protocore
v4.0.0
Published
Specify and deploy performant binary protocol structures in Node
Downloads
44
Maintainers
Readme
protocore
Specify and deploy performant binary protocol structures in Node
Install
npm i protocoreThen include the library in your code:
const {Schema, StreamingAbstractor, types, protospec} = require('protocore')What is Protocore?
Protocore makes building custom binary protocols a snap.
It's a lightweight Node library that takes the pain out of making binary protocols for games, databases, and other performance-dependent applications!
Protocore allows developers to create advanced protocols with powerful functionality and maximum efficiency.
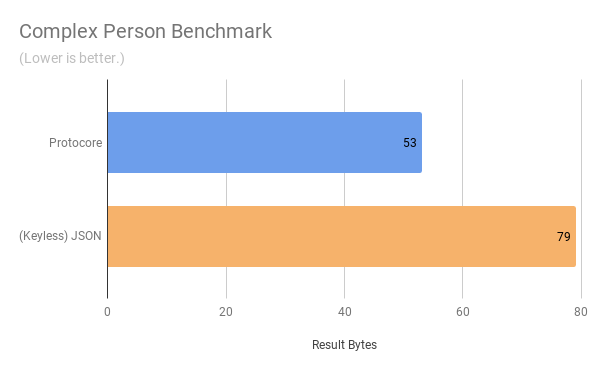
Define a Schema
const personSchema = new Schema([
{
'name': 'firstName',
'type': types.string
},
{
'name': 'age',
'type': types.uint,
'size': 8
},
{
'name': 'alive',
'type': types.boolean
}
])The above code defines a simple schema which represents a person.
It includes a firstName string field and an age, which is a UInt8.
Build a Buffer from a Schema
const ethanBuf = personSchema.build({
'name': 'Ethan Davis',
'age': 17,
'alive': true
})
// Now ethanBuf is a buffer representation of a person!Here we've built a buffer from Ethan's data using the personSchema Schema. The Schema.build method returns a Buffer.
Parse a Buffer from a Schema
// ^ Let's say ethanBuf is a buffer created with the personSchema Schema
const parsed = personSchema.parse(ethanBuf)
// parsed will now be an object with the original information about Ethan!
// parsed = {'name': 'Ethan Davis', 'age': 17, 'alive': true}Above a buffer was parsed using personSchema, which returned an object representation of the data!
Lists in Schemas
Lists can be defined in schemas as well.
const citySchema = new Schema([
{
'name': 'name',
'type': types.string
},
{
'name': 'buildings',
'type': types.list,
'of': new Schema([
{
'name': 'name',
'type': types.string
},
{
'name': 'constructed',
'type': types.uint,
'size': 16
}
])
}
])We've now defined citySchema, which represents a city with buildings. Buildings have names and also contain the year they were constructed.
Serializing Lists in Schemas
const sanFranciscoBuf = citySchema.build({
'name': 'San Francisco',
'buildings': [
{
'name': 'Salesforce Tower',
'constructed': 2018
},
{
'name': 'Ferry Building',
'constructed': 1898
}
]
})Parsing Lists in Schemas
const sanFrancisco = citySchema.parse(sanFranciscoBuf)sanFrancisco will be similar to the object we built sanFranciscoBuf from. It will have an array of building objects.
Utilizing StreamingAbstractor
StreamingAbstractors allow us to create duplex, event-based streaming systems for applications.
Let's create a StreamingAbstractor.
const myAbstractor = new StreamingAbstractor()
myAbstractor.register('login', new Schema([
{
'name': 'username',
'type': types.string
},
{
'name': 'number',
'type': types.uint,
'size': 16
}
]))
// Now we can bind myAbstractor to a stream using myAbstractor.bind(stream)Above we've registered an event called 'login' in our abstractor. Now it can recieve login events from a stream connected to another StreamingAbstractor.
Recieving Events Through StreamingAbstractor
Now that we have a StreamingAbstractor (myAbstractor) with the login event registered, we'll listen for login on our end.
myAbstractor.on('login', (data) => {
console.log('Login with username ' + data.username + ' and number ' + data.number + '.')
})Sending Events Through StreamingAbstractor
Because we've registered the login event, we can send login events using myAbstractor.
myAbstractor.send('login', {
'username': 'ethan',
'number': 5135
})Creating Custom Types
It's possible to build custom types for Protocore schemas to use, and it's not too complex either.
Protocore ships with its own built in types (ex. string, buffer, int, double, etc), and those are available for inspection in the types directory.
Writing Protocols with Protospec
Protospec is Protocore's protocol specification format. It is nice to write.
// my.pspec
def player private
string username
varint score
int x size=16
int y size=16
def join
instance player of=player
def updateAllPlayers
list players of=playerTo import a Protospec as a StreamingAbstractor:
// ... load spec, ex. fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, 'my.pspec'))
const myAbstractor = protospec.importAbstractor(spec)
myAbstractor.on('updateAllPlayers', (data) => {
// Do something with data.players
})To import a Protospec as an Object of Schemas:
const mySchemas = protospec.importAll(spec).schemas
const builtJoin = mySchemas.join.build({
'player': {
'username': 'a',
'score': 2,
'x': 100,
'y': 200
}
})