rivalz-client
v1.2.8
Published
This is a TypeScript library that provides functionalities for Rivazl Ai
Downloads
72
Readme
Rivalz File Worker
This is a TypeScript library that provides functionalities for Rivazl Ai
Installation
Before you start, make sure you have Node.js and npm/yarn installed on your machine.
npm install rivalz-clientor
yarn add rivalz-client Usage
1. Creates key in Rivalz Dashboard and use it to initialize the RivalzClient class.
After installing the package, Please come in the Rivalz Dashboard to create a encrypted key and secret key.
- Encrypt key used for encrypting the file
- Secret key used for authentication
2. Import and use the RivalzClient class in your TypeScript/JavaScript code:
import RivalzClient from 'rivalz-client';
const rivalzClient = new RivalzClient('your-secret-key');API:
1 Upload File
rivalzClient.uploadFile(file)- file: A readable stream of the file to be uploaded.
- Returns a promise that resolves to the IPFS hash of the uploaded file.
2. Upload passport file
rivalzClient.uploadPassport(file)- file: A readable stream of the file to be uploaded.
- Returns a promise that resolves to the IPFS hash of the uploaded file.
3. Download File and save it to the local file system (Node.js only)
rivalzClient.downloadFile(ipfsHash, savePath)- ipfsHash: The IPFS hash of the file to be downloaded.
- savePath: The path where the downloaded file will be saved.
- Returns a promise that resolves to the path of the saved file.
4. Download File and return it as buffer
rivalzClient.download(ipfsHash)- ipfsHash: The IPFS hash of the file to be downloaded.
- Returns a promise that resolves to a buffer containing the downloaded file.
Please replace 'your-secret', file, passport, ipfsHash, and savePath with actual values when using the RivalzClient class.
## Example
Example upload file for node.js project:
```typescript
const RivalzClient = require('rivalz-client');
// import RivalzClient from 'rivalz-client';
const fs = require('fs');
// import fs from 'fs';
const file = fs.createReadStream('file_path');
const rivalzClient = new RivalzClient('your-secret-key');
rivalzClient.uploadFile(file)Example download file for node.js project:
const RivalzClient = require('rivalz-client');
const rivalzClient = new RivalzClient('your-secret-key');
rivalzClient.downloadFile('ipfs_hash_uploaded', 'save_path')
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) API
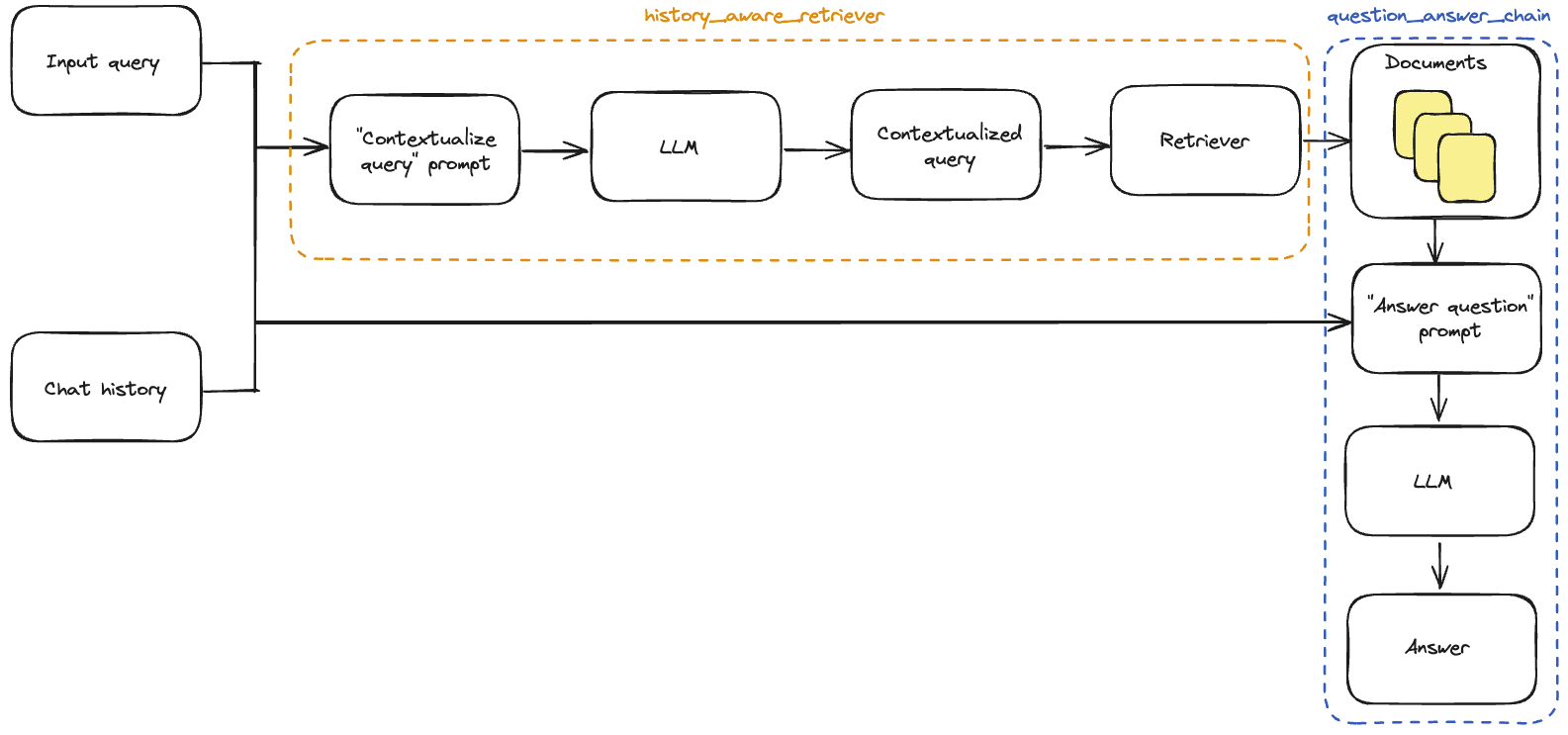
Prerequisites
Before using the RAG API, you need some rivalz credits. Claim for free now here
Creating knowledge base from a document
To vectorize a document (which will be used as embedding for the RAG) and create a knowledge base, use the
createRagKnowledgeBase method with the path to the document. This
method returns the knowledge base id which can be used to create a conversation.
We now only support PDF files for creating knowledge bases.
const response = await client.createRagKnowledgeBase('path/to/your/document.pdf', 'knowledge_base_name')
console.log(response)
// {'id': '66fa5bf022e73c17073768f0', 'name': 'test', 'files': '1727683567711_sample.pdf', 'userId': '66c4151c98bd0d3d47de682a'}Adding document to an existed knowledge base
To add document to existed knowledge base, use the addDocumentToKnowledgeBase method with the knowledge base id
