s3lite
v0.0.6
Published
A wrapper library for SQLite that keeps database file on Amazon S3 storage and adds support for promises and async/await.
Downloads
35
Readme
 S3Lite → SQLite + S3
S3Lite → SQLite + S3
A wrapper library for SQLite that keeps database file on Amazon S3 storage and adds support for promises and async/await.
Usage
npm i --save s3liteconst S3Lite = require('s3lite')
const db = S3Lite.database(
'https://bucket-name.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/database.sqlite',
{
s3Options: {
accessKeyId: 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
secretAccessKey: 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY'
}
}
)
const data = await db.all('SELECT * FROM table WHERE column = ?', 'value')Table of contents
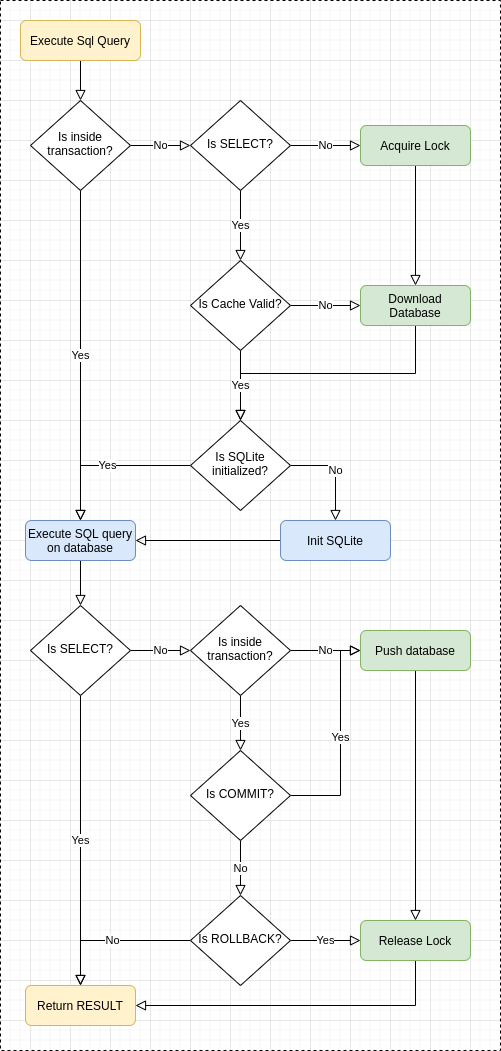
How It Works
- To execute select-like sql query S3Lite pull the database file from s3 bucket if database file has changed. Then initialize the Sqlite object if needed, execute query and return result on success.
- To execute non-select-like sql query S3Lite acquire lock on s3 bucket, then pull the database file from s3 bucket if database file has changed. Then initialize the Sqlite object if needed, execute query. After successful executing query S3Lite push the database to S3 bucket and release lock, then return result.
Minimal AWS S3 Policy to library works:
{
"Id": "S3LitePolicyId",
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "S3LiteStatementPolicyId",
"Action": ["s3:DeleteObject", "s3:GetObject", "s3:PutObject"],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/database.sqlite",
"arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/database.sqlite.lock"
],
"Principal": {
"Your": "Principal ARN"
}
}
]
}API Documentation
Since this library is using node-sqlite3 under the hood all information about parameters in the specified methods can be found here.
S3Lite
S3Lite.database
static database (s3FileName, [options]) → {Database}
Init Database object. It doesn't fetch database file or open SQLite connection. Database object is in lazy mode, it means during first query it will fetch the database file and open connection to SQLite.
If you need to open database before executing the sql query use the db.open() method.
