react-native-barometer
v1.0.19
Published
Obtain barometric and altitude readings for both Android and iOS
Downloads
105
Maintainers
Readme
react-native-barometer
Provides barometric and altitude information for React-native apps for both IOS and Android.
Getting started
yarn add react-native-barometer
or
npm install react-native-barometer --save
Mostly automatic installation (react-native 0.59 and lower)
react-native link react-native-barometer
Manual installation (react-native 0.59 and lower)
Open RNBarometer.xcodeproj in Xcode
Drag RNBarometer.xcodeproj to your project on Xcode (usually under the Libraries group on Xcode):
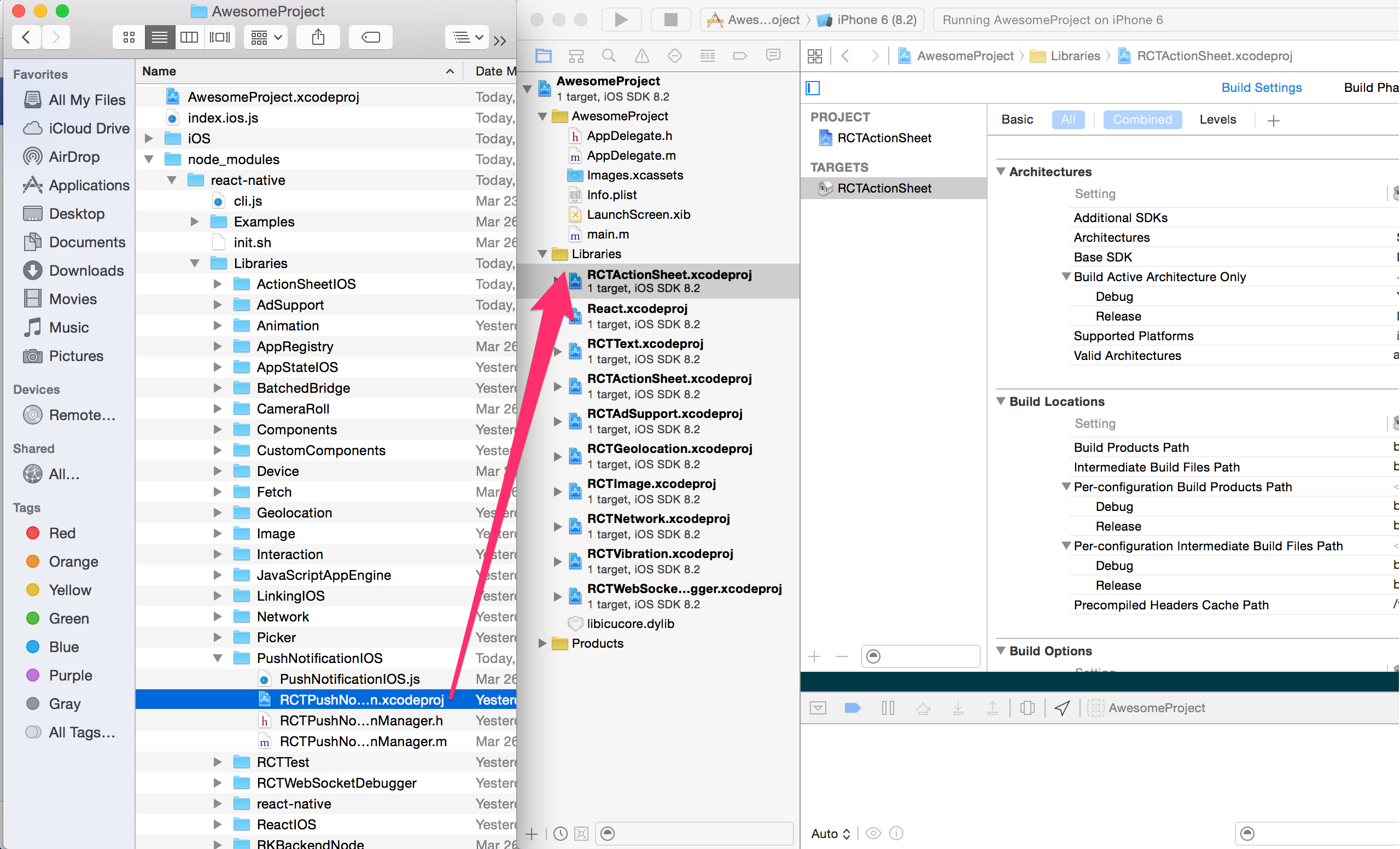
Link libRNBarometer.a binary with libraries
Click on your main project file (the one that represents the .xcodeproj) select Build Phases and drag the static library from the Products folder inside the Library you are importing to Link Binary With Libraries (or use the + sign and choose library from the list):

Using CocoaPods
Update your Podfile
pod 'react-native-barometer', path: '../node_modules/react-native-barometer'android/settings.gradle
include ':react-native-barometer'
project(':react-native-barometer').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-barometer/android')
android/app/build.gradle
dependencies {
...
implementation project(':react-native-barometer')
}
android/app/src/main/.../MainApplication.java
On top, where imports are:
import com.sensorworks.RNBarometerPackage;
Add the RNBarometerPackage class to your list of exported packages.
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.asList(
new MainReactPackage(),
new RNBarometerPackage()
);
}
Since react-native 0.60 and higher, autolinking makes the installation process simpler
Usage
Example
import Barometer from 'react-native-barometer';
Barometer.watch((payload => {});
Methods
Summary
Details
isSupported()
Before using, check to see if barometric updates are supported on the device.
const isSupported = Barometer.isSupported();
setInterval()
Optionally request an update interval in ms. The default update rate is (approx) 200ms, i.e. 5Hz.
// request updates once every second
Barometer.setInterval(1000);
setLocalPressure()
The altitude event contains two altitudes. The first is the standard atmosphere altitude based upon the standard atmospheric pressure of 1013.25hPa. The second is an altitude based upon a pressure that you can configure. You typically use this to calibrate the altitude to a reference altitude, for example the field elevation of an airport.
// set the local pressure to 985hPa
Barometer.setLocalPressure(985);
watch()
Barometer.watch(success);
Invokes the success callback whenever the pressure or altitude changes. The payload delivered via the callback is defined in the example below.
Returns a watchId (number).
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Required | Description | | ------- | -------- | -------- | ----------------------------------------- | | success | function | Yes | Invoked at a default interval of 5hz This can be changed by using the setInterval method. |
Example:
const watchId = Barometer.watch((payload) =>{
/*
payload.timestamp - sample time in ms referenced to January 1, 1970 UTC
payload.pressure - current air pressure in hPa
payload.altitudeASL - altitude in metres based upon standard atmosphere
payload.altitude - altitude in metres based upon the local pressure
payload.relativeAltitude - altitude gained or lost since `watch()` was called.
payload.verticalSpeed - current vertical speed (+/-) in metres per second
*/
);
clearWatch()
Barometer.clearWatch(watchID);
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
| ------- | ------ | -------- | ------------------------------------ |
| watchID | number | Yes | Id as returned by watch(). |
stopObserving()
Barometer.stopObserving();
Stops observing for all barometric updates.
In addition, it removes all listeners previously registered.
Note that this method does nothing if the Barometer.watch(successCallback) method has not previously been called.
