stack-graph
v1.10.2
Published
Build graphviz from stack definition file. Outputs .dot file, .json file (structure), .md file (todo list), and .png or .svg graph. Companion to sst-serverless microservice stack
Downloads
17
Readme
Dependency graph
Service to create visual dependency graphs of services setup.
Getting started
Install npm package
npm install stack-graphCreate a stackdef folder and stackdef file
└───stackdef/
└───stackdef.jsThe stackdef file's export default should be a javascript object containing a stack definition
Running locally
Install the graphviz locally, e.g. with Homebrew
brew install graphvizLocal use with a index.js file
const { resolve } = require('path')
const { localGraph, localVerify } = require('stack-graph')
const currentPath = resolve('./')
async function main() {
const result = await localGraph({
inputFilename: 'stackdef.js',
outputFilename: 'service-map',
graphFormat: 'png', // or 'svg'
path: currentPath // required
})
console.log(result.valid) // true (or errors)
const validationResult = await localVerify({
inputFilename: './stackdef.js',
path: currentPath // required
})
console.log(result.valid) // true (or errors)}
}
main()The function can be called through node function, which takes arguments as well:
node index.js -i stackdef.js -o stackdef -e png -p "/Users/wintvelt/DEV/stack-graph/stackdef"Parameters are:
-istackdef input filename-ooutput filename (without extension)-eexport format (png is default, could be svg too)-ppath where input can be found and output will be stored
Function will evaluate args inindex.js file first, then check parameters passed in through node call.
Functions of this service
Converts a stack definition object (of a single service) to
- a
.dotformatted text string fodc, containing internal entities and event flow (for rendering with graphviz) - a
.jsonfile with the raw, cleaned up structure of nodes and edges - a
.mdfile containing all the todos needed to build the code according to the stackdef structure - a
.pngor.svgfile with a picture of the stack stucture
If you update the stackdef source and run the function again
- the
.mdfile with update: any items that were checked in the old file, will also remain checked in the new file - all other files will be overwritten
Stack definition format
Basic structure of stack definition is
// stackdef.js
module.exports = {
serviceName: "spqr-user",
nodes: []
}In this structure, nodes are an array of objects. Each object is a node.
A typical node object has following structure
{
name: "createUser.js",
type: "function",
subs: [], // only for functions or queues
pubs: [], // only for functions
queries: [], // only for functions
description: "add non-obvious notes" // optional
cluster: "internal", // optional, can also be "input" or "output"
}name or type must be provided, where options are
type:function|table|auth|bucket|topic|queue|email|schedulenamecan be anything, with following remarks- function type names should end in
.js - if the name ends in type, e.g.
visit-topic, then type does not need to be provided. Because type can be derived from the name - if the name is a clear API - e.g.
GET /user- then the API type will be inferred
- function type names should end in
API nodes - input to many services - can optionally be setup in a different way:
{
path: '/',
method: 'GET' // or any other valid http method
type: 'API' // optional, does not need to be provided
}Best practice is to define nodes only for functions. All other nodes will then be derived from the dependencies.
Use pubs, subs and queries to make connections between nodes. Each item can be a name string (make sure that the type can be derived from the name, e.g. POST /user (API), createUser.js (another function), table (table)
Or an item can be an object
{
name: 'POST /user',
serviceName: 'external-service', // optional, add if the dependency is to external item
async: true, // optional for pub, use to indicate if connection is async
isQuery: true, // optional for pub, use to indicate if connection is a query (read not write)
filters: {}, // optional for pubs and subs
description: "add non-obvious notes" // optional
}Filters are relevant for pub or sub to topics:
- for
pubthey should include the relevant attributes added to topic message, e.g.{ sections: "profile, photo, address" } - for
subthey should include the relevant attributes to filter messages for this sub, e.g.{ eventName: "MODIFY", sections: "profile" }
Query dependencies get a different color. Async calls are indicated by an open arrow. NB: Streamed events (from auth and db) are technically not asynchronous. For sake of schema, they are noted as async calls. For both 'real' async calls and streamed events, consideration should be given to capture dead letters and/or failed calls from stream.
