roguelike
v0.5.0
Published
Generate 2D levels
Downloads
33
Readme
Roguelike Level Generators
This repository contains multiple 2D "dungeon" level generator algorithms. Depending on the genre of game you're building, one algorithm will be better than another.
npm install roguelikeTable of Contents
- Level: Classic Roguelike Level Generator
- Level: Grid with Keys and Locks Level Generator
- Level: Metroidvania with Snaking Room Shapes
- Room: Odd Square Room Generator
- Utility: Random Functions
- Utility: Grid Functions
- Utility: Grid Collection
roguelike/level/roguelike: Classic Roguelike Level Generator
The concept is simple, inspired by sliding system used by Brogue. Random rooms are generated, and slid into the level in a random direction until they collide with an existing room. Once they collide a door is generated randomly in the colliding surface. We only generate rooms on odd rows and columns so that everything fits together perfectly.
This generator is useful when you care about every wall and room and you want them to fit together in interesting ways.
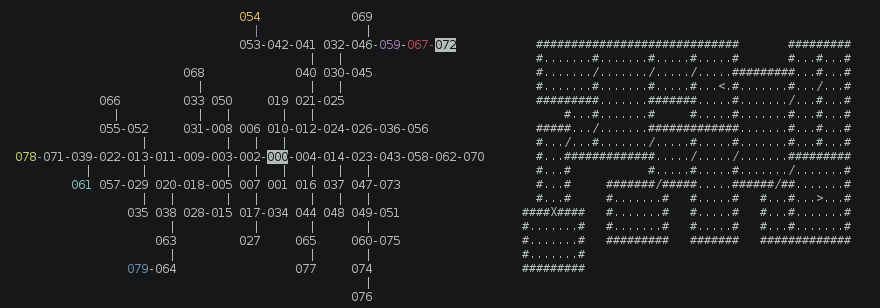
Example Generated Level
This is a simple visual representation (visualized using test/level/roguelike.js).
#########
#.......#
#.......#####
#.......#...#
#####.......X...#
#.../.......#...#
#...####/####...#
#.<.# #...# #...#
#...# #.>.# #####
#...# #...#
##### #####
In the above diagram, a . period represents floor, a # octothorp represents a wall, a / forward slash represents a normal door, and a X capital X represents a special door.
The entrance to the level is a < less than symbol and the exit is a > greater than symbol.
Usage
const LevelRoguelike = require('roguelike/level/roguelike');
let level = LevelRoguelike({
width: 17, // Max Width of the world
height: 11, // Max Height of the world
retry: 100, // How many times should we try to add a room?
special: true, // Should we generate a "special" room?
room: {
ideal: 5, // Give up once we get this number of rooms
min_width: 3,
max_width: 7,
min_height: 3,
max_height: 7
}
});
console.log(level);Example Output
A typical level takes about 3ms to generate on my laptop. YMMV.
A special room can be used for whatever you want. I like to use them for shops and hidden rooms (you'll know when a door is special, too).
The world attribute is entirely optional for you to use. All the data within it can be recreated using the other attributes.
Output JSON
{
"width": 17, // Maximum units wide the world needs to fit within (could be less)
"height": 11, // Maximum units tall the world needs to fit within (could be less)
"enter": {
"room_id": 1,
"x": 2,
"y": 7
},
"exit": {
"room_id": 2,
"x": 8,
"y": 8
},
"deadends": [], // List rooms with a single door, NOT including enter/exit/special
"special": {
"room_id": 2,
"door_id": 1
},
"door_count": 3,
"doors": {
"0": {
"id": 0,
"rooms": [ 0, 1 ],
"x": 4,
"y": 5,
"enter": true
},
"1": {
"id": 1,
"rooms": [ 0, 2 ],
"x": 8,
"y": 6,
"exit": true
},
"2": {
"id": 2,
"rooms": [ 0, 3 ],
"special": true,
"x": 12,
"y": 4
}
},
"room_count": 4,
"rooms": {
"0": {
"doors": [ 0, 1, 2 ],
"height": 5,
"id": 0,
"left": 5,
"neighbors": [ 1, 2, 3 ],
"top": 1,
"width": 7
},
"1": {
"doors": [ 0 ],
"height": 5,
"id": 1,
"left": 1,
"neighbors": [ 0 ],
"top": 5,
"width": 3,
"deadend": true,
"enter": true
},
"2": {
"doors": [ 1 ],
"height": 3,
"id": 2,
"left": 7,
"neighbors": [ 0 ],
"top": 7,
"width": 3,
"deadend": true,
"exit": true
},
"3": {
"doors": [ 2 ],
"height": 5,
"id": 3,
"left": 13,
"neighbors": [ 0 ],
"special": true,
"top": 3,
"width": 3,
"deadend": true
}
},
"walls": [ // X/Y coordinates of every wall in the map
[4, 0],
[4, 1],
[4, 2],
[10, 10]
// ... Truncated List of Walls ...