Parameters:
{string} s3FileNameAccess url to a database on s3 bucket. Supports three different access url styles:- Virtual Hosted Style Access:
https://bucket.s3.region.amazonaws.com/key - Path-Style Access:
https://s3.region.amazonaws.com/bucket-name/key - Aws-Cli Style Access:
s3://bucket-name/keyAs you can see in this case there is no information about region (which is required by aws-cli). To provide region uses3Optionsparameter. For more information see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSJavaScriptSDK/latest/AWS/S3.html#constructor-property
- Virtual Hosted Style Access:
{Object} [options](optional):
| Type | Name | Default | Description |
| ---------- | ------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| {string} | localFilePath | /tmp/s3lite | This is directory where downloaded database form s3 has been saved. |
| {number} | mode | S3Lite.OPEN_READWRITE | S3Lite.OPEN_CREATE | Mode to open the Sqlite. Combination of: S3Lite.OPEN_READONLY, S3Lite.OPEN_READWRITE, S3Lite.OPEN_CREATE |
| {Object} | s3Options | {} | Object passed to AWS.S3 constructor. |
| {number} | acquireLockRetryTimeout | 100ms | Timeout in milliseconds to wait before retrying acquire lock again. |
| {number} | remoteDatabaseCacheTime | 1000ms | Timeout in milliseconds to wait before checking database update on s3 bucket. |
| {number} | maxLockLifetime | 60000ms | Maximum lock lifetime on s3 bucket. |
| {number} | minLockLifetime | 1000ms | Minimum lock lifetime on s3 bucket. |
Returns:
{Database}: Database object
const db = S3Lite.database(
'https://bucket-name.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/database.sqlite',
{
localFilePath: '/tmp',
s3Options: {
accessKeyId: 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
secretAccessKey: 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY'
}
}
)Database
Database.all
async all (sql, [params...]) → {Promise<Array>}
Runs the sql query with the specified parameters and returns Promise of Array if the query has been executed successfully.
If no data found, empty array has been resolved by the promise.
Parameters:
{string} sql: The sql query to run. It can contains placeholder to be bound by the given parameters.{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<Array>}: If the query has been executed successfully method returnsPromiseofArrayof objects.
// async/await
const data = await db.all('SELECT id, name FROM table LIMIT ?', 10)
// promise
db.all('SELECT id, name FROM table LIMIT $a', { $a: 10 }).then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
/*
[
{ id: 1, name: 'test1' },
{ id: 2, name: 'test2' }
]
*/Database.get
async get (sql, [params...]) → {Promise<Object>}
Runs the sql query with the specified parameters and returns Promise of Object if the query has been executed successfully.
If no data found, undefined has been resolved by the promise.
Parameters:
{string} sql: The sql query to run. It can contains placeholder to be bound by the given parameters.{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<Object|undefined>}: If the query has been executed successfully method returnsPromiseofObjectorundefinedif nothing found.
// async/await
const data = await db.get('SELECT id, name FROM table')
// promise
db.get('SELECT id, name FROM table').then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
/*
{ id: 1, name: 'test1' }
*/Database.exec
async exec (sql) → {Promise<Database>}
Run all the sql queries. No results have been returned here.
Parameters:
{string} sql: Sql queries to run.
Returns:
{Promise<Database>}: If the query has been executed successfully method returnsPromiseofDatabaseobject.
// async/await
await db.exec(`
CREATE TABLE test(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, control INTEGER);
INSERT INTO test VALUES(1, 'foo1', 1);
INSERT INTO test VALUES(2, 'foo2', 2);
`)
// promise
db.exec(
'CREATE TABLE test(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, control INTEGER)'
).then(() => {
// success
})Database.run
async run (sql, [params...]) → {Promise<{lastID: number, changes: number, sql: string}>}
Runs the sql query with the specified parameters and returns Promise of Object containing {lastID: number, changes: number, sql: string} if the query has been executed successfully.
