petrol
v1.0.12
Published
A javascript unit testing tool designed to be simple, to install it and start writing tests. that's it. No webpack, No karma. No distractions.
Downloads
21
Maintainers
Readme
Petrol JS
A javascript unit testing tool designed to be simple, install it and start writing tests straight away... that's it. No webpack, No karma. No distractions.
What can you do with this package?
Write tests in a class, extending the Petrol TestCase with all the assertion methods
Create custom TestCase classes, importing all the libraries you need there and keep your test classes clean
Run tests in the console, run them individually, filter them by name and stop them on first failures
Assert elements on vue component templates using the VueTestCase
Create test classes with the
petrol make:testcommand. Runpetrol help make:testfor additional options.- You can create VueJS tests using the
--for=vueoption.
- You can create VueJS tests using the
The easiest way to try Petrol
Clone the example repository and run the test suite
git clone https://github.com/mgmonge/petrol-example petrol_example
cd petrol_example
npm install
./node_modules/petrol/bin/petrol runInstallation
npm install --save-dev petrolor
yarn add -D petrolUsage
Create your test file
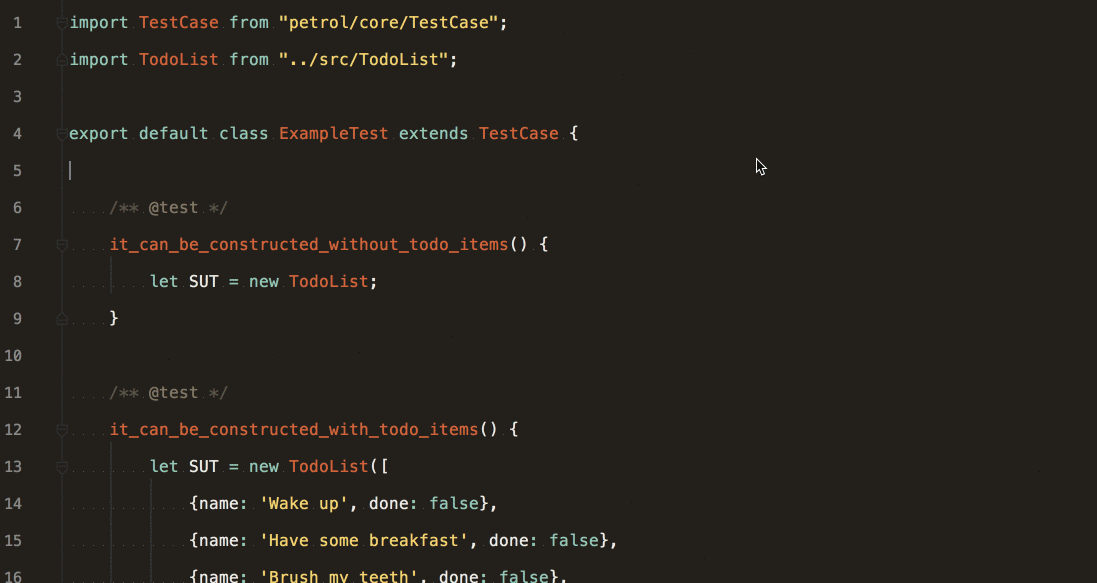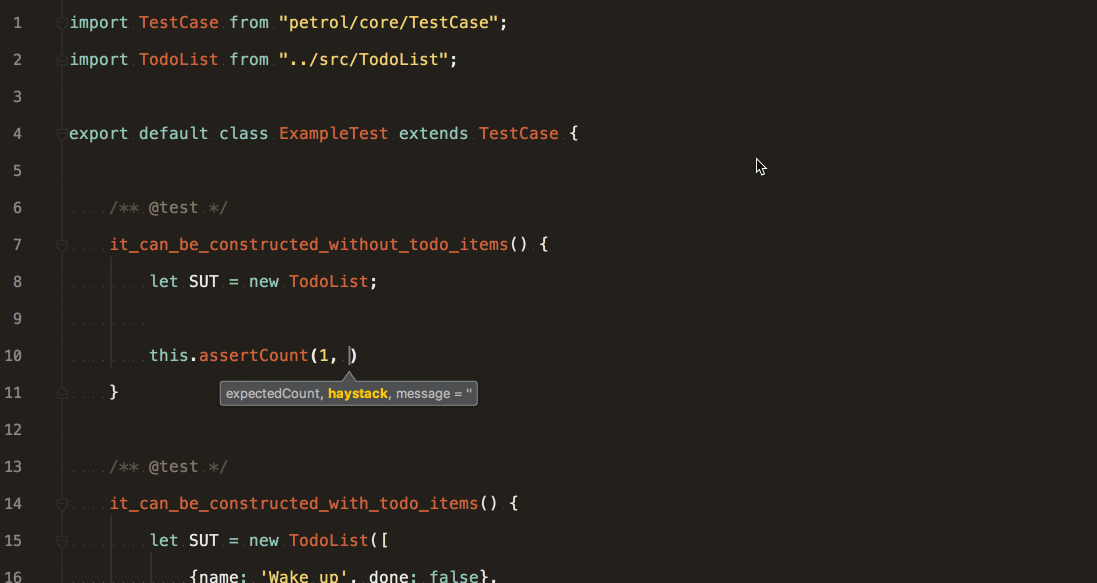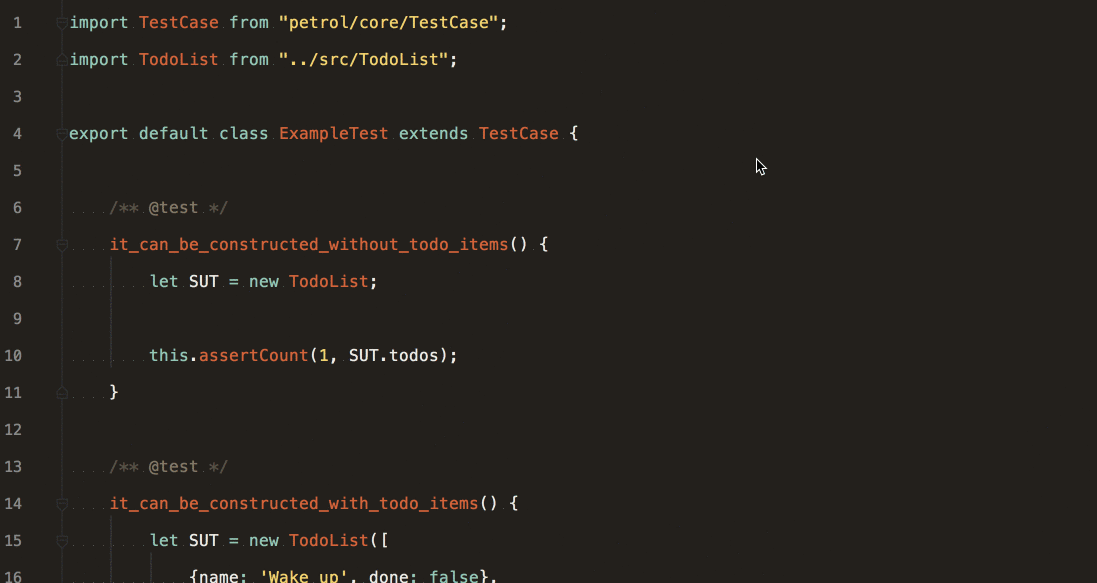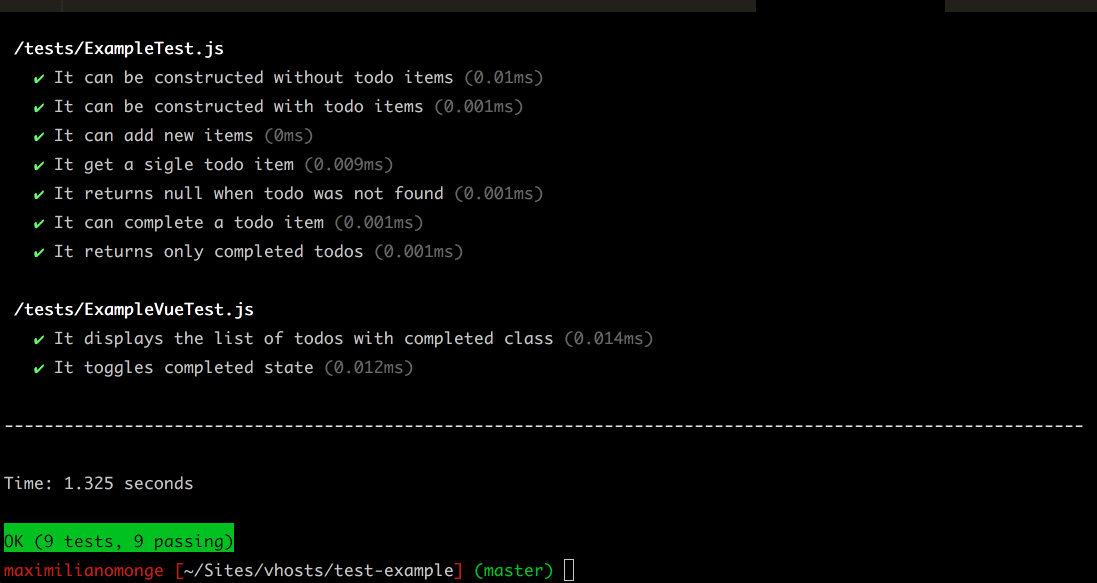
Create a file named ExampleTest.js in the project tests/ directory:
import TestCase from 'petrol/core/TestCase';
export default class ExampleTest extends TestCase {
/** @test */
it_counts_the_elements_of_an_array() {
let array = ['apples', 'bananas', 'oranges'];
this.assertCount(3, array);
}
}Run it
./node_modules/petrol/bin/petrol runPetrol will run all files ending with Test.js in the specified directory, by default tests/ directory.
