str-temp
v1.0.5
Published
A tool to combine your string and data more effectively.
Downloads
3
Maintainers
Readme
str-temp
This is a tool used to process and insert data inside a string in a proper format according to your needs.
This uses template strings to make processing and storing flexible. Use {} in your string and pass the variable as parameters or pass them later by calling the returned function.
Basic
The program adds the data to the brackets based on a predefined flow. The function will take it's first argument as the template string and then the parameters.
The parameters, except Objects, are added to an array. If a multi dimensional array is passed as parameter, it flattens into a single dimensional array and is added with the other array containing data parameters.
The function will first place Index and Key values in the brackets and then it will fill the Empty or Comment brackets. The function will place the values from
left to rightbrackets for the Empty or Comment brackets.The called function will return a function until all the brackets are occupied. If all the brackets are occupied, the resultant string will be returned. If you want to see the current state of the string, Refer this Section.
Comments
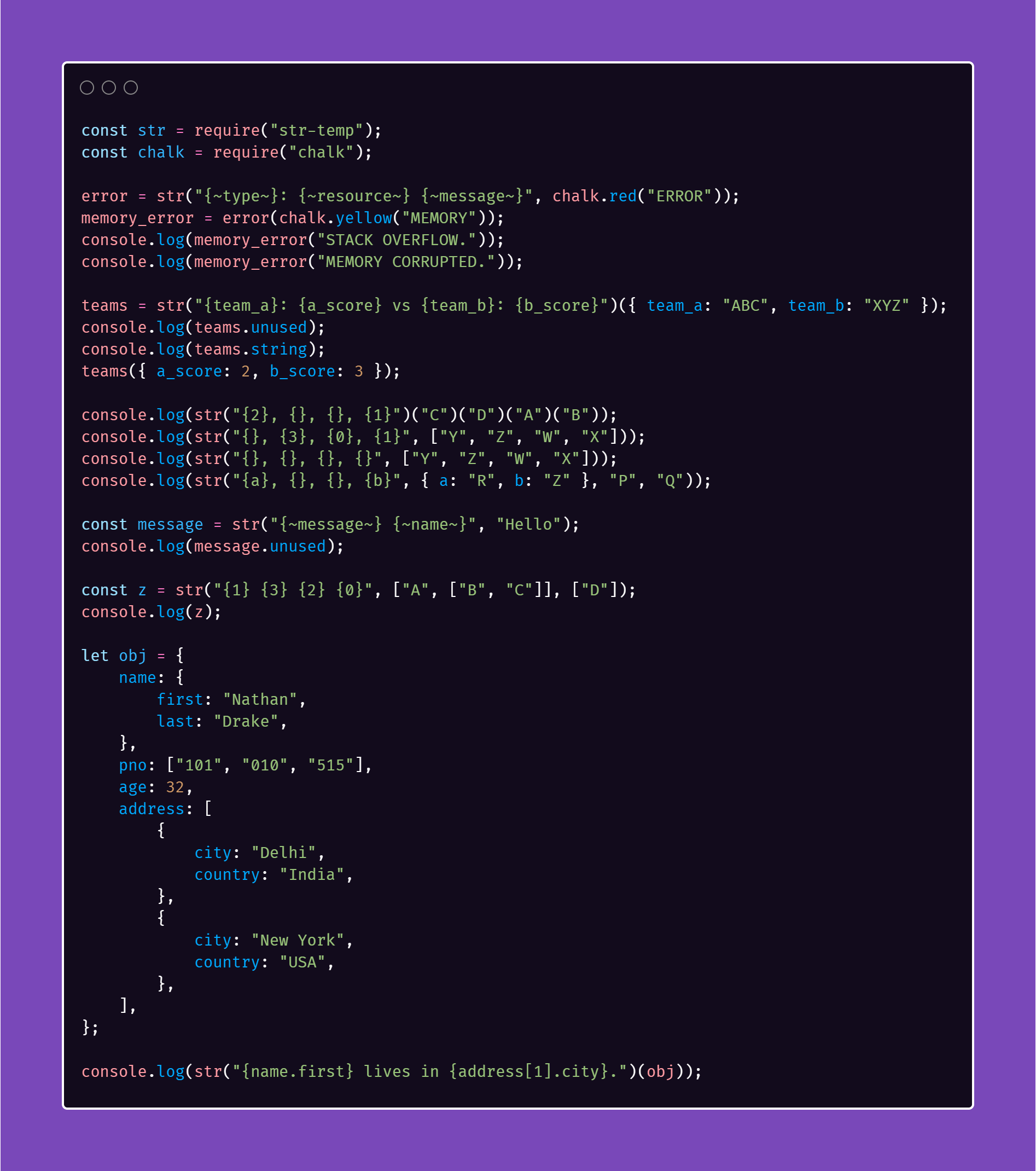
You can use comments in {} by writing the text between ~ for better readability.
str("{~message~} {~name~}", "Hello", "Node");
>> Hello Node
str("{~resource~} {}", "Memory", "Stack Overflow");
>> Memory Stack OverflowEscape Character
To escape the brackets and prevent yourself from errors, use {{ and }}
and the code will treat the brackets like normal characters.
str("{~message~} {~name~} {{🙃}}", "Hello", "Node");
>> Hello Node {🙃}Referencing
Empty
You can simply use {} where you want to substitute data in the string. The data will be picked and placed from left to right. Brackets with comments ( eg. {~message~}` ) will be also treated as empty brackets.
str("{} {} {} {}", "A")("B", "C", "D")
>> A B C DIndexes
Sometimes the order of passed elements does not match their order in the string. Use Indexes starting from 0 and the function will replace the passed Strings or Data from left to right as if they are in an array.
str("{1} {3} {2} {0}", "A", "B", "C", "D")
>> B D C AKeys
You can also pass valid JS keys between the {} and then pass the JS Object to
with the same keys and their values. Values will be overridden from left to right.
str("{message} {name}", { message: "Hello", name: "Nathan" })
>> Hello NathanHere you can also pass the key as a nested object.
str("{message} {info.name.first}", { message: "Hello", info: { name: {
first: "Nathan",
last: "Drake"
}}})
>> Hello NathanWith the nested objects, there will be arrays and you will be able to pass those array indexes too.
str("{fruit[1]} is tasty 🤤.", { fruit: [ "Banana", "Apple", "Orange"] })
>> Apple is tasty 🤤.Arrays
Pass the array rather together rather than passing the parameters individually. The values are extracted from the array and sorted out in 2 portions, ie. Strings and Numbers; and Objects. The Strings are then added from left to right. The Objects are evaluated in the same way.
str("{1} {3} {2} {0}", ["A", ["B", "C"]], ["D"])
>> B D C ATry combining it with chalk.js to see the different possibilities.
Current State
Current state of the string in returned function:
const message = str("{~message~} {~name~}", "Hello");
console.log(message.string);
>> Hello {~name~}Current state of unused brackets in returned function:
const message = str("{~message~} {~name~}", "Hello");
console.log(message.unused);
>> [ { unused: '{~name~}', index: 6 } ]Examples
CODE
OUTPUT

Note
In the case of strings like
str("{5}")You will need to pass 6 arguments where the first 5 arguments will be dumped and the 6th one will be placed in the string and the resultant will be returned.