Parameters:
{string} sql: The sql query to run. It can contains placeholder to be bound by the given parameters.{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<{lastID: number, changes: number, sql: string}>}: If the query has been executed successfully method returnsPromiseofObject:lastId: id of the last inserted rowchanges: number of changes done by the sql querysql: executed sql query
// async/await
const result = await db.run("INSERT INTO test VALUES(NULL, 'foo1', 1)")
// promise
db.run("INSERT INTO test VALUES(NULL, 'foo1', 1)").then(result => {
console.log(result)
})
/*
{ lastID: 1, changes: 1, sql: "INSERT INTO test VALUES(NULL, 'foo1', 1)" }
*/Database.prepare
async prepare (sql, [params...]) → {Promise<Statement>}
Prepare a statement
Parameters:
{string} sql: The sql query to run. It can contains placeholder to be bound by the given parameters.{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<Statement>}: Statement object (self)
// async/await
const stmt = await db.prepare('INSERT INTO test VALUES(NULL, ?, ?)')
// promise
db.prepare('INSERT INTO test VALUES(NULL, ?, ?)').then(stmt => {
// stmt {Statement}
})Database.open
async open () → {Promise<Database>}
Open the database, fetch database file from s3 bucket and open the SQLite connection.
Returns:
{Promise<Database>}: Database object
// async/await
await db.open()
// promise
db.open().then(() => {
// database opened
})Database.close
async close () → {Promise<Database>}
Close the SQLite connection
Returns:
{Promise<Database>}: Database object
// async/await
await db.close()
// promise
db.close().then(() => {
// database closed
})Statement
Statement object created by db.prepare() method.
It contains three properties:
lastId: id of the last inserted rowchanges: number of changes done by the sql querysql: executed sql query
Statement.all
async all ([params...]) → {Promise<Array>}
Execute the statement with the specified parameters and returns Promise of Array if the query has been executed successfully.
If no data found, empty array has been resolved by the promise.
Parameters:
{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<Array>}: If the query has been executed successfully method returnsPromiseofArrayof objects.
// async/await
const stmt = await db.prepare('SELECT * FROM test WHERE column = ? LIMIT ?')
const data = await stmt.all(1, 5)
// promise
db.prepare('SELECT * FROM test WHERE column = ?').then(stmt => {
stmt.all().then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
})
/*
[
{ id: 1, name: 'test1' },
{ id: 2, name: 'test2' }
]
*/Statement.get
async get ([params...]) → {Promise<Object>}
Execute the statement with the specified parameters and returns Promise of Object if the query has been executed successfully.
If no data found, undefined has been resolved by the promise.
Parameters:
{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<Object|undefined>}: If the query has been executed successfully method returnsPromiseofObjectorundefinedif nothing found.
// async/await
const stmt = await db.prepare('SELECT * FROM test WHERE column = ? LIMIT 1')
const data = await stmt.get(3)
// promise
db.prepare('SELECT * FROM test WHERE column = ?').then(stmt => {
stmt.get(3).then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
})
/*
{ id: 1, name: 'test1' }
*/Statement.run
async run ([params...]) → {Promise<Statement>}
Execute the statement with the specified parameters and returns Promise of Object containing {lastID: number, changes: number, sql: string} if the query has been executed successfully.
Parameters:
{...*|Object|Array} [params](optional): Parameters to bind. There are three ways to pass parameters: as an arguments, as an array or as na object.
Returns:
{Promise<Statement>}: Statement object (self)
// async/await
const stmt = await db.prepare('INSERT INTO test VALUES (NULL, ?)')
await stmt.run('foo')
// promise
db.prepare('INSERT INTO test VALUES (NULL, ?)').then(stmt => {
stmt.run('foo').then(stmt => {
console.log(stmt)
})
})
/*
// stmt {Statement}
*/Statement.reset
async reset () → {Promise<Statement>}
Reset the cursor of the statement. It's require for re-execute the query with the same params.
Returns:
{Promise<Statement>}: Statement object (self)
// async/await
const result = await stmt.reset()
// promise
stmt.reset().then(stmt => {
console.log(stmt)
})
/*
// stmt {Statement}
*/Statement.finalize
async finalize () → {Promise<Statement>}
Finalize the statement
Returns:
{Promise<Statement>}: Statement object (self)
// async/await
const result = await stmt.finalize()
// promise
stmt.finalize().then(stmt => {
console.log(stmt)
})
/*
// stmt {Statement}
*/