Documentation
Structure of test files
All Tests files need to be an exportable ES2015 class and must extends the Petrol TestCase
// SomeTest.js
import TestCase from 'petrol/core/TestCase';
export default class SomeTest extends TestCase {}Petrol will run all the methods starting with the word test or with the block comment /** @test */ above as an individual test.
// SomeTest.js
import TestCase from 'petrol/core/TestCase';
export default class SomeTest extends TestCase {
testFoo() {
// assertions here
}
/** @test */
anotherTest() {
// assertions here
}
someOtherMethod() {
// this won't be run
}
}Run test files individually
./node_modules/petrol/bin/petrol run tests/SomeTest.jsFilter tests
Run only anotherTest() from SomeTest.js file
./node_modules/petrol/bin/petrol run tests/SomeTest.js:anotherTestStop on failure
Stop running the tests after the first failure using the flag --stop-on-failure or -f
./node_modules/petrol/bin/petrol run tests/ -fAssertions
assertEquals(expected, actual [, message]) Asserts that two variables are equal.
assertNotEquals(expected, actual [, message]) Asserts that two variables are not equal.
assertCount(expectedCount, haystack [, message]) Asserts the number of elements of an array.
assertInstanceOf(expected, actual [, message]) Asserts that a variable is of a given type.
assertSame(expected, actual [, message]) Asserts that two variables have the same type and value. Used on objects, it asserts that two variables reference the same object.
assertNotSame(expected, actual [, message]) Asserts that two variables do not have the same type and value. Used on objects, it asserts that two variables do not reference the same object.
assertTrue(condition [, message]) Asserts that a condition is true.
assertFalse(condition [, message]) Asserts that a condition is false.
assertObjectHasProperty(property, object [, message]) Asserts that an object has a specified property.
assertObjectNotHasProperty(property, object [, message]) Asserts that an object does not have a specified property.
assertContains(needle, string [, message]) Asserts that a string contains a needle.
assertNotContains(needle, string [, message]) Asserts that a string does not contain a needle.
assertNull(actual [, message]) Asserts that givel value is null.
assertNotNull(actual [, message]) Asserts that givel value is not null.
expectsError(callback [, message]) Asserts that a script executed on callback throws an error.
Example of assertions
import TestCase from 'petrol/core/TestCase';
export default class ExampleTest extends TestCase {
/** @test */
it_tests_some_stuff() {
let object = {foo: 'bar'};
class Foo {
}
let testClass = new Foo;
this.assertInstanceOf(Foo, testClass);
this.assertContains('world', 'Hello world!');
this.assertNotContains('foo', 'Hello world!');
this.assertNotEquals('foo', 'bar');
this.assertNotSame(1, '1');
this.assertEquals(1, '1');
this.assertNotSame(object, {foo: 'bar'});
this.assertEquals(object, {foo: 'bar'});
this.assertSame(object, object);
this.assertObjectHasProperty('foo', object);
this.assertObjectNotHasProperty('bar', object);
this.assertCount(3, [1, 2, 3]);
this.expectsError(() => {
throw new Error('Whoops!');
});
}
}
VueTestCase Assertions
Important note: It's necesary to mount the component using the test case method mount() to make assertions on its template.
