position
v1.1.0
Published
简单实用的定位工具,将一个 DOM 节点相对于另一个 DOM 节点进行定位操作。
Downloads
87
Readme
Position
简单实用的定位工具,将一个 DOM 节点相对于另一个 DOM 节点进行定位操作。
⿻
安装
$ npm install spm -g
$ spm install position定位原理
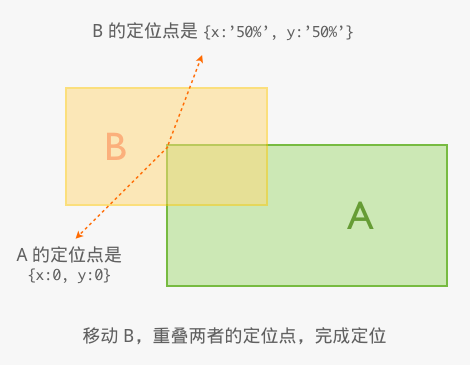
Position 组件的定位原理是,通过两个对象分别描述定位元素及其定位点,然后将其定位点重合。
比如有基准元素 A 和 目标元素 B ,先设定 A 的定位点为左上角,B 的定位点为中央。
则分别描述为 { element: A, x: 0, y: 0 } 和 { element: B, x: '50%', y: '50%' },然后将 B 的中央定位到 A 的左上角,就完成了定位。
定位原理如下图,x 代表横轴,y 代表纵轴。
使用说明
pin Position.pin(pinObject, [baseObject])
基础定位方法,接收两个参数。
pinObject:目标定位元素,必选。类型为字面量对象
{ element: a, x: 10, y: 10 },element 为需定位元素, x 和 y 表示定位元素的定位点。也可简单写成 DOM 节点 a,相当于
{ element: a, x: 0, y: 0 },表示定位点是节点左上角。baseObject:基准定位元素,可选。类型为字面量对象
{ element: b, x: 10, y: 10 },element 为基准定位元素,x 和 y 表示基准定位元素的定位点。也可简单写成 DOM 节点 a,相当于
{ element: a, x: 0, y: 0 },表示定位点是节点左上角。当 element 缺省时,表示 pinObject 相对屏幕可见区域的左上角定位。比如可以写成
Position.pin(a, { x: 10, y: 10 }); // 这样后一个参数可简单理解为偏移量或写成
Position.pin({ element: a, x: -10, y: -10 });
center Position.center(pinElement, [baseElement])
居中定位,接收两个参数,将 pinElement 定位在 baseElement 元素的中央位置。
pinElement:定位节点,必选。baseElement:基准定位节点,可选。缺省时表示将 pinElement 定位在屏幕中央。
VIEWPORT Position.VIEWPORT
当前可视区域的伪元素,当需要相对于当前可视区域定位时,上述参数的 element 可传入 Position.VIEWPORT。
比如相对于屏幕中央定位:
Position.pin(
{ element: a, x: 'center', y: 'center' },
{ element: Position.VIEWPORT, x: 'center', y: 'center' }
);或写成
Position.center(a, Position.VIEWPORT);最佳实践
定位元素到可视区域左上角
Position.pin(a, { x: 0, y: 0 }); // 后一个参数可理解为偏移量定位元素到基准元素位置向右偏移 20px
Position.pin(a, { element: b, x: '20px', y: 0 });定位元素到基准元素下方 20px 的位置
Position.pin(a, { element: b, x: 0, y: '100%+20px' });定位元素到基准元素正中央
Position.center(a, b);定位元素到基准元素右方中间位置
Position.pin(a, { element: b, x: 'right', y: 'center' });或者
Position.pin(a, { element: b, x: '100%', y: '50%' });定位元素到可视区域中央
Position.center(a);
注意事项
- IE8 下,当文档流中定位元素在基准元素的相邻前方,并且不是body的第一个元素时,基准元素有可能会因为未 reflow 而导致 margin-top 失效,所以要尽量避免定位元素与基准元素相邻并在其之前。


