react-three-component
v1.0.1
Published
React component using three.js library to display 3d graphics
Downloads
28
Maintainers
Readme
react-three-component
React-three-component is a TypeScript library providing React components for building 3D scenes in Three.js.
Usage
Exemplary component rendering two rotating meshes:
import { useCallback } from "react";
import {
BoxGeometry,
Canvas,
CapsuleGeometry,
DirectionalLight,
MainScene,
Mesh,
MeshStandardMaterial,
OrbitControls,
PerspectiveCamera,
} from 'react-three-component';
import * as THREE from 'three';
export const ThreeComponent = () => {
const meshAnimation = useCallback((ref: THREE.Mesh, timestamp: number, elapsed: number) => {
ref.rotation.x += elapsed * 0.001;
ref.rotation.z += elapsed * 0.001;
}, []);
const initializeMainScene = useCallback((ref: THREE.Scene | null) => {
if (ref) {
ref.background = new THREE.Color(0xffffff);
}
},[]);
return (
<Canvas>
<PerspectiveCamera position={[0, 0, 5]}/>
<OrbitControls/>
<MainScene ref={initializeMainScene}>
<DirectionalLight params={[0xffffff, 1]} position={[-5, 0, 0]}/>
<DirectionalLight params={[0xffffff, 0.8]} position={[5, 0, 3]}/>
<Mesh position={[-1, 0, 0]} animate={meshAnimation}>
<BoxGeometry/>
<MeshStandardMaterial params={[{color: 0x47b9db}]}/>
</Mesh>
<Mesh position={[1, 0, 0]} animate={meshAnimation}>
<CapsuleGeometry params={[0.5, 0.5, 10, 10]}/>
<MeshStandardMaterial params={[{color: 0xdb47b9}]}/>
</Mesh>
</MainScene>
</Canvas>
);
};Result:
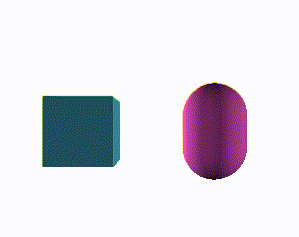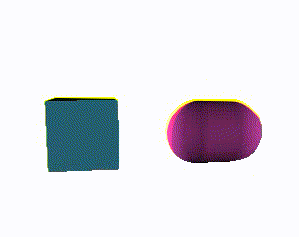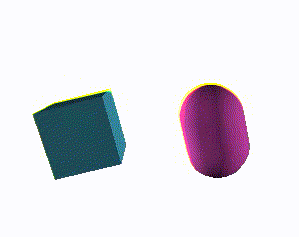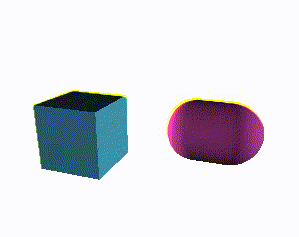
Canvas
Canvas is the main element that is responsible for the whole rendering process.
To work properly it need to be provided with some camera and a MainScene.
The canvas returned by this component is responsive. It always takes a 100% width and height of its parent.
MainScene
Main THREE.Scene element used by the renderer. Children of this Scene are
rendered.
Camera
Any camera added as a Canvas child will be used for rendering.
Props
The props of every component contains the following arguments:
- ref - React.ForwardedRef that can be used to get a reference to the THREE object or as in the example to set additional properties of the object;
- params - constructor parameters of the THREE object represented by the component;
- animate - uses to animate THREE objects.
All the props expect params can be modified between rerenders. Components
detects changes and applies new values. Therefore, it is useful to wrap animate function in
useMemo, so the same function reference is passed every rerender.
It may increase the performance.
Post processing
react-three-component supports post processing via postprocessing package.
To use post processing add a EffectComposer component as a Canvas children.
Usage
Exemplary Canvas with two passes - a RenderPass and an EffectPass. The EffectPass
applies two effects - a FXAAEffect and a BloomEffect:
<Canvas>
<EffectComposer>
<RenderPass />
<EffectPass>
<FXAAEffect />
<BloomEffect />
</EffectPass>
</EffectComposer>
</Canvas>Supported passes:
- EffectPass
- RenderPass
Supported effects:
- BloomEffect
- FXAAEffect
- NoiseEffect
Objects
react-three-component supports the following objects:
- Scene
- Mesh
- Points
- Line
- LineLoop
- LineSegments
They have special props to simplify creation of scenes:
- position - allow to position an object in the scene
- rotation - sets rotation of the object
Objects are added to the nearest parent, which is an object. Thanks to that it is possible to nest multiple objects:
<Mesh>
<Points>
</Points>
</Mesh>Cameras
- PerspectiveCamera
- OrthographicCamera
Geometries
Supported geometries:
- BoxGeometry
- BufferGeometry
- PlaneGeometry
- SphereGeometry
- CylinderGeometry
- TorusGeometry
- CapsuleGeometry
Geometries are automatically added to their nearest parent, which is an object (e.g., Mesh, Points):
<Mesh>
<BoxGeometry/>
<Mesh/>Materials
Supported materials:
- MeshBasicMaterial
- MeshStandardMaterial
- ShaderMaterial
- PointsMaterial
- LineBasicMaterial
Materials are automatically added to their nearest parent, which is an object (e.g., Mesh, Points):
<Points>
<PointsMaterial/>
<Points/>Lights
- AmbientLight
- DirectionalLight
Loaders
- OBJLoader