],
"world": [ // [Y][X] array
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 1, 5, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2 ],
[ 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 6, 1, 2, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
]
}World Matrix Cell Types
|TYPE | ID | |---------------|----| |VOID | 0 | |FLOOR | 1 | |WALL | 2 | |DOOR | 3 | |SPECIAL DOOR | 4 | |ENTER | 5 | |EXIT | 6 |
Caveats
- Rooms must be odd sized, and at least 3 units wide/tall
- World should likewise be odd sized
- Weird things will happen if you try to generate rooms larger than the world
roguelike/level/gridKeys: Grid with Keys and Locks Level Generator
Unlike the Roguelike level generator, this level generator doesn'actually care about the content of each "room". These rooms could be Zork/Adventure style, where a room is a field or a whole building or a room. If specified, this level generator will lock doors and place keys throughout the level.
Example Generated Level
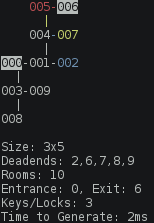
In this diagram, numbers are rooms, with room 000 being the entrance and room 006 the exit.
If a room is colored than the room contains a key.
A - hyphen or | pipe represents a door between two rooms.
If the door is colored it means that door is locked.
Usage
const LevelGridKeys = require('roguelike/level/gridKeys');
const level = new LevelGridKeys({rooms: 10, keys: 3});
let result = level.generate();
console.log(result);Room Types
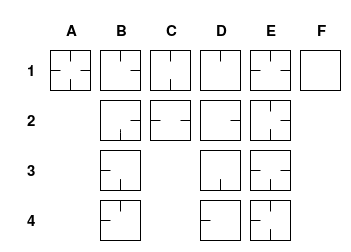
Each room will contain a template field.
This is a convenience for figuring out which prefabricated room designs you would like to use.
This diagram explains the design of each room.
In theory you can simply design one level for each letter and then rotate them for each number.
Example Output
{
// The bounds of the level will fit within this many room units
"size": {
"height": 6,
"width": 3
},
// The entrance and exit are important. The deadends isn't as useful.
"terminals": {
"deadends": [ 2, 6, 7, 8, 9 ],
"entrance": 0,
"exit": 8
},
// Here is a 2D grid of the map, stored as [Y][X]. Numbers represent Room IDs
"grid": [
[ 7, 0, 2 ],
[ 6, 1, null ],
[ null, 3, null ],
[ 9, 4, null ],
[ null, 5, null ],
[ null, 8, null ]
],
// This is an array of keys.
