phaser3-hadoken
v0.2.0-r1
Published
An input manager library that supports easy fighting-game style input events for Phaser 3.
Downloads
10
Maintainers
Readme
Table of Contents
Demo
A super compact (13k minimized, 55k with source map!) library to match fighting game style move sequences and generally help map user input into your game.
A live demo is available and a gif is too:
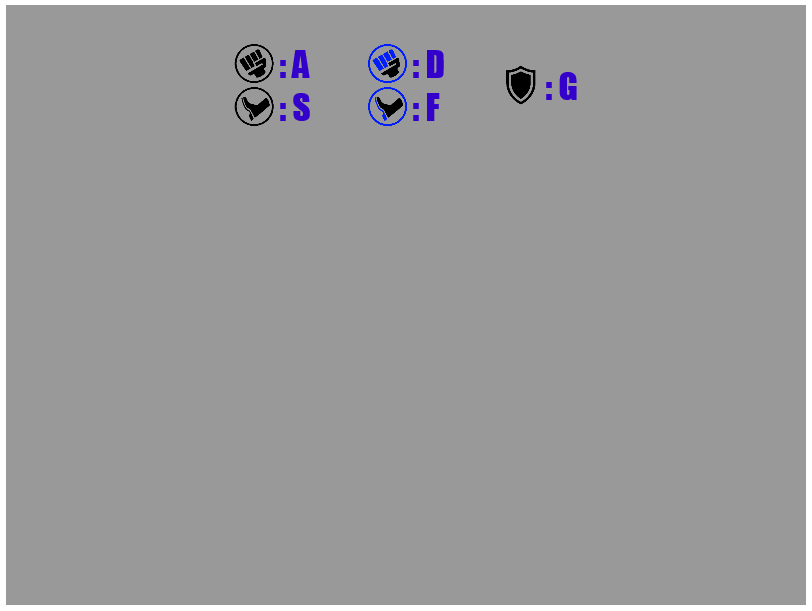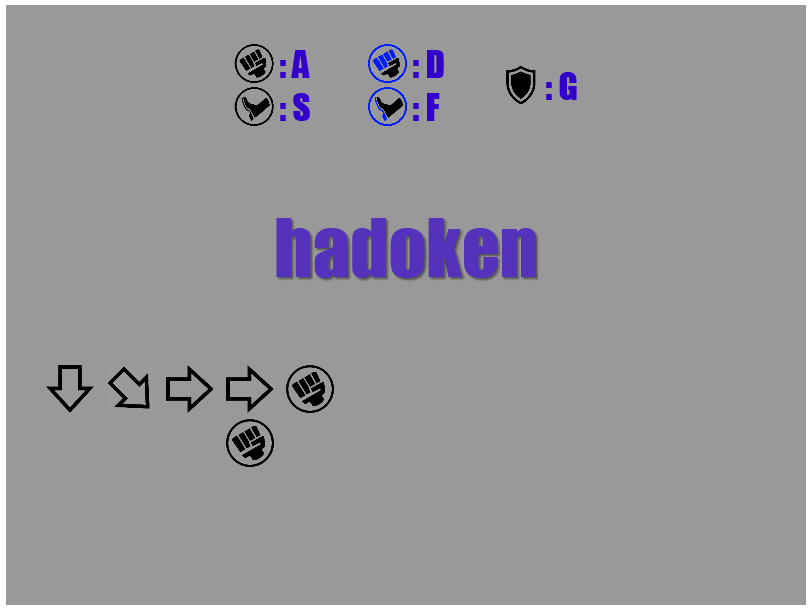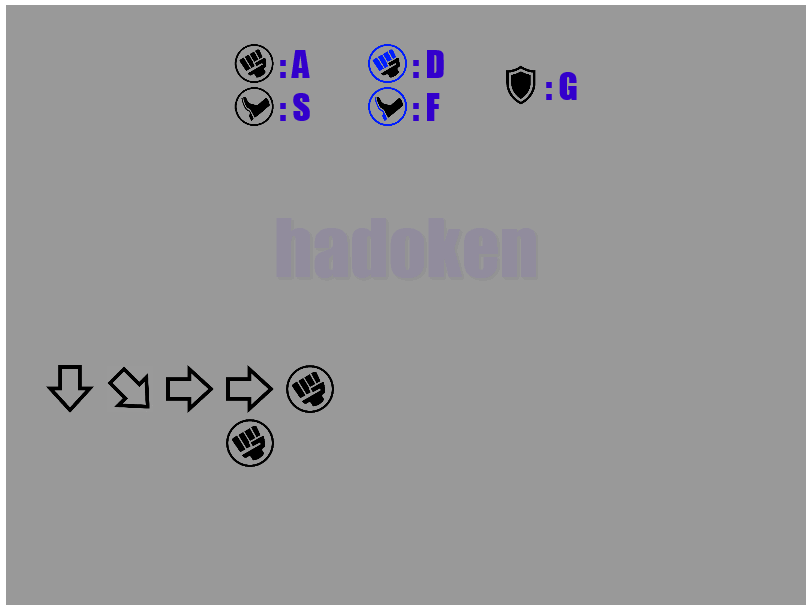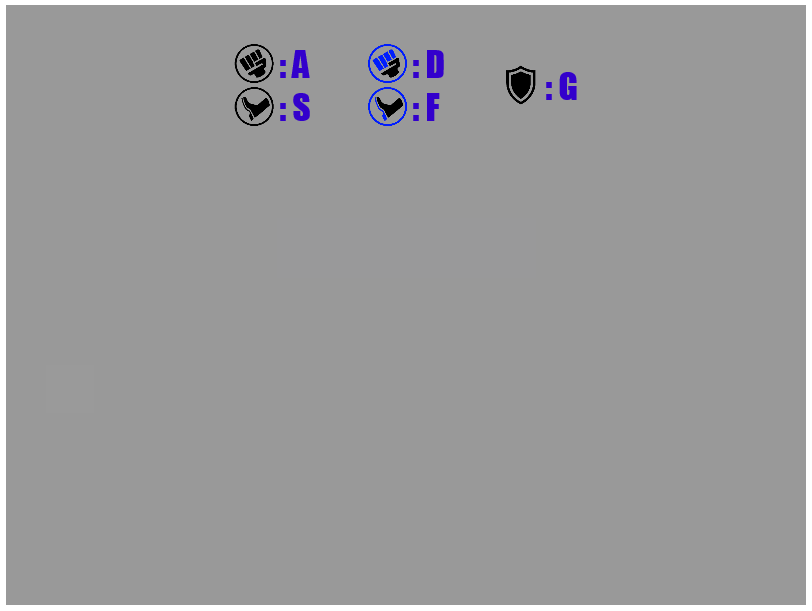
Get it: direct link
Direct downloads of phaser3-hadoken can be had through the
releases list on github. You can then include it as normal by
script tag:
<script
type="text/javascript"
src="https://github.com/jdotrjs/phaser3-hadoken/releases/download/v0.2.0-r1/hadoken.min.js"
></script>I use this approach in the demo. The source is included, see the Sample Project section in this doc.
Get it: npm and yarn
This library is published under phaser3-hadoken and can be added to your project via:
# npm
npm install phaser3-hadoken --save
# yarn:
yarn add phaser3-hadoken
yarn installUsing Hadoken
Hadoken should work for many users with just the provided code. But if it is behaves differently than you'd like most aspects of how it processes and matches inputs and be replaced. This README will cover a summary of how it works by default and then get into the details of most of the code that comes with the library.
How it Works
Hadoken can be thought of as an interface between your game and how Phaser manages input. You tell it what an input "means" to your game + what sequence of inputs constitute a special move and Hadoken will tell you when those things happen. It's worth noting here that "input" can be anything. At launch time it ships with an understanding of how to read Keyboard and Gamepad input.
Terminology: For better or worse I refer to things that your game cares about as "Semantic Input" pretty much throughout this doc and in many places within the codebase. I do this because it's makes a clear separation between "something happened on a controller" and "something the game cares about." This approcah is useful if you wish to support multiple inputs but only deal with understanding the difference in a single part of your codebase.
The data flow for an input is:
- Controller adapter — understands how to read the controller state and reports their state (pressed/unpressed) to hadoken internal state; the adapter is responsible for translating between a controller value and a semantic input, e.g., if the player presses "A" the adapter might report that "Attack" or "Jump" was pressed;
- Filter chain — once Hadoken recieves a new input it runs the known state of semantic inputs through a series of filters; this allows modifications to be made such as rewritting input based on player facing. The filter chain operates on input as captured at a single point in time;
- Matchers — once the filter chain is complete the input buffer is passed to the collection of matchers to determine if any of the defined moves have been performed;
- Buffer culling — Finally the inputs are matched (or not) and we need to clean up after ounselves to limit memory usage.
So, if that's how Hadoken works how does it inform your game that things are happening? Well, take your pick:
- Whenever a move is matched a
Hadoken.Events.Matchis emitted and carries with it aHadoken.MatchData. You can listen for these onhadokenObj.emitter. - Hadoken runs in
preupdateand will set thematchedMoveattribute to the name of the move that was matched; this check gets run before each update somatchedMovewill only be set for one frame. That means you can do a simpleif (hadokenObj.matchedMove !== null) { ... }or the like to check for move matching.
Additionally, if you care about specific inputs and not move matching you have a few other options
- For a point-in-time check you can called
hadokenObj.pressed()for mapped inputs or, often, adapter specific methods for exposing data; - input begin and end events are also emitted from
hadokenObj.emitter. They are aHadoken.Events.InputUpdatewith a data argument of typeHadoken.InputUpdateData.
Details and Examples
Now that you have a high level understanding of how input works its way through Hadoken and how it signals to you that moves are matching let's talk in detail about some of those components.
Adapters
As a user of Hadoken you'll probably be creating instances of the adapters based
on which controller you want to use. Each of these adapters take their own config
that they are responsible for documenting. Let's look at KeyboardHadoken and
all the pieces that go into configuring it:
export class KeyboardHadoken extends Hadoken<HadokenKeyboardConfig> {
constructor(scn: Phaser.Scene, cfg: HadokenKeyboardConfig) { /* ... */ }
}
type MappingFn = (keycode: number) => SemanticInput | null
type HadokenKeyboardConfig = HadokenPipelineConfig & {
// responsible for converting from a keycode to game-relevant input
keymapFn: MappingFn,
}
export type HadokenPipelineConfig = {
// indicates how Hadoken should cull the input buffer. If 'depth' then
// bufferLimit is the raw number of input states to store; if 'time' then
// we will drop frames older than bufferLimit milliseconds
bufferLimitType: 'depth' | 'time',
// argument whose meaning is determined by bufferLimitType
bufferLimit: number,
// a collection of filters that will be applied to the raw input states to
// collect the processed state which will be fed into the matchers
filters?: FilterFn,
// list of matchers that will be run in priority order, the first matcher
// that returns true will result stop matching process
matchers?: MoveDef[],
}For the moment let's ignore filters and matchers, we'll deal with those
below and in the sample project.
To create a Hadoken that supports keyboard input there are three things that
are required: bufferLimitType, bufferLimit, and keymapFn. The buffer
related parameters are common to all Hadoken adapters and control how much
hadoken will remember when it's trying to find move matches. keymapFn is
specific to the keyboard adapter and just tells it how to map keyboard keys
to your game.
Taken all together we can pretty easily create a matcher that will watch keyboard inputs and map them to directions and an action command:
const key = Phaser.Input.Keyboard.KeyCodes
const keymap = {
[key.LEFT]: 'left',
[key.RIGHT]: 'right',
[key.A]: 'action',
}
const hadoken = new Hadoken.KeyboardHadoken(scene, {
bufferLimitType: 'time',
bufferLimit: 4000,
keymapFn: k => !!keymap[k] ? keymap[k] : null,
})Now that we understand how to map from arbitrary controller input to something meaningful lets look at applying filters to that input.
Filters
A filter is a series of functions that can be applied to a snapshot of input state. Specifically:
type FilterFn = (input: InputSnapshot) => InputSnapshot
// Represents a single point at time and the state of any input
export type InputSnapshot = { timestamp: number, state: InputState }
// Maps input by name to tracked data about it
export type InputState = { [name: string]: InputData }
export type InputData = { pressed: number }To continue with our example let's say we want the action input to differ
depending on which item our player is holding. We can start with our previous
hadoken object and just build a filter that knows how to make that translation:
import { HasKey, ReplaceKey } from 'hadoken/InputSnapshot'
const player = { item: null }
const inputFilter = s => {
// no change if 'action' not pressed
if (!HasKey(s, 'action')) { return s }
// the default action is just to jump
let newAction = 'jump'
if (player.item === 'boots') { newAction = 'rocket_jump' }
if (player.item === 'sword') { newAction = 'slash' }
if (player.item === 'shield') { newAction = 'guard' }
// now rewrite the action based on what item the player is holding
return ReplaceKey(s, 'action', newAction)
}
const hadoken = new Hadoken.KeyboardHadoken(scene, {
bufferLimitType: 'time',
bufferLimit: 4000,
keymapFn: k => !!keymap[k] ? keymap[k] : null,
filters: inputFilter,
})Our Hadoken will now map the A button to jump, rocket_jump, slash, and guard
based on player state. If you would like to apply more than one filter you can
combine a series of filter functions via Hadoken.Filters.NewChain.
Some common filter usage is:
Filters.CoalesseInputs— Combining multiple controller inputs into a single sythesized input, e.g.,upandrightgetting mapped to a singleup+right.Filters.MapToFacing— Translates usage of 8-way direction set to be in terms offorwardandbackwardbased on a function that can return the player's facing. See the sample project for detailed usage.Filters.OnlyMostRecent— only the most recent of a set of inputs is considered pressed.
Matchers
To close out let's actually start matching move sequences based on our filtered input. To do that we need to understand how moves are defined for Hadoken:
// Checks an array if input snapshots and returns true + metadata if it matches
// the associated move
export type MatchFn = (history: InputSnapshot[]) => [boolean, object | null]
// Defines a move that Hadoken should understand
export type MoveDef = { name: string, match: MatchFn }
// And, finally, from the Hadoken config:
// list of matchers that will be run in priority order, the first matcher
// that returns true will result stop matching process
matchers?: MoveDef[],So, basically, we can just give the Hadoken config a list of objects that pair a named move with some function that returns true if the input history fulfills its requirements:
import * as SimpleMatcher from 'hadoken/Common/SimpleMatcher'
import { Events, MatchData } from 'hadoken'
const moveList = [
{ name: 'dash_stab', match: new SimpleMatcher([ 'right', 'right', 'slash' ]) },
{ name: 'shield_bash', match: new SimpleMatcher([ 'right', 'right', 'guard' ]) },
{ name: 'dodge', match: new SimpleMatcher([ 'left', 'left', 'rocket_jump' ]) },
]
const hadoken = new Hadoken.KeyboardHadoken(scene, {
bufferLimitType: 'time',
bufferLimit: 4000,
keymapFn: k => !!keymap[k] ? keymap[k] : null,
filters: inputFilter,
matchers: moveList,
})
hadoken.emitter.on(Events.Match, (data: MatchData) => {
console.log(`matched move: ${data.name}`)
})At this point hadoken is listening for input, translating inputs based on player item state, and examining history to watch for one of three special moves then emitting a signal when it has been entered. All of this with a relatively small amount of work.
Integrating this to your game should be pretty straight forward; instead of logging that a move was matched you would have your character start taking the action indicated by the move that was matched.
Some things aren't handled, though. For example if you wanted to specify that a move must have cooled down for a certain amonut of time before being used again this library doesn't handle that... instead you would need to handle managing that state yourself. That may sound complicated but can be as simple as:
const cooldownEmitter = new Phaser.Events.EventEmitter()
const cooldownSpec = {
dash_stab: 1000,
shield_bash: 1250,
}
const cooldownState = {}
hadoken.emitter.on(Hadoken.Events.Match, (data: MatchData) => {
const reqCD = cooldownSpec[data.name] || 0
// no cooldown required
if (reqCD == 0) {
cooldownEmitter.emit(Hadoken.Events.Match, data)
return
}
const now = Date.now()
const last = cooldownState[data.name] || 0
// we want to require a cooldown so check to see if it's been > the required
// cooldown MS since the move was last performed
if (now - last > reqCD) {
cooldownState[data.name] = now
cooldownEmitter.emit(Hadoken.Events.Match, data)
}
})You can then use cooldownEmitter in place of hadoken.emitter and your will
receive at most 1 of a move in however many milliseconds are specified in
cooldownSpec (or no cooldown will be required if a move has no entry, like
dodge).
SimpleMatcher
Hadoken comes with a simple matcher function that takes a sequence of moves (or
for the more advanced case move predicate) and looks for that sequence in its
input buffer. It does not require that those moves are sequential. That means
that A A B would match against all of the following input histories:
A A BA C A BA B C B A B
This is to handle allowing for inexact inputs resulting from ... well anything. You can control how permissive the simple matcher is by setting its timing tolerances between each step or for the whole input. The defaults are that each step of an input must happen with 250ms of the next and the whole input may not exceed 3s.
More details can be found in code+docs of SimpleMatcher.ts.
Other uses
If you were paying close attention you might have noticed that while Hadoken says it's about matching fighting came inputs on the box it's really just a generalized input manager. To that end you can use it as an interface to the Phaser input system.
Support for this is currently less well developed than the move-matching behavior but is supported by
Hadoken.Events.InputUpdateevent which contains all the keys pressed or released since the last update;hadokenObj.pressed()which returns an array of all pressed inputs which makes checking for key state trivial in your input loop.
Even weirder usages
We've been speaking of adapters as if they can only map from some controller that the user has. But really an adapter could be built around anything.
- On screen virtual controls? obvious fit;
- You want your websocket to generate inputs? okay;
- What about playback recording? yea, could see that;
- Got an AI that you want to play your game? A++ go for it.
The adapter abstraction means literally anything can be used to drive your game, be creative.
Sample project
The sample project is currently live on the demo site site. The source is available with it's owmn README.
License

tl;dr: Creative Commons BY-NC, basically, means you can use this however you want as long as you:
- Provide a link back to this library in your credits;
- Are not using it in a commercial work.
Full text available here.
If you would like alternate licensing for your project get in touch and we can work something out.

