyan> - </cyan></bg-white>"'
//
// Note that we should use a margin of 3, since the bullet will be
// 3 characters long.
},
'styled-error > trace > item > header > pointer > file': {
color: 'bright-cyan',
},
'styled-error > trace > item > header > pointer > colon': {
color: 'cyan',
},
'styled-error > trace > item > header > pointer > line': {
color: 'bright-cyan',
},
'styled-error > trace > item > header > what': {
color: 'bright-white',
},
'styled-error > trace > item > footer > addr': {
display: 'none',
},
})This is how our minimal theme will look like: 
Read RenderKid's docs to learn about all the css rules that are supported.
Customization
There are a few methods to help you customize the contents of your error logs.
Let's instantiate first:
StyledError = require('styled-error')
se = new StyledError()
// or:
se = require('styled-error').start()Shortening paths
You might want to substitute long paths with shorter, more readable aliases:
se.alias('E:/open-source/theatrejs/lib', '(Theatre.js)')Skipping packages
You might want to skip trace lines that belong to specific packages (chai, when, socket.io):
se.skipPackage('chai', 'when', 'socket.io')Skipping node files
// this will skip node.js, path.js, event.js, etc.
se.skipNodeFiles()Skipping paths
se.skipPath('/home/dir/someFile.js')Skipping by callback
You can customize which trace lines get logged and which won't:
se.skip(function (traceLine, lineNumber) {
// if we know which package this trace line comes from, and it isn't
// our 'demo' package ...
if (
typeof traceLine.packageName !== 'undefined' &&
traceLine.packageName !== 'demo'
) {
// then skip this line
return true
}
// You can console.log(traceLine) to see all of it's properties.
// Don't expect all these properties to be present, and don't assume
// that our traceLine is always an object.
})Modifying each trace line's contents
se.filter(function (traceLine, lineNumber) {
// the 'what' clause is something like:
// 'DynamicTimeline.module.exports.DynamicTimeline._verifyProp'
if (typeof traceLine.what !== 'undefined') {
// we can shorten it with a regex:
traceLine.what = traceLine.what.replace(
/(.*\.module\.exports\.)(.*)/,
'$2',
)
}
})Disabling colors
se.withoutColors() // Errors will be rendered without coloringIntegrating with frameworks
StyledError is very simple to set up, so it should be easy to use within other frameworks.
Integrating with express
Most frameworks such as express, catch errors automatically and provide a mechanism to handle those errors. Here is an example of how you can use StyledError to log unhandled errors in express:
// this is app.js
const express = require('express')
const StyledError = require('styled-error')
const app = express()
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
// this will throw an error:
const a = b
})
const server = app.listen(3000, function () {
console.log('Server started \n')
})
// we can now instantiaite StyledError:
se = new StyledError()
// and use it for our app's error handler:
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
console.log(se.render(err))
next()
})
// we can optionally configure styledError to simplify the stack trace:
se.skipNodeFiles() // this will skip events.js and http.js and similar core node files
se.skipPackage('express') // this will skip all the trace lines about express` core and sub-modulesTroubleshooting
StyledError.start() modifies the stack traces of all errors thrown anywhere in your code, so it could potentially break packages that rely on node's original stack traces. I've only encountered this problem once, and it was with BlueBird when Promise.longStackTraces() was on.
In order to avoid this problem, it's better to not use StyledError.start() and instead, manually catch errors and render them with StyledError:
const StyledError = require('styled-error')
const se = new StyledError()
// To render exceptions thrown in non-promies code:
process.on('uncaughtException', function (error) {
console.log(se.render(error))
})
// To render unhandled rejections created in BlueBird:
process.on('unhandledRejection', function (reason) {
console.log('Unhandled rejection')
console.log(se.render(reason))
})
// While StyledError.start() works out of the box with when.js` unhandled rejections,
// now that we're manually rendering errors, we have to instead use npmjs.org/packages/styled-monitor
// to handle when.js rejections.The only drawback with this approach is that exceptions thrown in the first tick are not prettified. To fix that, you can delay your application's startup for one tick:
// (continued form above)
throw new Error() // not prettified
process.nextTick(function () {
throw new Error() // prettified
})License
MIT
