rest-bridge
v1.0.41
Published
Expose REST service in private network to public network, via connector (in private network) and hub (public service).
Downloads
93
Maintainers
Readme
rest-bridge
Expose REST service in private network to public network, via connector (in private network) and hub (public service).
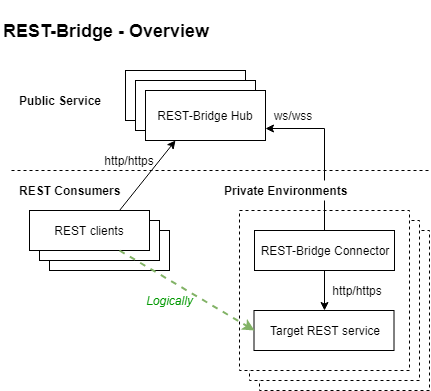
Features
- Firewall friendly: all http/ws
- HA
- Registration process to control valid connectors
Example - Hub
const hub = require('rest-bridge/hub')
let options = {
port: 80
}
hub.create(options).then(() => {
//demo purpose
hub.registry.register({
key: 'demoKey',
description: 'demo connector'
})
}).catch(console.error)
Example - Connector
const rbconnector = require('rest-bridge/connector')
process.env.NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED = 0
rbconnector.start({
hub: 'ws://localhost', //which hub to connect to
info: { //information of this connector
key: 'demoKey', //the pairing key
id: 'demoConnector'
},
target: 'http://localhost:10762', //the target http service
//additionally, path based routing an be specified using a map,
//regular expression for request path as key, and target as value.
//Example:
/*
routes: {
'/demo': {
target: 'http://localhost:8081'
},
'/products': 'https://www.vmware.com',
'.*': 'https://www.vmware.com'
}
*/
})
Example - rest-bridge client
const http = require('http')
//To do a rest-bridge call, a pairing key must be specified, so as to distinguish
//which connector to use. The pairing key can be specified either in request
//header, or request path.
//Method 1 - Specify pairing key in header
let options = {
host: 'localhost',
path: '/hello',
headers: {
'x-rest-bridge-key': 'demoKey' //specify which connector we are using
}
}
http.get(options, resp => {
let body = ''
resp.setEncoding('utf8')
.on('data', chunk => body += chunk)
.on('end', () => console.log(body))
}).on('error', console.error)
.end()
//Method 2 - Specify pairing key in request path.
//This method requires a fixed base path to be added
//http.get('http://localhost/rest-bridge-forward/<pairingKey>/hello')
Configuration Details
https://github.com/nanw1103/rest-bridge/blob/master/demo/myConfig.js
Management Interface
http://<hub_host>:<management_port>/rest-bridge
[
{
"name": "register",
"method": "post",
"path": "/registry",
"description": "Register a new connector",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/registry"
},
{
"name": "Delete registered connector",
"method": "delete",
"path": "/registry/<key>",
"description": "Remove a connector",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/registry/<key>"
},
{
"name": "registry",
"method": "get",
"path": "/registry",
"description": "Get registry information",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/registry"
},
{
"name": "registry.connector",
"method": "get",
"path": "/registry/<connector-key>",
"description": "Get information of specific connector",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/registry/<connector-key>"
},
{
"name": "nodes",
"method": "get",
"path": "/nodes",
"description": "Get nodes in this cluster instance",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/nodes"
},
{
"name": "connectors",
"method": "get",
"path": "/connectors",
"description": "Get connector information. Scope: cluster instance",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/connectors"
},
{
"name": "stat",
"method": "get",
"path": "/stat",
"description": "Get statistics. Scope: cluster instance",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/stat"
},
{
"name": "env",
"method": "get",
"path": "/env",
"description": "Get environments. Scope: cluster instance",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/env"
},
{
"name": "node",
"method": "get",
"path": "/node",
"description": "Get single node info",
"href": "http://localhost/rest-bridge/node"
}
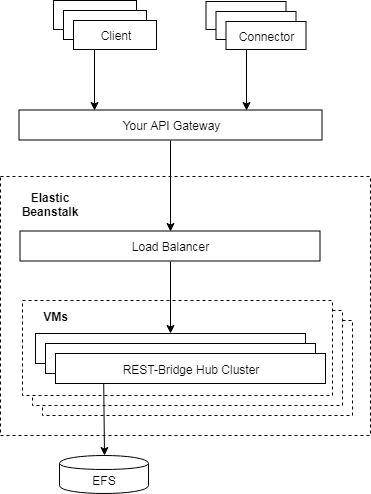
]High Availability
Create each hub instance as a cluster, using a shared store:
let hubOptions = {
port: 80,
nodes: require('os').cpus().length,
store: 'fs-store:/efs/rest-bridge-repo'
}And then create multiple clusters with load balancers, e.g. AWS Elasticbeanstalk + EFS or ElasticCache
Requests will be forwarded internally between the nodes on demand. So clients or connectors only care about connecting to a single service point.
Security
Access Control
Method 1: In hub options, specify different network interface for management endpoint, client endpoint, and connector endpoint. Use firewall/security group/api gateway to control the access
Method 2: Control context based access on api gateway or load balancer, etc.
HTTPS/WSS
Consider adding HTTPS/WSS on your load balancer or API gateway
The Storage
What is the storage for
The storage is used for two purposes:
- Record the registered connector (pairing key), so only registered connector is able to connect to the service. You may or may not need this according to specific scenario. There is also option to disable the pairing key check so as to allow any incoming connector.
- Used for internal routing in multi-machine cluster environment. For each node, upon connector connection, a record consists of node info and connector info will be created in the store. Upon a call from client, the receiving node will first search itself for the connected connector. If the connection is not on the node itself, the storage is searched to identify the node holding the connection. Then the current node will forward the http request to the target node.
If there are more than one machine/container, an external shared storage is a must. If there is only one machine (even it has a nodejs cluster), external shared storage is not needed and memory based (or cluster RPC based) internal storage can be used.
Test
Built-in test cases covers basic scenarios as well as stress testing on local computer.
npm i
npm test