// door = ID of door this key unlocks
// id = ID of this specific key (always matches array index)
// location = ID of room where this key is located
"keys": [
{
"door": 7,
"id": 0,
"location": 5
},
{
"door": 4,
"id": 1,
"location": 9
},
{
"door": 8,
"id": 2,
"location": 4
}
],
// This is an array of all doors
// exit = Whether this door leads to an exit room
// id = ID of this door (always matches array index)
// key = ID of the key required to unlock this door
// orientation = Whether this door is (v)ertical or (h)orizontal
// rooms = Array of room IDs this door connects to
"doors": [
{
"exit": false,
"id": 0,
"key": null,
"orientation": "v",
"rooms": [ 0, 1 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 1,
"key": null,
"orientation": "h",
"rooms": [ 0, 2 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 2,
"key": null,
"orientation": "v",
"rooms": [ 1, 3 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 3,
"key": null,
"orientation": "v",
"rooms": [ 3, 4 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 4,
"key": 1,
"orientation": "v",
"rooms": [ 4, 5 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 5,
"key": null,
"orientation": "h",
"rooms": [ 1, 6 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 6,
"key": null,
"orientation": "h",
"rooms": [ 0, 7 ]
},
{
"exit": true,
"id": 7,
"key": 0,
"orientation": "v",
"rooms": [ 5, 8 ]
},
{
"exit": false,
"id": 8,
"key": 2,
"orientation": "h",
"rooms": [ 4, 9 ]
}
],
// Array of rooms used in this map
// distance = distance from room to spawn. Room 0 is always spawn
// doors = object containing IDs of doors connected to this room
// entrance = whether this room is the entrance to the level
// exit = whether this room is the exit from the level
// id = ID of this room (always matches array index)
// keyInRoom = ID of a key which should be located in this room
// template = shape of this room as doors are concerned, see above
// x = X Coordinate of this room
// y = Y Coordinate of this room
"rooms": [
{
"distance": 0,
"doors": { "e": 1, "n": null, "s": 0, "w": 6 },
"entrance": true,
"exit": false,
"id": 0,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "E3",
"x": 1,
"y": 0
},
{
"distance": 1,
"doors": { "e": null, "n": 0, "s": 2, "w": 5 },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 1,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "E4",
"x": 1,
"y": 1
},
{
"distance": 1,
"doors": { "e": null, "n": null, "s": null, "w": 1 },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 2,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "D4",
"x": 2,
"y": 0
},
{
"distance": 2,
"doors": { "e": null, "n": 2, "s": 3, "w": null },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 3,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "C1",
"x": 1,
"y": 2
},
{
"distance": 3,
"doors": { "e": null, "n": 3, "s": 4, "w": 8 },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 4,
"keyInRoom": 2,
"template": "E4",
"x": 1,
"y": 3
},
{
"distance": 4,
"doors": { "e": null, "n": 4, "s": 7, "w": null },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 5,
"keyInRoom": 0,
"template": "C1",
"x": 1,
"y": 4
},
{
"distance": 2,
"doors": { "e": 5, "n": null, "s": null, "w": null },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 6,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "D2",
"x": 0,
"y": 1
},
{
"distance": 1,
"doors": { "e": 6, "n": null, "s": null, "w": null },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 7,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "D2",
"x": 0,
"y": 0
},
{
"distance": 5,
"doors": { "e": null, "n": 7, "s": null, "w": null },
"entrance": false,
"exit": true,
"id": 8,
"keyInRoom": null,
"template": "D1",
"x": 1,
"y": 5
},
{
"distance": 4,
"doors": { "e": 8, "n": null, "s": null, "w": null },
"entrance": false,
"exit": false,
"id": 9,
"keyInRoom": 1,
"template": "D2",
"x": 0,
"y": 3
}
]
}roguelike/level/metroidvania: Metroidvania with Snaking Room Shapes
This level generator is useful for creating Metroidvania style dungeons. Each individual unit in the grid is referred to as a zone. Rooms are made up of one or more zones and can be of arbitrary shapes. Levels will contain one exit in each of the cardinal directions. There is also an online Level Generator to give a better feel of level generation.
Example Generated Level

Usage
const LevelMetroidvania = require('roguelike/level/metroidvania');
const result = LevelMetroidvania({
width: 5, // Max number of zones wide
height: 5, // Max number of zones tall
minZonesPerRoom: 1, // Minimum number of zones per room
maxZonesPerRoom: 3, // Maximum number of zones per room
minRoomsPerMap: 1, // Minimum number of rooms per map
maxRoomsPerMap: 9, // Maximum number of rooms per map
newDoors: 2, // How many additional doors to add to prevent tedious linear mazes
roomDiff: 2, // When adding a new door, at least how far should their room ID's be
roomDiffOdds: 1/2 // Odds of inserting a new door when an opportunity happens
});
console.log(result);Example Output
The resulting object contains three properties.
