responser
v2.5.6
Published
Simplify, standardize and format HTTP Status Code responses in JSON with express
Downloads
716
Maintainers
Readme
Responser
Simplify, standardize and format HTTP Status Code responses in JSON with express
No need to remember which is the code for each HTTP status anymore!
Responser provides a simple way to return standardized responses for each available HTTP status. It overwrites the express interface, making all methods accessible through your response or res variable.
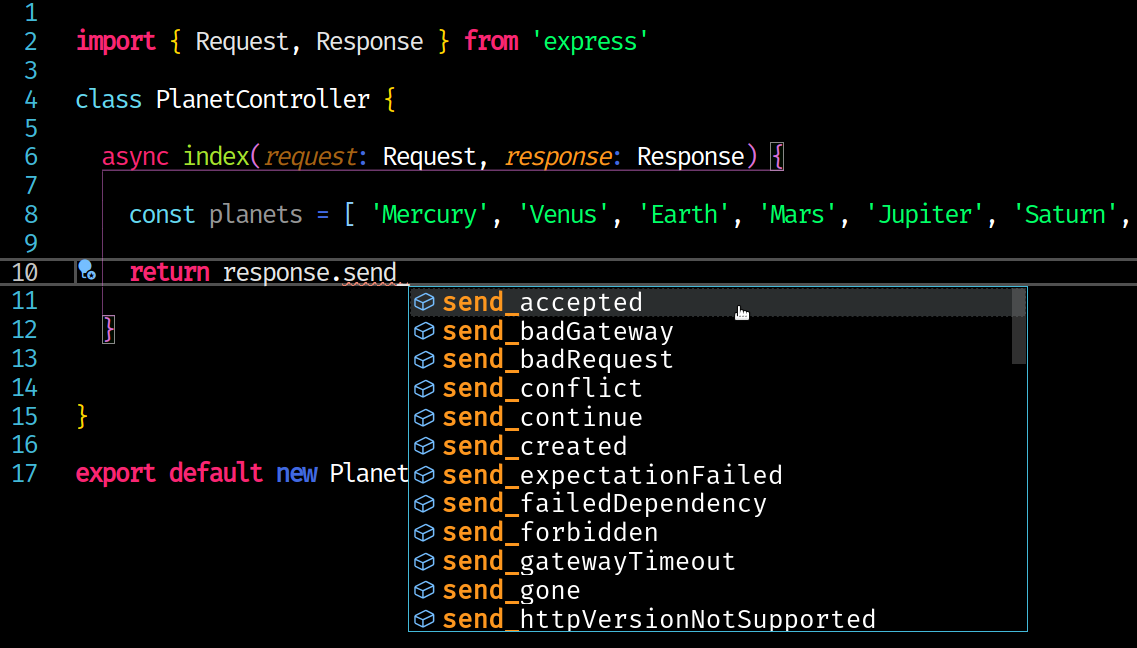
Simple Usage
Install
Add responser with your favorite package manager:
yarn add responserTypescript
Express response without the use of responser:
import express, { Request, Response } from 'express'
const app = express()
const router = express.Router()
app.use(router)
router.get('/hello', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
res.status(400).json({
status: 'BAD_REQUEST',
code: 400,
message: 'Request is wrong!',
success: false
})
})Now same code using responser:
import responser from 'responser'
import express, { Request, Response } from 'express'
const app = express()
const router = express.Router()
app.use(responser) // add responser middleware
app.use(router)
router.get('/hello', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
res.send_badRequest('Request is wrong!')
})As you can see from the example above, using responser makes code a bit cleaner and less error-prone.
Require (CommonJS) version:
const responser = require("responser").default
const express = require("express")
const app = express()
const router = express.Router()
app.use(responser) // add responser middleware
app.use(router)
router.get('/hello', (req, res) => {
res.send_badRequest('Request is wrong!')
