storage-facade-localstoragethin
v1.0.6
Published
An simple way to store data in localStorage.
Downloads
9
Maintainers
Readme
🔥 Storage facade localStorage: LocalStorageThin
An simple way to store data in localStorage. Supports caching, iteration and default values. Written in TypeScript. Uses the storage-facade library which is provides a single storage API that abstracts over the actual storage implementation.
Installation
npm install storage-facade@4 storage-facade-localstoragethin@1Data structure
The following code
import { createStorage } from 'storage-facade';
import { LocalStorageThin } from 'storage-facade-localstoragethin';
const storage = createStorage({
use: new LocalStorageThin(),
useCache: true,
});
try {
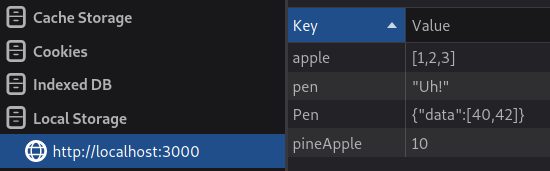
storage.Pen = { data: [40, 42] };
storage.pineApple = 10;
storage.apple = [1, 2, 3];
storage.pen = 'Uh!';
} catch (e) {
console.error((e as Error).message);
// If you are not using TypeScript replace this line with
// console.error(e.message);
}will create such keys in localStorage:
If you need virtual storages inside localStorage that can be cleared without
affecting other data stored in localStorage, use library
storage-facade-localstorage
instead.
There are similar libraries for other storages: indexedDB, sessionStorage, Map.
Usage
Storage methods
.clear()- removes all key-value pairs from the storage.entries()- returns an array of key-value pairs.deleteStorage()- delete storage.size()- returns the number of key-value pairs.key(index: number)- returns the name of the key by its index
The key and size methods can be used to create custom iterators.
'...Default' methods
The default values are used if the value in the storage is undefined.
Default values are not stored in the storage, but in the instance.
.addDefault(obj)- adds keys and values from the passed object to the list of default values.setDefault(obj)- replaces the list of default values with the given object.getDefault()- returns an object containing default values.clearDefault()- replaces a list of default values with an empty object
Examples
Read/Write/Delete
import { createStorage } from 'storage-facade';
import { LocalStorageThin } from 'storage-facade-localstoragethin';
const storage = createStorage({
use: new LocalStorageThin(),
// If you are using a cache,
// do not create more than one instance at the same time
useCache: true, // false by default
});
try {
// Write value
storage.value = { data: [40, 42] };
// Read value
console.log(storage.value); // { data: [40, 42] }
// When writing, accesses to first-level keys are intercepted only,
// so if you need to make changes inside the object,
// you need to make changes and then assign it to the first level key.
// Get object
const updatedValue = storage.value as Record<string, unknown>;
// Make changes
updatedValue.data = [10, 45];
// Update storage
storage.value = updatedValue; // Ok
// Read value
console.log((storage.value as Record<string, unknown>).data); // [10, 45]
// OR
const value = storage.value as Record<string, unknown>;
console.log(value.data); // [10, 45]
// Delete value
delete storage.value;
console.log(storage.value); // undefined
storage.value = 30;
console.log(storage.value); // 30
// Clear storage
storage.clear();
console.log(storage.value); // undefined
// Delete storage
// Removes all key-value pairs from the storage
storage.deleteStorage();
// An error will be thrown when trying to access
// console.log(storage.value); // Error: 'This Storage was deleted!'
} catch (e) {
console.error((e as Error).message);
}Iteration .entries()
import { createStorage } from 'storage-facade';
import { LocalStorageThin } from 'storage-facade-localstoragethin';
const storage = createStorage({
use: new LocalStorageThin(),
useCache: true,
});
try {
storage.value = 4;
storage.other = 5;
const array = storage
.entries()
.map(([key, value]) => {
// ... add code here ...
return [key, value];
});
console.log(array);
/*
[
['value', 4],
['other', 5],
]
*/
} catch (e) {
console.error((e as Error).message);
}'...Default' methods
import { createStorage } from 'storage-facade';
import { LocalStorageThin } from 'storage-facade-localstoragethin';
const storage = createStorage({
use: new LocalStorageThin(),
useCache: true,
});
try {
console.log(storage.value) // undefined
storage.addDefault({ value: 9, other: 3 });
storage.addDefault({ value: 1, value2: 2 });
// Since `storage.value = undefined` the default value is used
console.log(storage.value); // 1
console.log(storage.value2); // 2
console.log(storage.other); // 3
storage.value = 42;
// When we set a value other than `undefined`,
// the default value is no longer used
console.log(storage.value); // 42
storage.value = undefined;
console.log(storage.value); // 1
storage.value = null;
console.log(storage.value); // null
delete storage.value;
console.log(storage.value); // 1
// getDefault
console.log(storage.getDefault()); // { value: 1, value2: 2, other: 3 }
// Replace 'default'
storage.setDefault({ value: 30 });
console.log(storage.value); // 30
console.log(storage.value2); // undefined
// clearDefault
storage.clearDefault();
console.log(storage.value); // undefined
console.log(storage.value2); // undefined
} catch (e) {
console.error((e as Error).message);
}Limitations
Use only first level keys when writing
When writing, accesses to first-level keys (like storage.a =,
but not storage.a[0] = or storage.a.b =) are intercepted only,
so if you need to make changes inside the object, you need to make changes
and then assign it to the first level key.
Assigning keys of the second or more levels will not give any effect.
// Read
console.log((storage.value as Record<string, unknown>).data); // Ok
// Write
// Don't do that
storage.value.data = 42; // no effectInstead, use the following approach:
// Read
console.log((storage.value as Record<string, unknown>).data); // Ok
// Write
// Get object
const updatedValue = storage.value as Record<string, unknown>;
// Make changes
updatedValue.data = 42;
// Update storage
storage.value = updatedValue; // ОкIf you are using caching
- Do not create more than one instance at the same time.
- Values should be of any structured-cloneable type (MDN).
Don't use banned key names
There is a list of key names that cannot be used because they are the same
as built-in method names: [clear, deleteStorage, size, key,
getEntries, entries, addDefault, setDefault, getDefault, clearDefault].
Use the keyIsNotBanned function to check the key if needed.
import { createStorage, keyIsNotBanned } from 'storage-facade';
import { LocalStorageThin } from 'storage-facade-localstoragethin';
const storage = createStorage({
use: new LocalStorageThin(),
useCache: true,
});
try {
const myNewKey = 'newKey';
if (keyIsNotBanned(myNewKey)) {
storage[myNewKey] = 42;
}
} catch (e) {
console.error((e as Error).message);
}Keys are string
Only values of type string can be used as keys.
Values for ...Default methods
Values for [addDefault, setDefault] methods
should be of any structured-cloneable type (MDN).
