sshp
v0.4.5
Published
simple, intuitive, no bullshit approach to parallel ssh
Downloads
42
Readme
sshp
simple, intuitive, no bullshit approach to parallel ssh
Installation
npm install -g sshpWhy?
there are thousands of programs that do this, but none of them do it well. I wanted something simple, clear, non-assumptive, and cross-platform compatible.
sshp takes a command to run (pass directly to ssh), and
a list of hosts with -f file or passed in over stdin. For every line of
output from the remote hosts, the hostname will be prepended and printed out to
the user. All stderr appears red and is written to stderr on the local
machine, and stdout green to stdout. The exit code will be printed as soon as
it is avaliable if -e is supplied, green for 0, red for != 0, as well as the ms
deltas for all operations so you know how long things took.
Most importantly, you can specify the maximum number of concurrent ssh
connections to use with -m or --max-jobs.
Send a SIGUSR1 to the process to get the current progress (like dd(1))
Examples
Parallel ssh into hosts supplied by a file, running uname -v
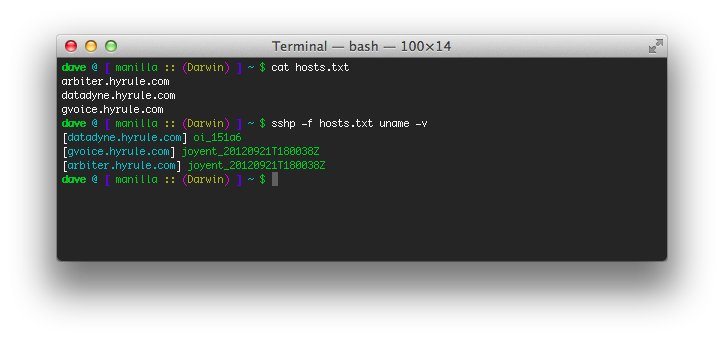
see how simple it is? you can get fancy and check the exit codes of the commands run remotely.
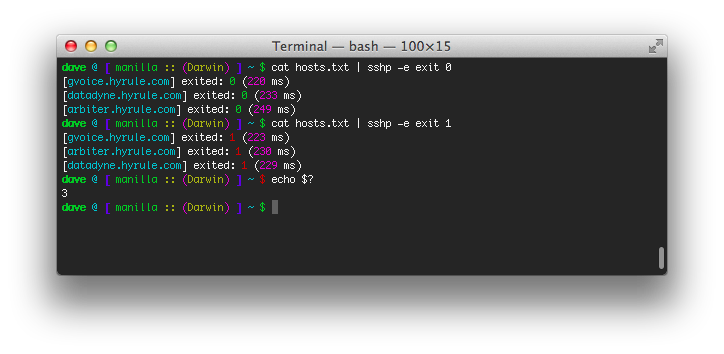
You can see the exit status of every command run remotely.
I'm also illustrating the point that sshp takes the input file
over stdin, I'm not trying to win a uuoc
award.
Run with -d to get full debug information, making it clear what
sshp will do.
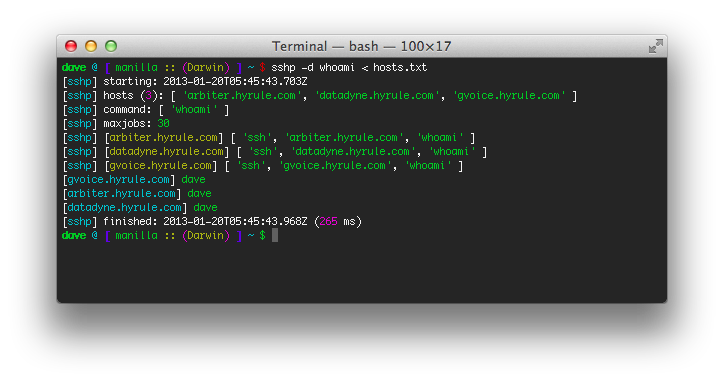
Just like ssh, sshp takes arguments like -l user, -p port and
-q. If these arguments are not present, it will be as if you ran ssh
without those arguments. This means ssh will run using your .ssh config
if it is present, and not assume you ssh out on port 22, or as your username
for instance.
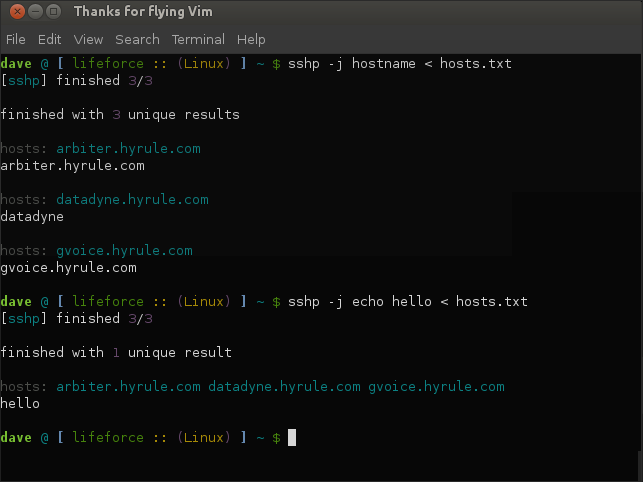
Join hosts together by unique output to clearly identify differences or discrepancies in the output generated by each host.
Usage
Usage: sshp [-m maxjobs] [-f file] command ...
parallel ssh with streaming output
examples
ssh into a list of hosts passed via stdin and get the output of `uname -v`
sshp uname -v < hosts
ssh into a list of hosts passed on the command line, limit max parallel
connections to 3, and grab the output of ps piped to grep on the remote end
sshp -m 3 -f my_hosts.txt "ps -ef | grep process"
options
-a, --anonymous hide hostname prefix, defaults to false
-b, --boring disable color output
-d, --debug turn on debugging information, defaults to false
-e, --exit-codes print the exit code of the remote processes, defaults to false
-f, --file a file of hosts separated by newlines, defaults to stdin
-g, --group group the output together as it comes in by hostname, not line-by-line
-h, --help print this message and exit
-j, --join join hosts together by unique output (aggregation mode)
-m, --max-jobs the maximum number of jobs to run concurrently, defaults to 300
-n, --dry-run print debug information without actually running any commands
-N, --no-strict disable strict host key checking for ssh, defaults to false
-s, --silent silence all stdout and stderr from remote hosts, defaults to false
-t, --trim trim hostnames from fqdn to short name (remove domain), defaults to false
-u, --updates check for available updates
-v, --version print the version number and exit
ssh options (options passed directly to ssh)
-i, --identity ssh identity file to use
-l, --login the username to login as
-q, --quiet run ssh in quiet mode
-p, --port the ssh port
-y, --tty allocate a pseudo-tty for the ssh sessionLicense
MIT License
Extra
If you're looking for cross-platform compatible see Installation above ;)