The first property is map and contains a grid of all zones in the map and is formatted [Y][X].
The next property is exits and gives us the coordinate of all four map exits.
The last property is rooms, an array of rooms and the zones contained in each room.
Each zone element in the map contains a few properties.
The open field is whether the zone is an open/passable/traversable area (if false, it's just void).
The room field gives us the ID of the room this zone is a part of.
The exit field tells us of the room contains a level exit.
The zone field gives us the ID of the Zone (not very useful).
The edges field describes the four edges of the zone.
An edge can be open if it connects to another Zone in the same room.
It can be wall if the edge should contain a wall.
It can be door if the edge shuld connect one room to another.
It can be exit if this edge is a connection to another map.
{
"map": [
[
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 1,
"exit": true,
"zone": 3,
"edges": { "n": "wall", "e": "open", "s": "wall", "w": "exit" }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
}
],
[
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 2,
"exit": null,
"zone": 4,
"edges": { "n": "wall", "e": "door", "s": "door", "w": "wall" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 1,
"exit": null,
"zone": 1,
"edges": { "n": "door", "e": "door", "s": "open", "w": "wall" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 1,
"exit": null,
"zone": 2,
"edges": { "n": "open", "e": "door", "s": "wall", "w": "open" }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
}
],
[
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 3,
"exit": null,
"zone": 5,
"edges": { "n": "wall", "e": "door", "s": "wall", "w": "door" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 0,
"exit": null,
"zone": 0,
"edges": { "n": "wall", "e": "wall", "s": "door", "w": "door" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 5,
"exit": null,
"zone": 9,
"edges": { "n": "door", "e": "door", "s": "door", "w": "door" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 6,
"exit": true,
"zone": 10,
"edges": { "n": "door", "e": "wall", "s": "exit", "w": "wall" }
}
],
[
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 4,
"exit": true,
"zone": 6,
"edges": { "n": "exit", "e": "wall", "s": "open", "w": "door" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 4,
"exit": null,
"zone": 7,
"edges": { "n": "open", "e": "wall", "s": "open", "w": "wall" }
},
{
"open": true,
"room": 4,
"exit": true,
"zone": 8,
"edges": { "n": "open", "e": "exit", "s": "wall", "w": "door" }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
}
],
[
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
},
{
"open": false,
"room": null,
"exit": null,
"zone": null,
"edges": { "n": null, "e": null, "s": null, "w": null }
}
]
],
"exits": {
"n": { "x": 3, "y": 1 },
"s": { "x": 2, "y": 4 },
"e": { "x": 3, "y": 3 },
"w": { "x": 0, "y": 3 }
},
"rooms": [
[
{ "x": 2, "y": 2 }
],
[
{ "x": 1, "y": 2 },
{ "x": 1, "y": 3 },
{ "x": 0, "y": 3 }
],
[
{ "x": 1, "y": 1 }
],
[
{ "x": 2, "y": 1 }
],
[
{ "x": 3, "y": 1 },
{ "x": 3, "y": 2 },
{ "x": 3, "y": 3 }
],
[
{ "x": 2, "y": 3 }
],
[
{ "x": 2, "y": 4 }
]
]
}roguelike/room/oddSquare: Odd Square Room Generator
This room generator was designed to play nicely with Grid with Keys and Locks Level Generator
Rooms must always contain odd dimensions. Rooms will always be squares.
Example Generated Level
Here's an example room of the A1 (four doors) template:
#####/#####
#.......,.#
#.I.I.I.I.#
#....,.,..#
#.I.....I.#
/....$..../
#.I.....I.#
#..,..,...#
#.I.I.I.I.#
#.,......,#
#####/#####The capital I's represent pillars. The #'s represent walls. The /'s represent doors. The periods represent floor. The comma is floor with non-blocking litter. The $ is treasure.
