real-men
v1.1.5
Published
MEN stack API generator
Downloads
46
Readme
MEN stack API generator
Installation
npm i -g real-men
(if npm is not installed you will need Node.js)
Simple example
men test1
The result would be:
where each controller (only one in this case) will have the typical CRUD functions:
- GET: getAllFromItem (gets all documents from a given collection)
- GET: getOneItem (gets only one, given an id)
- POST: saveNewItem (saves a new document)
- PUT: updateItem (updates a document)
- DELETE: deleteItem (deletes a document)
Specifying entities
Many entities can be specified (being an entity the union controller + model + routes) as long as they're separated by commas with no spaces, for instance:
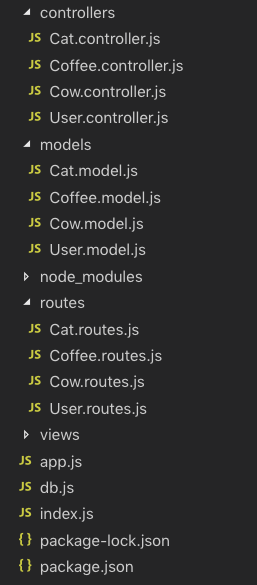
men test1 -e user,cat,cow,coffee
will generate:
Attributes specification
For a more specific data structure, a configuration file is needed. Such file must have a json extension and it looks like this:
{
"entities": {
"user": {
"name": "String",
"email": "String",
"age": "Number"
},
"cat": {
"isItAJerk": "Boolean",
"catName": "String"
},
"cow": {
"isItHoly": "Boolean",
"birthday": "Date"
},
"coffee": {
"isDecaf": "Boolean",
"hasMilk": "Boolean"
}
}
}and instead of this:
men test1 -e user,cat,cow,coffee
the line would be:
men test1 -e customMapping.json
API tester
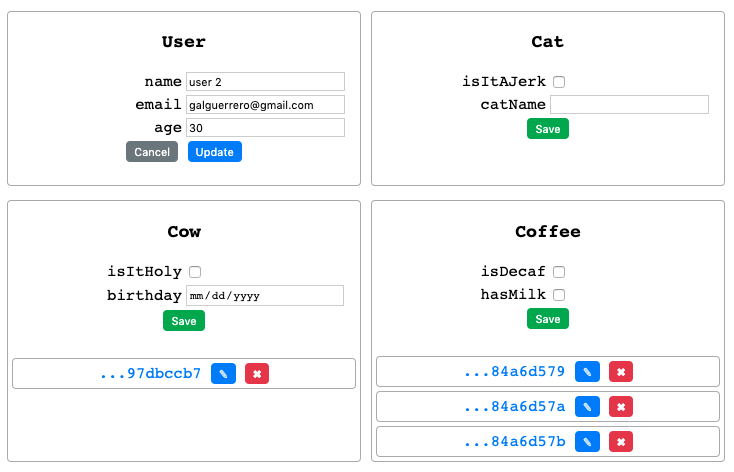
The API tester will look different depending on the level of detail specified (being the highest the config file). For instance, the one for men test1 -e user,cat,cow,coffee would be:
and the one for men test1 -e customMapping.json would look like this (note that some data has been added):
Notes
- The default entity name is 'Item' and its model has just a string attribute:
data - Currently, the API tester does have support for String, Number, Date and Boolean types (based on the moongoose SchemaTypes), any type should be functional with the appropriate settings though
- The config file attribute types must always be strings ("String", "Number", "[]", etc.)
- If not given, the default database to connect/create will be
<your-proyect-name>_DB, to specify a database use--databaseor-d - The default port to run the server is 5501, change it with
--portor-p - Use
--openor-oto automatically open the broswer and test the API - Entity names and attributes must match
^[a-zA-Z_][0-9a-zA-Z_]*$ - Entity names are automatically capitalized
- Mongo daemon (mongod) must be running to be able to create/connect to the DB
- More info with
men --help