and the path to the document.
const response = await client.addDocumentToKnowledgeBase('knowledge_base_id', 'path/to/your/document.pdf')
console.log(response)Deleting document from an existed knowledge base
To delete document from existed knowledge base, use the deleteDocumentFromKnowledgeBase method with the knowledge
base id and the document name.
const response = await client.deleteDocumentFromKnowledgeBase('knowledge_base_id', 'document_id')
console.log(response)Getting all knowledge bases
To get all knowledge bases, use the getKnowledgeBases method.
const response = await client.getKnowledgeBases()
console.log(response)Getting details of a knowledge base
To get details of a knowledge base, use the getKnowledgeBase method with the knowledge base id.
const response = await client.getKnowledgeBase('knowledge_base_id')
console.log(response)Creating a conversation
To create a conversation, use the createChatSession method with the knowledge base id and the question. This will
return the AI response along with the chat session id.
const response = await client.createChatSession('knowledge_base_id', 'question')
console.log(response)
// {'answer': 'Hello! How can I help you today? \n', 'session_id': '66fa625fb58f5a4b9a30b983', 'userId': '66c4151c98bd0d3d47de682a'}Adding a message to a conversation
To add a message to a conversation, use the same method createChatSession with the chat session id and the message.
const response = await client.createChatSession('knowledge_base_id', 'message', 'chat_session_id')
console.log(response)Getting all conversations
To get all conversations, use the getChatSessions method.
const response = await client.getChatSessions()
console.log(response)Getting details of a conversation
To get details of a conversation (which contains chat history for this conversation), use the getChatSession method
with the chat session id.
const response = client.getChatSession('chat_session_id')
console.log(response)Get uploaded documents
To get all uploaded documents, use the getUploadedDocuments method.
const response = await client.getUploadedDocuments()
console.log(response)Examples
Here is a complete example demonstrating how to use the rivalz-client to create a simple RAG conversation based on a
PDF document:
/*
main.ts
*/
import RivalzClient from 'rivalz-client';
const main = async () => {
// Initialize the RivalzClient with the secret token
const client = new RivalzClient('your-secret-key');
// create knowledge base
const knowledgeBase = await client.createRagKnowledgeBase('sample.pdf', 'knowledge_base_name');
const knowledgeBaseId = knowledgeBase.id;
// create conversation
let conversation = await client.createChatSession(knowledgeBaseId, 'what is the document about?');
const conversationId = conversation.session_id;
// add message to conversation
conversation = await client.createChatSession(knowledgeBaseId, 'What is a RAG application ?', conversationId);
console.log(conversation.answer);
}
main()Dependencies
This project uses the following dependencies:
- axios: For making HTTP requests.
- buffer: For handling binary data.
- @types/node: For TypeScript definitions for Node.js.
- typescript: For writing and compiling TypeScript code.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