})Input Parameters
All respose.send_* methods accept two parameters:
(message: string, content?: any) => void| parameter | description | type | required | |-----------|-----------------------------------|--------|----------| | message | Human-readable message | string | yes | | content | Anything you would like to return | any | no |
Output Properties
| property | description | type | e.g.1 | e.g.2 | |----------|----------------------------|---------|--------------|------------------------| | code | HTTP Status Code | number | 200 | 400 | status | HTTP Status Name | string | OK | BAD_REQUEST | success | Success Flag | boolean | true | false | data | content if success=true | any | { items: [] } | - | errors | content if success=false | any | - | [{ err: "err1 text"}]
Details
For each responser method,
When code is < 300 (✅ successful):
- Property
successwill betrue contentgiven will be accessible as propertydata
When code is >= 300 (❌ unsuccessful):
- Property
successwill befalse contentgiven will be accessible as propertyerrors
List of Methods (method, code and status):
send_continue 100 // Continue
send_switchingProtocols 101 // Switching Protocols
send_processing 102 // Processing
send_ok 200 // OK
send_created 201 // Created
send_accepted 202 // Accepted
send_nonAuthoritativeInformation 203 // Non Authoritative Information
send_noContent 204 // No Content
send_resetContent 205 // Reset Content
send_partialContent 206 // Partial Content
send_multiStatus 207 // Multi-Status
send_multipleChoices 300 // Multiple Choices
send_movedPermanently 301 // Moved Permanently
send_movedTemporarily 302 // Moved Temporarily
send_seeOther 303 // See Other
send_notModified 304 // Not Modified
send_useProxy 305 // Use Proxy
send_temporaryRedirect 307 // Temporary Redirect
send_permanentRedirect 308 // Permanent Redirect
send_badRequest 400 // Bad Request
send_unauthorized 401 // Unauthorized
send_paymentRequired 402 // Payment Required
send_forbidden 403 // Forbidden
send_notFound 404 // Not Found
send_methodNotAllowed 405 // Method Not Allowed
send_notAcceptable 406 // Not Acceptable
send_proxyAuthenticationRequired 407 // Proxy Authentication Required
send_requestTimeout 408 // Request Timeout
send_conflict 409 // Conflict
send_gone 410 // Gone
send_lengthRequired 411 // Length Required
send_preconditionFailed 412 // Precondition Failed
send_requestTooLong 413 // Request Entity Too Large
send_requestUriTooLong 414 // Request-URI Too Long
send_unsupportedMediaType 415 // Unsupported Media Type
send_requestedRangeNotSatisfiable 416 // Requested Range Not Satisfiable
send_expectationFailed 417 // Expectation Failed
send_imATeapot 418 // I'm a teapot
send_insufficientSpaceOnResource 419 // Insufficient Space on Resource
send_methodFailure 420 // Method Failure
send_unprocessableEntity 422 // Unprocessable Entity
send_locked 423 // Locked
send_failedDependency 424 // Failed Dependency
send_preconditionRequired 428 // Precondition Required
send_tooManyRequests 429 // Too Many Requests
send_requestHeaderFieldsTooLarge 431 // Request Header Fields Too Large
send_unavailableForLegalReasons 451 // Unavailable For Legal Reasons
send_internalServerError 500 // Internal Server Error
send_notImplemented 501 // Not Implemented
send_badGateway 502 // Bad Gateway
send_serviceUnavailable 503 // Service Unavailable
send_gatewayTimeout 504 // Gateway Timeout
send_httpVersionNotSupported 505 // HTTP Version Not Supported
send_insufficientStorage 507 // Insufficient Storage
send_networkAuthenticationRequired 511 // Network Authentication RequiredFull example: Successful response
const express = require('express')
const responser = require('responser').default
const app = express()
const router = express.Router()
app.use(responser)
app.use(router)
router.get('/planets', (request, response, next) => {
const planets = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune']
response.send_ok('Planets were found successfully', {
planets,
planetsCount: planets.length
})
})
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on port 3000'))
The route /planets generates the following response to a GET request:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
X-Powered-By: Express
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8{
"status": "OK",
"code": 200,
"success": true,
"message": "Planets were found successfully",
"data": {
"planets": [
"Mercury",
"Venus",
"Earth",
"Mars",
"Jupiter",
"Saturn",
"Uranus",
"Neptune"
],
"planetsCount": 8
}
}Full example: Unsuccessful response
const express = require('express')
const responser = require('responser').default
const app = express()
const router = express.Router()
app.use(responser)
app.use(router)
router.post('/planets', (request, response, next) => {
const planetName = request.body?.name
let myErrors = []
if(!planetName) myErrors.push({
name: 'planetName',
message: 'Planet name was not given!'
})
if(myErrors.length) return response.send_badRequest(
'The request contains one or more errors!', myErrors
)
})
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on port 3000'))Example response if planetName is not given on a POST request body.
HTTP/1.1 400 BAD REQUEST
X-Powered-By: Express
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8{
"status": "BAD_REQUEST",
"code": 400,
"success": false,
"message": "The request contains one or more errors!",
"errors": [
{
"name": "planetName",
"message": "Planet name was not given!"
}
]
}Tip: if you would like a way to check all request variables automatically, consider using request-check. It will return an array of error messages for each field.
Testing
Run the test suit with yarn test.
Contributing
If you want to contribute in any of theses ways:
- Give your ideas or feedback
- Question something
- Point out a problem or issue
- Enhance the code or its documentation
- Help in any other way
You can (and should) open an issue or even a pull request!
Thanks for your interest in contributing to this repo!
Author
Luiz Felipe Zarco ([email protected])
License
This code is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE.md file for more info.