Usage
The type property is described at in the section on Room Types.
const Gen = require('roguelike/room/oddSquare');
const gen = new Gen({
size: 5
});
const room = gen.generate({
type: 'E2',
pillars: true,
treasure: true,
litter: 0.25, // 25% of free space (after decor) will be litter
chasm: true, // Surroundings is "emptyness" as opposed to walls
holes: 3, // Adds random holes (defaults to 0)
circle: true, // Generates a circular room, must be combined with chasm
gashes: 2, // Number of gashes (empty lines) to add
decor: [ // Add blocking decoration to the map
{id: 'cobweb', rate: 0.1, location: 'any'}, // 10% of free tiles will be cobweb
{id: 'desk', count: 1, location: 'central'}, // 1 free tile not by a chasm will be a desk
{id: 'books', rate: 0.05, location: 'edge'} // 5% of free tiles by chasm will be books
],
focalpoint: { // Force focalpoint to be a certain coordinate, otherwise random
x: 3,
y: 4
}
});Example Output
The size property contains the dimensions of the room. The center property is the calculated center coordinate of the room. The doors property is an array of door objects.
The layers property contains four different layers. The composite layer is interesting in that it contains essentially a summary of the other three layers.
Output JSON
{
"size": {
"width": 5,
"height": 5
},
"center": {
"x": 2,
"y": 2
},
"type": "E2",
"doors": [
{
"direction": "n",
"orientation": "v",
"x": 2,
"y": 0
},
{
"direction": "e",
"orientation": "h",
"x": 4,
"y": 2
},
{
"direction": "s",
"orientation": "v",
"x": 2,
"y": 4
}
],
"layers": {
"composite": [
[
{ "x": 0, "y": 0, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 1, "y": 0, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 2, "y": 0, "door": "n", "wall": false, "block": "special", "protected": true },
{ "x": 3, "y": 0, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 4, "y": 0, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false }
],
[
{ "x": 0, "y": 1, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 1, "y": 1, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true },
{ "x": 2, "y": 1, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true, "litter": true },
{ "x": 3, "y": 1, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true },
{ "x": 4, "y": 1, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false }
],
[
{ "x": 0, "y": 2, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 1, "y": 2, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true },
{ "x": 2, "y": 2, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": "special", "protected": true, "treasure": true },
{ "x": 3, "y": 2, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true, "litter": true },
{ "x": 4, "y": 2, "door": "e", "wall": false, "block": "special", "protected": true }
],
[
{ "x": 0, "y": 3, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 1, "y": 3, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true },
{ "x": 2, "y": 3, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true },
{ "x": 3, "y": 3, "door": null, "wall": false, "block": false, "protected": true, "litter": true },
{ "x": 4, "y": 3, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false }
],
[
{ "x": 0, "y": 4, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 1, "y": 4, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 2, "y": 4, "door": "s", "wall": false, "block": "special", "protected": true },
{ "x": 3, "y": 4, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false },
{ "x": 4, "y": 4, "door": null, "wall": true, "block": true, "protected": false }
]
],
"floor": [
[ "solid", "solid", "solid", "solid", "solid" ],
[ "solid", "solid", "litter", "solid", "solid" ],
[ "solid", "solid", "solid", "litter", "solid" ],
[ "solid", "solid", "solid", "litter", "solid" ],
[ "solid", "solid", "solid", "solid", "solid" ]
],
"mid": [
[ "wall", "wall", "door", "wall", "wall" ],
[ "wall", null, null, null, "wall" ],
[ "wall", null, "treasure", null, "door" ],
[ "wall", null, null, null, "wall" ],
[ "wall", "wall", "door", "wall", "wall" ]
],
"ceiling": [
[ null, null, null, null, null ],
[ null, null, null, null, null ],
[ null, null, null, null, null ],
[ null, null, null, null, null ],
[ null, null, null, null, null ]
]
}
}
roguelike/utility/random: Utility Random
These are useful random functions which I find myself rewriting for many games.
