react-manage-state
v1.1.48
Published
**react-manage-state is the simplest way to manage your global state with little boilerplate code. It uses React's createContext and useState under the hood with first class typescript support.**
Downloads
77
Maintainers
Readme
react-manage-state
react-manage-state is the simplest way to manage your global state with little boilerplate code. It uses React's createContext and useState under the hood with first class typescript support.
Note:
- Make sure your code editor supports typescript v4 or above or just use latest version of Visual Studio code
- If you are using react-manage-state in a typescript project, make sure you set declaration: false in your tsconfig.json
Examples:
Set Up:
import React from "react";
import { createContext,useProvider } from "react-manage-state";
//Create your global store (which is just a javascript object)
const defaultstore = {
app:{
user:{
firstName:"",
lastName:"",
middleName:""
}
}
}
//Create a context by passing defaultStore to createContext method provided by library
const StoreContext = createContext(defaultStore);
//Library gives you "state","setState" methods after you passing defalutStore to useProvider hook.
//"state" can be used to access state, "setState" can be used to change state
//Create a "context provider" by passing "state","setState" values to "ContextProvider"
export const StoreProvider = ({ children }) => {
const { state, setState } = useProvider(defaultStore);
return (
<StoreContext.Provider value={{ state, setState }}>{children}</StoreContext.Provider>
);
};
//Create a "useStoreContext" hook which returns "state","setState"
export const useStoreContext = () => {
const { state, setState } = React.useContext(StoreContext);
return { setState, state };
};
Wrap above StoreProvider function at your App top level in app's entry file:
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<StoreProvider>
<App />
</StoreProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById("root")
);That's it boiler plate is done, now you can import useStoreContext anywhere in your app to access and change store values.
How to access and change store values.
As you can see defaultStore has user property and user has firstName , middleName and lastName as properties, we will create 3 input fields whose values are firstName , middleName and lastName respectively, There are 3 ways to change state using setState function, now we will learn how to change state using all 3 ways.
import React from "react";
import useStoreContext from "../Store/useStoreContext";
const Input = () => {
const { setState , state} = useStoreContext();
const handleChangeType1 = (e)=>{
setState(e.target.value, "store.app.user.firstName")
}
const handleChangeType2 = (e) => {
setState( ()=> e.target.value, "store.app.user.lastName")
}
const handleChangeType3 = (e)=>{
setState((prevMiddleName)=>`${prevMiddleName}${e.target.value}`, "store.app.user.middleName")
}
return (
<>
<input
value={state.store.user.firstName}
placeholder="firstname"
onChange={handleChangeType1}
/>
<input
placeholder="lastname"
value={state.store.user.lastName}
onChange={handleChangeType2}
/>
<input
placeholder="middlename"
onChange={handleChangeType3}
/>
</>
);
};About setState:
setState uses react's useState hook under the hood, so as useState is asynchronous function setState is also asynchronous function.
setState takes 2 parameters, 1st parameter is the value which you want to store or a function which returns the value you want to store, 2nd parameter is a string, where we provide path of property in a store.
For example store has firstName property and you want to update firstName value then 2nd parameter i.e., path can be written as "store.app.user.firstName". similarly if we want to update lastName then we can specify the path as "store.app.user.lastName".
If we have multiple properties or a nested object structured properties , we can specify the path accordingly ( similar to accessing json key value in a object).
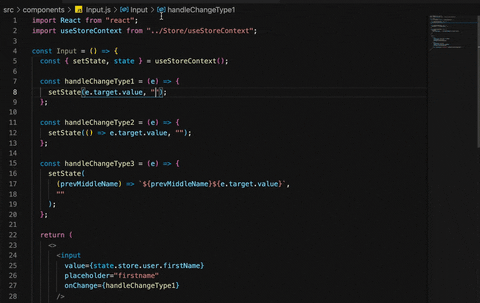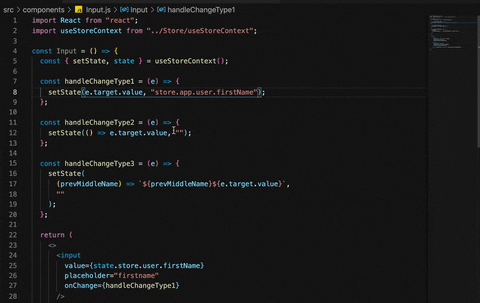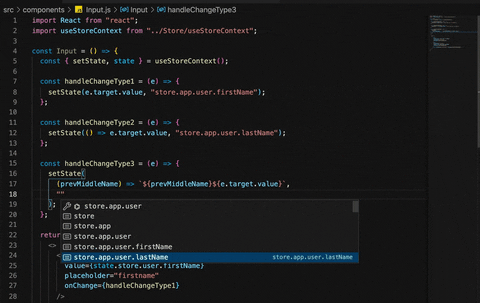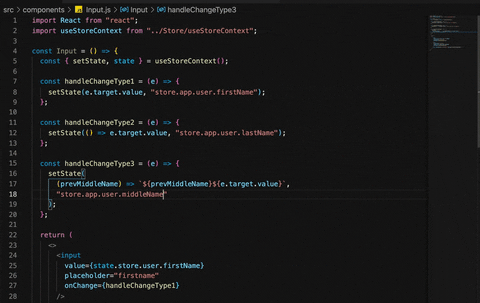
Too make it easy or to avoid minor errors like spelling mistakes , library will suggest you all possible paths , so when ever we write the "store" ,library will auto suggest the next possible paths which has store.
Checkout below gif.