solidbench
v2.0.0
Published
A benchmark for Solid to simulate vaults with social network data.
Downloads
527
Maintainers
Readme
SolidBench.js
A benchmark for Solid to simulate vaults with social network data.
This benchmark allows you to generate a large amount of Solid data vaults with simulated social network data, and serve them over HTTP using a built-in Solid Community Server instance. Furthermore, different SPARQL queries will be generated to simulate workloads of social network apps for Solid.
This benchmark is based on the LDBC SNB social network dataset.
Requirements
- Node.js (16 or higher)
- Docker (required for invoking LDBC SNB generator)
Installation
$ npm install -g solidbenchor
$ yarn global add solidbench --ignore-enginesQuick start
$ solidbench generate: Generate Solid data vaults with social network data.$ solidbench serve: Serve datasets over HTTP.- Initiate HTTP requests over
http://localhost:3000/, such as$ curl http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000933/profile/card
Usage
1. Generate
The social network data can be generated using the default options:
$ solidbench generateFull usage options:
solidbench generate
Generate social network data
Options:
--version Show version number [boolean]
--cwd The current working directory
[string] [default: .]
--verbose If more output should be printed [boolean]
--help Show help [boolean]
-o, --overwrite If existing files should be overwritten
[string] [default: false]
-s, --scale The SNB scale factor [number] [default: 0.1]
-e, --enhancementConfig Path to enhancement config
[string] [default: enhancer-config-pod.json]
-f, --fragmentConfig Path to fragmentation config
[string] [default: fragmenter-config-pod.json]
-q, --queryConfig Path to query instantiation config
[string] [default: query-config.json]
--validationParams URL of the validation parameters zip file
[string] [default: https://.../validation_params.zip]
-v, --validationConfig Path to validation generator config
[string] [default: validation-config.json]
--hadoopMemory Memory limit for Hadoop
[string] [default: "4G"]Memory usage
For certain scale factors, you may have to increase your default Node memory limit. You can do this as follows (set RAM limit to 8GB):
NODE_OPTIONS=--max-old-space-size=8192 solidbench.js generateWhat does this do?
This generate command will first use the (interactive) LDBC SNB generator
to create one large Turtle file with a given scale factor (defaults to 0.1, allowed values: [0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300, 1000]).
The default scale factor of 0.1` produces around 5M triples, and requires around 15 minutes for full generation on an average machine.
Then, auxiliary data will be generated using ldbc-snb-enhancer.js
based on the given enhancement config (defaults to an empty config).
Next, this Turtle file will be fragmented using rdf-dataset-fragmenter.js
and the given fragmentation strategy config (defaults to a Solid vault-based fragmentation).
Then, query templates will be instantiated based on the generated data.
This is done using sparql-query-parameter-instantiator.js
with the given query instantiation config (defaults to a config instantiating all LDBC SNB interactive queries).
Finally, validation queries and results will be generated.
This is done using ldbc-snb-validation-generator.js with the given validation config.
This defaults to a config instantiating all queries and results from the validation_params-sf1-without-updates.csv file from LDBC SNB.
This default config will produce queries and expected results in the out-validate/ directory,
which are expected to be executed on a scale factor of 1.
2. Serve
The social network data can be served over HTTP as actual Solid vaults:
$ solidbench serveFull usage options:
solidbench serve
Serves the fragmented dataset via an HTTP server
Options:
--version Show version number [boolean]
--cwd The current working directory [string] [default: .]
--verbose If more output should be printed [boolean]
--help Show help [boolean]
-p, --port The HTTP port to run on [number] [default: 3000]
-b, --baseUrl The base URL of the server [string]
-r, --rootFilePath Path to the root of the files to serve
[string] [default: "out-fragments/http/localhost_3000/"]
-c, --config Path to server config
[string] [default: server-config.json]
-l, --logLevel Logging level (error, warn, info, verbose, debug, silly)
[string] [default: "info"]What does this do?
The fragmented dataset from the preparation phase is loaded into the Solid Community Server so that it can be served over HTTP.
The provided server config uses a simple file-based mapping, so that for example the file in out-fragments/http/localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000933/profile/card is served on http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000933/profile/card.
Once the server is live, you can perform requests such as:
$ curl http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000933/profile/cardData model
By default, the following data model is used where all triples are placed in the document identified by their subject URL.