Usage
const random = require('roguelike/utility/random');random.shuffle(array)
Returns an array where the element order has been randomized
random.shift(array)
Maintains the order of array elements but randomly shifts them. As an example:
let result = random.shift([1,2,3,4,5,6]);
console.log(result);
// [4,5,6,1,2,3]random.range(minInteger, maxInteger)
Returns an integer between the supplied integers, inclusive.
random.element(array)
Returns a random element from the given array.
random.elementWeighted(array, weightArray)
Returns a random element from array, based on the weights provided in weightArray. As an example, consider the following:
let result = random.elementWeighted(['A', 'B'], [1, 2]);
console.log(result);
// result is 33% likely to be A and 67% likely to be Brandom.dice(diceSyntax, allowNegative=false)
Returns the result of a dice roll. By defaultl negative numbers are not allowed unless the second parameter is set to true. Here are some example dice syntaxes:
d6: 1 -> 6, evenly spread1d4: 1 -> 4, evenly spread2d8: 2 -> 16, mostly 91d3 + 2: 3 -> 5, evenly spread2d7-7: 0 -> 7, mostly 020: always 20
random.decide(floatThreshold)
Makes a decision (returns a boolean) based on the supplied floatThreshold. Here's an example:
let result = random.decide(0.7);
console.log(result);
// Result is 70% likely to be true and 30% likely to be falseroguelike/utility/grid: Utility Grid
Utility functions for working with a 2d grid. Each function makes use of points. The only properties used with a point are point.x and point.y, both of which need to be integers.
Usage
const grid = require('roguelike/utility/grid');grid.adjacent(p1, p2)
Returns true if p2 is immediately North, East, South, or West of p1.
grid.line(p1, p2, cardinal)
Implementation of Bresenham's Line Algorithm. Generates a line between two points. Tiles won't be cardinal neighbors unless you set cardinal to true. Returns an array of points.
grid.distance(p1, p2)
Returns a floating point number representing the distance between the two points.
grid.fastDistance(p1, p2)
Returns an integer representing a very fake distance. This distance is simply the max absolute value difference between either the X or Y coordinates.
grid.sameSpot(p1, p2)
Returns a boolean of whether or not the two points occupy the same coordinate.
grid.ahead(point, direction, distance=1)
Returns a new point, distance units away from the origin point, in the supplied direction. The direction must be one of north, east, south, west.
Will throw a TypeError if the supplied direction is invalid.
roguelike/utility/gridCollection: Utility Grid Collection
Useful for creating a collection of dynamic entries associated with a coordinate in a grid. Each entry should have an .x and .y integer property (if they don't exist they'll be created).
Usage
const GridCollection = require('roguelike/utility/gridCollection');
const gc = new GridCollection();gc.add(coord, entry)
Returns false if the entry already exists or if another entry already exists at the same coord otherwise true on success.
gc.get(coord)
Returns an entry if one exists, otherwise returns null
gc.has(coord)
Returns true if an entry exists at the coordinate or false if not.
gc.destroyAtCoordinate(coord)
Attempts to remove an entry at the coordinate. Returns true if the operation was successful or false if not (e.g. no entry exists).
gc.destroy(entry)
Removes the entry if it exists and returns a true, otherwise false if it's missing.
gc.moveAtCoordinate(oldCoord, newCoord)
Moves an entry from the old coordinate to the new coordinate, updating .x and .y properties if applicable. Returns true on success or false on failure. Will fail if new coordinate is occupied or old coordinate doesn't have an entry.
gc.move(entry, coord)
Moves the entry from its curent location to the specified coordinate. Updates the .x and .y properties if successful. Returns a false if either the entry doesn't exist or the new coord is occupied, otherwise returns true.
gc.each()
Returns an iterable representing each of the entries. Can be used like so:
for (let entry of gc.each()) {
console.log(entry);
}gc.clear()
Clears the collection of all entries. Returns the number of entries cleared in this manner.
gc.size()
Returns the number of entries in the collection.