mount(component [, props]) It mounts the vue components whith given props
click(selector) It triggers a click event on element with given selector
fillField(selector, value) Set given value to element with given selector. Element must be an input or textarea
checkOption(selector) Checks element with given selector. Element must be a checkbox
uncheckOption(selector) Unchecks element with given selector. Element must be a checkbox
selectOption(selector, value) Set given value from element with given selector. Element must be a selector or radio button
assertNumberOfElements(selector, expected) Assert the number of elements with given selector
assertElementContains(selector, needle) Assert that element with given selector contains a needle
assertElementNotContains(selector, needle) Assert that element with given selector does not contain a needle
assertElementExists(selector) Assert that element with given selector exists
assertElementNotExists(selector) Assert that element with given selector does not exist
nextTick(callback) An alias of $nextTick() from mounted component
Example of VueTestCase assertions
// Form.vue
<template>
<div>
<form action="#">
<input type="text" v-model="form.email" class="email" />
<input type="password" v-model="form.password" class="password" />
<textarea v-model="form.message" class="message"></textarea>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="form.terms" class="terms"> Accept Terms
<select v-model="form.method" class="method">
<option value="">Select method</option>
<option value="GET">GET</option>
<option value="POST">POST</option>
<option value="PUT">PUT</option>
<option value="DELETE">DELETE</option>
</select>
<input type="radio" class="active" v-model="form.active" value="Yes"> Yes
<input type="radio" class="active" v-model="form.active" value="No"> No
</form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
form: {
email: '',
password: '',
terms: false,
method: 'GET',
active: 'No'
}
}
}
}
</script>// FormTest.js
import Form from "../src/Form.vue";
import VueTestCase from "petrol/core/VueTestCase.js";
export default class ExampleVueTest extends VueTestCase {
beforeEach() {
this.SUT = this.mount(Form);
}
/** @test */
async it_populates_the_form() {
this.fillField('.email', '[email protected]');
this.fillField('.password', '123456');
this.fillField('.message', 'This is a message');
this.checkOption('.terms');
this.selectOption('.method', 'POST');
this.selectOption('.active', 'Yes');
await this.nextTick();
this.assertEquals('[email protected]', this.SUT.form.email);
this.assertEquals('123456', this.SUT.form.password);
this.assertEquals('This is a message', this.SUT.form.message);
this.assertTrue(this.SUT.form.terms);
this.assertEquals('POST', this.SUT.form.method);
this.assertEquals('Yes', this.SUT.form.active);
this.uncheckOption('.terms');
await this.nextTick();
this.assertFalse(this.SUT.form.terms);
}
}Before & after hooks
Petrol lets you register hooks that are run before and after your tests. This allows you to run setup and/or teardown code.
import TestCase from 'petrol/core/TestCase';
export default class SomeTest extends TestCase {
before() {
// this will be run before the first test of the file
}
baforeEach() {
// this will be run before each test
}
after() {
// this will be run after the last test of the file
}
afterEach() {
// this will be run after the each test
}
}Extend TestCase and create custom assertions
This example is using the Vue js sintax. see https://github.com/vuejs/vue
Lets say we have a vue component like this
// ExampleComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<div v-if="shouldShowAlert" class="alert">Warning</div>
<button v-on:click="showAlert()" class="alert-trigger">Click me!</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
shouldShowAlert : false
}
},
methods:
showAlert() {
this.shouldShowAlert = true;
}
}
}
</script>To create custom assertions you will need:
- Extend the TestCase
// CustomVueTestCase.js
import VueTestCase from 'petrol/core/VueTestCase';
class CustomVueTestCase extends VueTestCase {
// Custom assertion methods
assertHasAlertMessages(expected, component) {
this.assertElementExist('.alert');
}
assertHasNotAlertMessages(expected, component) {
this.assertElementNotExist('.alert');
}
}
export default CustomVueTestCase;- Import your custom TestCase
// ExampleComponentTest.js
import CustomVueTestCase from './CustomVueTestCase';
import ExampleComponent from './ExampleComponent';
export default class ExampleComponentTest extends CustomVueTestCase {
beforeEach() {
this.SUT = this.mount(ExampleComponent);
}
/** @test */
it_displays_an_alert_message() {
this.assertHasNotAlertMessages();
this.click('.alert-trigger');
this.nextTick(() => {
this.assertHasAlertMessages();
});
}
}License
Licensed using the MIT license.
Copyright (c) 2016 Maximiliano Monge <https://github.com/mgmonge>
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.Contributing
Guidelines
- All pull requests must have an open issue to reference the bug / change
- All pull requests must include unit tests to ensure the change works as expected and to prevent regressions.
Running the tests
In order to contribute, you'll need to checkout the source from GitHub and install Petrol's dependencies using npm:
git clone https://github.com/mgmonge/petrol.git
npm installPetrol is unit tested using its own core and tests should be on the /core-tests folder. Run
the tests using the petrol bash command:
./bin/petrol run core-tests/