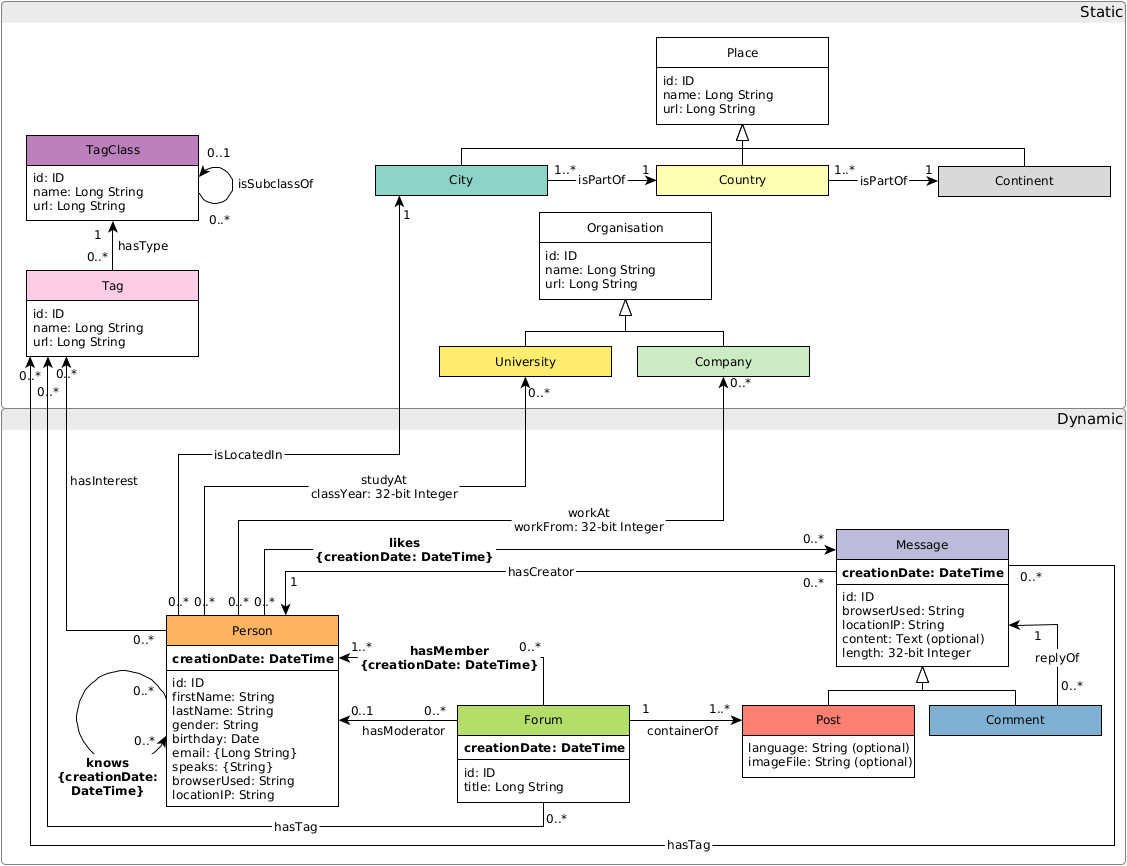
Query templates can be found in templates/queries/.
Pod-based fragmentation
By default, data will be fragmented into files resembling Solid data pods.
For example, a generated pod can contain the following files:
pods/00000000000000000290/
comments/
2010-12-02
2012-07-14
noise/
NOISE-1411
NOISE-83603
posts/
2010-02-14
2012-09-09
profile/
card.
settings/
publicTypeIndexAll files are serialized using the N-Quads serialization.
The noise/ directory contains dummy triples with the main purpose of increasing the size of a pod.
The amount of noise that is produced can be configured using the enhancement config file.
Below, a minimalized example of the contents of a profile can be found:
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://www.w3.org/ns/solid/terms#publicTypeIndex> <http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/settings/publicTypeIndex> .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#type> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/Person> .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://www.w3.org/ns/pim/space#storage> <http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/> .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/id> "290"^^<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#long> .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/firstName> "Ayesha" .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/lastName> "Baloch" .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/gender> "male" .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/hasInterest> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/tag/John_the_Baptist> .
<http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000000290/profile/card#me> <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/knows> _:b4_knows00000000000000124063 .
_:b4_knows00000000000000124063 <http://localhost:3000/www.ldbc.eu/ldbc_socialnet/1.0/vocabulary/hasPerson> <http://localhost:3000/pods/00000000000000001753/profile/card#me> .Limitations
At this stage, this benchmark has the following limitations:
- Vaults don't make use of authentication, and all data is readable by everyone without authentication.
- SPARQL update queries for modifying data within vaults are not being generated yet: https://github.com/SolidBench/SolidBench.js/issues/3
- All vaults make use of the same vocabulary: https://github.com/SolidBench/SolidBench.js/issues/4
License
This software is written by Ruben Taelman.
This code is released under the MIT license.