If a node or dependency item has the string dlq (for dead letter queue) of failover in its name, the node will get a different layout. You would want to monitor these from somewhere else. Best practice is to include a
- dead letter queue for any function that is invoked asynchronously (from other Lambda, SQS, SNS, S3 etc)
- or failover queue needed for any function that is invoked by a stream (from db) - needs setup in eventSourceMapping/ trigger. NB: events only logged if the real event source makes the call NB: Auth/ Cognito does not have any options to queue failed events. Cognito triggers are called synchronously, but these triggers are not configured in Lambda. Any failures should be gracefully fed back to invoking API or call - usually a user/ front-end
Example
The following stackdef.js definition:
Will generate this image:
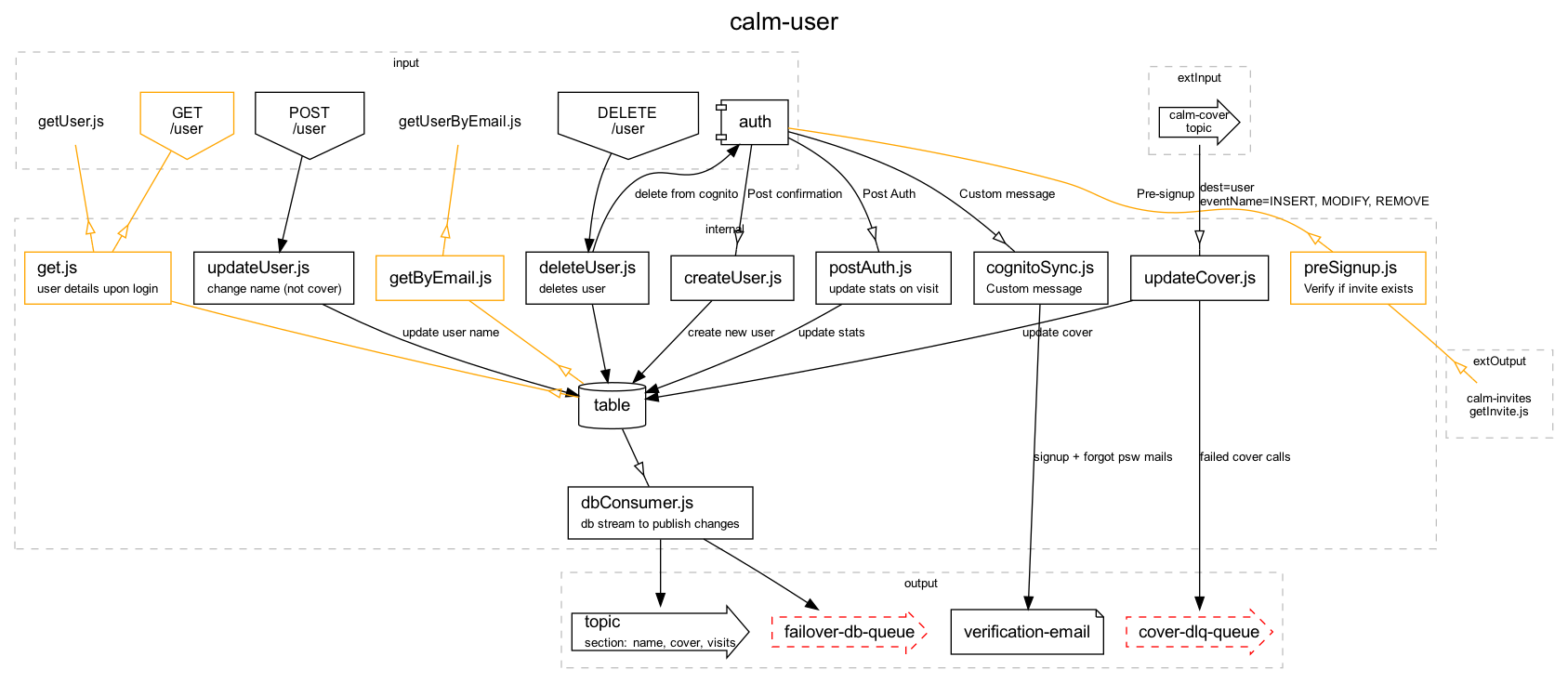
And this todo list:
