rust-like-match
v1.0.7
Published
## 简介
Downloads
9
Maintainers
Readme
Rust-Like-Match
简介
rust-like-match 提供了在 javascript 或 typescript 中使用 Rust-Like 的模式匹配. 并且在 typescript 环境下, rust-like-match 能够利用类型校验来实现 rust 中 match 的穷尽匹配以及提供优秀的类型提示.
什么是 Rust-Like 的模式匹配?
在说到模式匹配之前, 我们先来看下 rust 中的枚举功能.
enum Message {
Quit,
Move { x: i32, y: i32 },
Write(String),
ChangeColor(i32, i32, i32),
}这里定义了一个名为 Message 的枚举类型, 包含了四个成员. 成员后的 {} 或者 () 代表着可以将什么类型的数据附加到该枚举成员上.
初始化枚举成员:
let msg1 = Message::Quit;
let msg2 = Message::Move { x: 10, y: 20 };
let msg3 = Message::Write("hello rust".to_string());
let mgs3 = Message::ChangeColor(255, 255, 255);接下来回到主题, 来看下 rust 中的 match 关键字.
match msg1 {
Message::Quit => quit(),
Message::Move { x, y } => move_item(x, y),
Message::Write(msg) => println!("{}", msg),
Message::ChangeColor(r, g, b) => change_color(r, g, b),
}match 关键字后跟一个表达式, 在这个栗子中是变量 msg1 的值. 接下来是一对大括号, 里面包含了 match 的分支. 一个分支由两部分组成: 一个模式和一些代码. 第一个分支的模式是枚举成员 Message::Quit, 之后的 => 运算符将模式和需要执行的代码分开, 这里的代码是执行函数 quit. 同时, 在匹配上附加了额外数据的枚举成员时, 可以将其作为参数传递给后续需要执行的代码. 这里的代码结构有点类型 javascript 中的箭头函数.
match 也支持通配模式:
match msg1 {
Message::Quit => quit(),
_ => other()
}上述代码中当匹配上 Message::Quit 之外的成员时, 都将执行 other 函数, 其中 _ 为 rust 特定的占位符.
Typescript 中的模式匹配
接下来我们使用 switch 来模仿下 match:
type Message =
| {
key: 'Quit';
}
| { key: 'Move'; value: { x: number; y: number } }
| { key: 'Write'; message: string }
| { key: 'ChangeColor'; r: number; g: number; b: number };
let msg!: Message;
switch (msg.key) {
case 'Quit': {
quit();
break;
}
case 'Move': {
move(msg.value);
break;
}
case 'Write': {
console.log(msg.message);
break;
}
case 'ChangeColor': {
change_color(msg.r, msg.g, msg.b);
break;
}
}Match 的优势
在我看来, match 主要的优势有以下三点:
- 当
match中没有使用通配模式时, 其中的分支必须覆盖了所有的可能性, 否则编译将不会通过. switch是一个语句, 而不是一个表达式, 无法使用类似const value = switch(...){...}的操作, 只能在每一个case里面去执行赋值语句, 而match为一个表达式, 其返回值为分支中执行的代码的返回值.- 优秀的多模式匹配机制.
switch中的多模式匹配需要移除case中的break语句, 也就是说对于每一个独立case都需要在尾部添加break语句, 但也容易因为break的丢失导致出现一些“误会”. 而match中的多模式采用类似Message::Quit | Message::Start => doSomething()的语法, 且每一个独立的分支不需要添加任何额外的语句.
使用方式
在了解了 match 的具体语法以及优势后, 我们回到主题 rust-like-match 中, 我们首先来看下具体的使用方式:
初始化
import { defineMatchObject, none } from "rust-like-match"; const Message = defineMatchObject({ Quit: none, Move: (x: number, y: number) => ({ x, y }), Write: (msg: string) => msg, ChangeColor: (r: number, g: number, b: number) => ({ r, g, b }), }); //or const obj = { Quit: none, Move: (x: number, y: number) => ({ x, y }), Write: (msg: string) => msg, ChangeColor: (r: number, g: number, b: number) => ({ r, g, b }), } as const; const Message = defineMatchObject(msg);首先从
rust-like-match中导出函数defineMatchObject以及变量none. 由于 typescript 中已经存在enum的概念. 所以, 这里将初始化过程命名为 定义一个具有Match功能的对象, 也就是defineMatchObject. 该函数接收一个字面量类型的对象,key值对应rust中的枚举成员名,value值的类型为None (typeof none)或者为一个函数.None的情况对应着未给枚举成员附加额外数据, 相应的, 值为函数即代表着附加额外数据的情况.赋值
我们来看下得到的
Message的具体格式: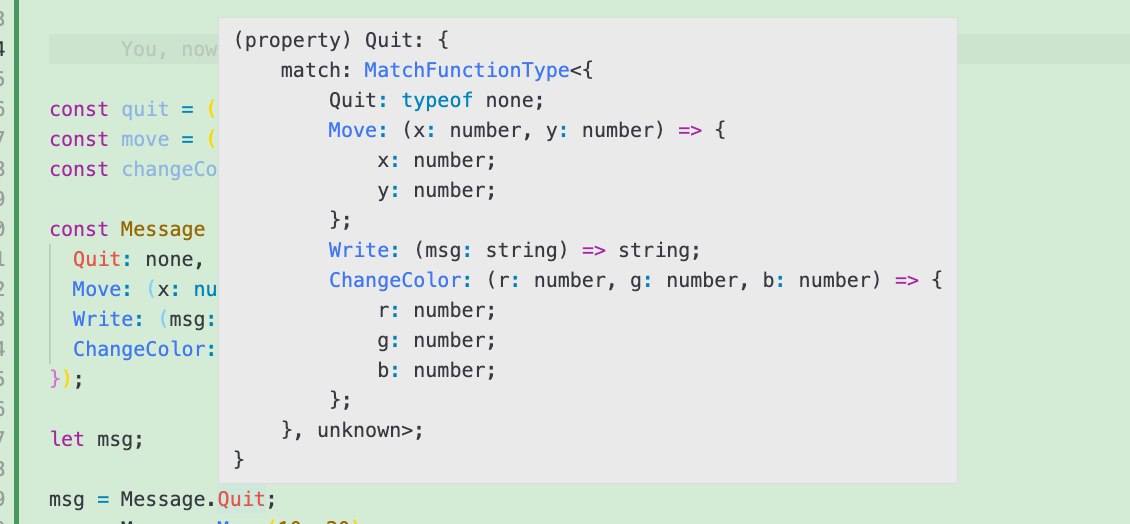
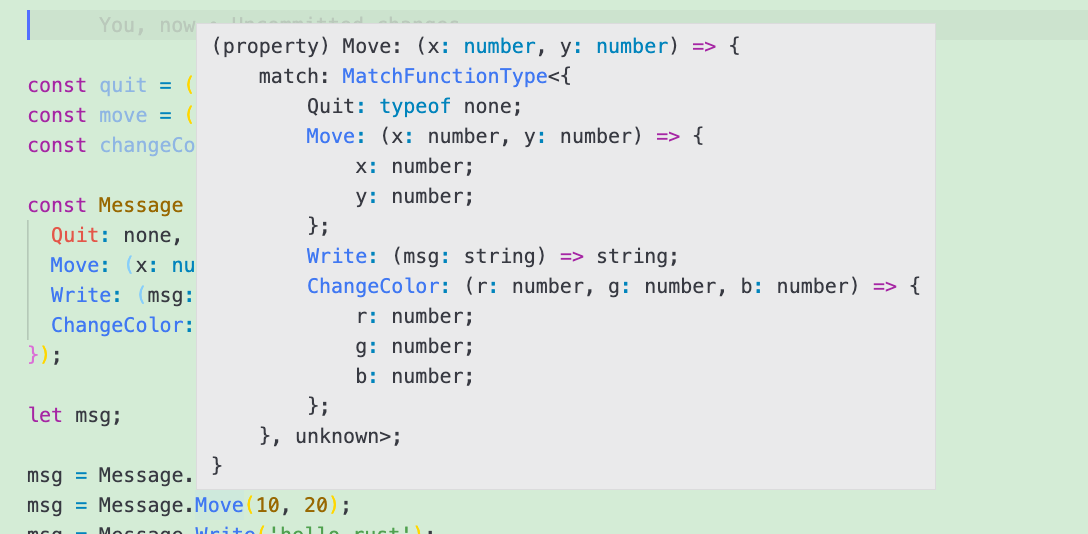
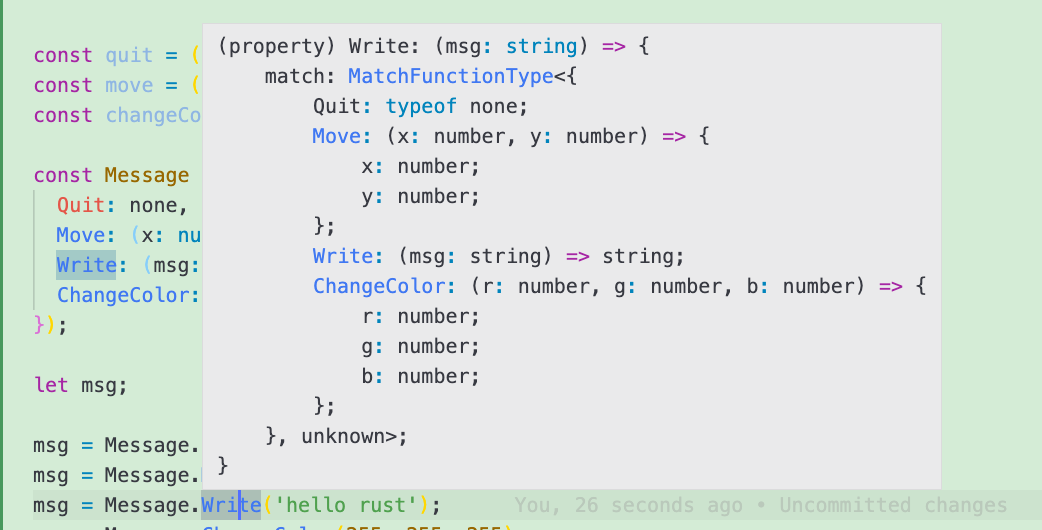
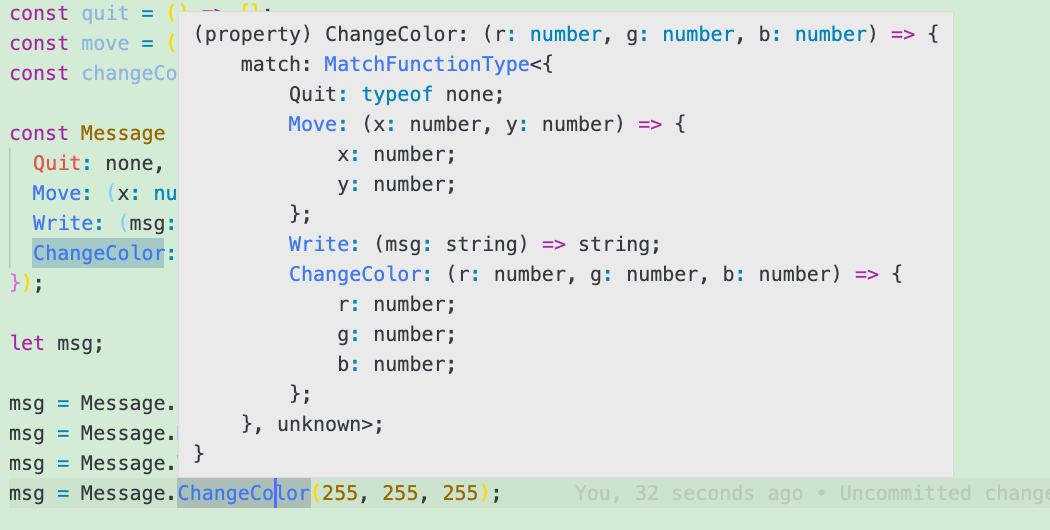
可以看到, 当初始值为
none时,Message的成员值(Quit)为一个拥有match属性的对象. 当初始值为函数时,Message的成员值同样也是一个函数, 且该函数的入参类型与初始的函数入参类型一致. 该函数的返回值为一个拥有match属性的对象.所以我们这样来进行赋值:
let msg; msg = Message.Quit; //or msg = Message.Move(10, 20); //or msg = Message.Write("hello rust"); //or msg = Message.ChangeColor(255, 255, 255);匹配
match函数接收一个对象作为参数, 对象的每一个key:value对应着一条分支,key值为一个模式, 必须满足穷尽模式或者使用通配模式,value为一个函数, 该函数能够接收到defineMatchObject时定义的函数的返回值, 并将其作为参数. 函数体为分支匹配上后执行的代码.接下来主要介绍在 typescript 环境下其拥有的一些特性:
支持通配模式, 当分支中存在
_时, 此分支涵盖了其他可能的值, 且无需满足全匹配.msg.match({ Quit:() => quit(), _ :() => other(), })穷尽匹配: 当分支中不存在
_时, 分支必须覆盖所有的情况, 否则typescript将编译失败.msg.match({ Quit: () => quit(), Move: ({ x, y }) => move(x, y), Write: (msg) => console.log(msg), ChangeColor: ({ r, g, b }) => changeColor(r, g, b), });参数类型自动推导. 每个分支中的函数的入参类型为定义时函数的返回类型.
支持泛型.
//此时 res 类型将自动推导为 number const res = msg.match({ Quit: () => 1, Move: ({ x, y }) => 2, Write: (msg) => 3, ChangeColor: ({ r, g, b }) => 4, }); //由于未标注泛型, 且存在分支的返回类型不一致, 此时 typescript 将会报错 const res = msg.match({ Quit: () => 1, Move: ({ x, y }) => '2', Write: (msg) => 3, ChangeColor: ({ r, g, b }) => 4, }); //res 的类型为 string | number | boolean | Array<number> const res = msg.match<string | number | boolean | Array<number>>({ Quit: () => 1, Move: ({ x, y }) => [x, y], Write: (msg) => false, ChangeColor: ({ r, g, b }) => `${r}-${g}-${b}`, });
拓展
在 React 项目中, 怎样在能保证支持类型校验的同时将其设置为一个
state?rust-like-match现支持导出类型MatchObjectType. 具体使用方式如下:import { defineMatchObject, none, MatchObjectType } from 'rust-like-match'; const statusEnum = { Loading: none, Success: (data?: Item) => data, Error: (err: string) => Error, } as const; const RequestStatus = defineMatchObject(statusEnum); const [status, setStatus] = useState<MatchObjectType<typeof statusEnum>>(); useEffect(() => { setStatus(RequestStatus.Loading); api .getData() .then((res) => { if (res.data.code === ResponseCode.SUCCESS) { setStatus(RequestStatus.Success(res.data.data)); } }) .catch((err) => { setStatus( RequestStatus.Error(err?.toString() ?? "unknown error") ); }); }, []); return ( //... { status?.match({ Loading: () => <Spin />, Success: (data) => renderData(data), Error: (err) => renderError(err) }) } //... )新增函数
baseTypeMatch, 支持对基础类型数据进行模式匹配. 具体使用方式如下:number 类型
const value1 = baseTypeMatch(1, { //val type is 1 1: (val) => val + 2, 2: (val) => val + 3, _: (val) => val, }); expect(value1).toBe(3); const value2 = baseTypeMatch(value1, { //val type is number 1: (val) => val + 2, 2: (val) => val + 3, '3 | 4': (val) => val + 1, _: (val) => val, }); expect(value2).toBe(4); const cases: BaseTypeMatchPatternType<number, number> = { '1 | 2': (val) => val + 1, 3: (val) => val + 1, _: (val) => val + 1, }; const value3 = baseTypeMatch(value2, cases); expect(value3).toBe(5);string 类型
const value1 = baseTypeMatch('foo', { //val type is foo foo: (val) => val + 2, bar: (val) => val + 3, _: (val) => val, }); expect(value1).toBe('foo2'); const value2 = baseTypeMatch(value1, { //val type is string foo: (val) => val + 2, bar: (val) => val + 3, 'foo2 | foo1': (val) => val + 1, _: (val) => val, }); expect(value2).toBe('foo21'); const cases: BaseTypeMatchPatternType<string, string> = { '1 | 2': (val) => val + 1, bar: (val) => val + 1, _: (val) => val + 1, }; const value3 = baseTypeMatch(value2, cases); expect(value3).toBe('foo211');boolean 类型
const value1 = baseTypeMatch<number>(false, { //val type is false false: (val) => (val ? 1 : 2), true: (val) => (val ? 1 : 2), }); expect(value1).toBe(2); const value2 = baseTypeMatch(value1, { //val type is number 2: (val) => true, _: (val) => false, }); expect(value2).toBeTruthy(); const cases: BaseTypeMatchPatternType<boolean, string> = { 'true | false': (val) => 'hello', bar: (val) => 'rust', _: (val) => 'javascript', }; const value3 = baseTypeMatch(value2, cases); expect(value3).toBe('hello');symbol 类型
const symbol = Symbol(); const value1 = baseTypeMatch<number | symbol>(Symbol(), { foo: () => 1, bar: () => 2, _: () => symbol, }); expect(value1).toBe(symbol); const cases: BaseTypeMatchPatternType<symbol, string | boolean | number | symbol> = { [value1 as symbol]: (val) => false, 'a | b': (val) => 1, 1: (val) => val, _: (val) => 'hello', }; const value2 = baseTypeMatch(value1 as symbol, cases); expect(value2).toBeFalsy();
未来将会支持的功能
- 实现多模式匹配, 预计会以
"Quit | Start": () => other()的形式来实现. - 兼容 typescript 中的
enum(实现方案考虑中).
