pepesan
v3.4.8
Published
Simple automatic WhatsApp message responder
Downloads
201
Readme
Thanks To
- @whiskeysockets for the awesome WhatsApp socket library Baileys
Installation
> npm i --save pepesanor directly install from the repository to get the latest beta version
> npm i --save github:mqad21/pepesanUsage
# Initialization
index.js
const Pepesan = require("pepesan");
const router = require("./router");
(async () => {
const pepesan = Pepesan.init(router)
await pepesan.connect()
})()You can add some configurations in second parameter.
index.js
const Pepesan = require("pepesan");
const router = require("./router");
(async () => {
const config = {
browserName: 'My first chat bot',
sessionPath: './example/session',
allowedNumbers: ['6281234567890', '6289876543210'],
db: {
path: './example/data.sqlite',
username: 'mqad21',
password: '4dm!n'
}
}
const pepesan = Pepesan.init(router, config)
await pepesan.connect()
})()# Define a Router
Router is an instance of Router class. Here you define some rules for bot replies.
router.js
const { Router, Response } = require("pepesan")
const BotController = require("./BotController")
const router = new Router()
/**
* If user send "ping",
* bot will reply "pong".
*/
router.keyword("ping", () => {
return "pong"
})
/**
* If user send "ping 3 times",
* method pingManyTimes in BotController will be called
* and "3" will be passed as parameter.
*/
router.keyword("ping {n} times", [BotController, 'pingManyTimes'])
/**
* If user send "get my number"
* and the state is equal to "loggedIn",
* method getMyNumber in BotController will be called.
*/
router.state("loggedIn").group(() => {
router.keyword("get my number", [BotController, 'getMyNumber'])
})
/**
* If user send "buy"
* or user click a button with value "buy"
* and AuthMiddleware function return true,
* method buy in BotController will be called.
*/
router.middleware(AuthMiddleware).group(() => {
router.keyword("buy", [BotController, 'buy'])
router.button("buy", [BotController, 'buy'])
})
module.exports = router# Define a Controller
Controller is a class that extends Controller class.
BotController.js
const { Controller, Response } = require("pepesan")
module.exports = class BotController extends Controller {
/**
* Bot will reply "pong" n times.
*/
pingManyTimes(request, n) {
return Array(Number(n)).fill("pong") // ["pong", "pong", ..., "pong"] n times
}
/**
* Bot will reply "Wait for a while..."
* then bot will reply an image
* after it has been received from server.
*/
async pingWithImage() {
await this.reply(Response.text.fromString("Wait for a while..."))
const image = await getImageFromServer()
return Response.image.fromBuffer(image)
}
/**
* Bot will reply user WhatsApp number.
*/
getMyNumber(request) {
return request.number
}
/**
* Bot will reply button "yes" and "cancel"
* with "Are you sure?" text.
*/
buy() {
const buttons = ["yes", "cancel"]
return Response.button.fromArrayOfString(buttons, "Are you sure?")
}
}# Define a Middleware
Middleware is an async/sync function that return Boolean or Response.
AuthMiddleware.js
const { Response } = require("pepesan")
module.exports = (request, next) => {
/**
* If user number is not equal to "6281234567890",
* bot will reply "You are not allowed"
* else bot will execute the routes below it.
*/
if (request.number !== "6281234567890") {
return "You are not allowed"
}
return next()
}Documentation
# Configuration
{
printQRInTerminal: boolean // default: true
sessionPath: string, // default: "./session"
browserName: string, // default: "Pepesan"
allowedNumbers: string[],
blockedNumbers: string[],
onOpen: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void
onClose: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void
onReconnect: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void
onQR: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void,
onMessage: (message: WAMessage) => Promise<void>,
db: {
name: string,
user: string,
pass: string,
path: string // default: "data.sqlite"
}
}printQRInTerminal: indicates whether or not the QR code should be print in terminal.sessionPath: folder path to save session files. e.g. "/mysession"browserName: name that display in the device list of your WhatsApp app.allowedNumbers: list of number you allowed for using bot. Let innullorundefinedif you want to allow all numbers. e.g. ["6281234567890", "6289876543210"]blockedNumbers: list of number you blocked for using bot. Let innullorundefinedif you want to allow all numbers. e.g. ["6281234567890", "6289876543210"]onOpen: a callback function when WhatsApp connection opened.onClose: a callback function when WhatsApp connection closed.onClose: a callback function when WhatsApp connection needs to reconnect.onQR: a callback function when WhatsApp QR code received.onMessage: a callback function when a new message received.db: configurations for your SQLite database.name: Database name.user: Database username.pass: Database password.path: Path to your ".sqlite" file. e.g. "/data.sqlite"'
# Router
1. Keyword Route
Keyword route handles user's message, media caption, or button response text that match the route pattern.
router.keyword("hello", ...) // only match to "hello" text.
router.keyword("hello*", ...) // match to all texts start with "hello".
router.keyword("(hello|hi)", ...) // only match to "hello" or "hi" text.
router.keyword("hello {name}", ...) // match to "hello muhammad", "hello qadri", etc.2. State Route
State route handles user's state that match with the route pattern.
router.state("idle", ...) // only match to "idle" state.
router.state("idle*", ...) // match to all states start with "idle".
router.state("(idle|active)", ...) // only match to "idle" or "active" state.
router.state("active {time}", ...) // match to "active today", "active tonight", etc.3. Middleware Route
Middleware route handles all user's message if only middleware function return true.
router.middleware(AuthMiddleware, ...) // if AuthMiddleware return true, the callback will be called.
router.middleware([AuthMiddleware, param1, param2, ...], ...) // Middleware also can receive parameters.4. Button Route
Button route handles text or value of button clicked by user that match with the route pattern.
router.button("buy", ...) // only match to "buy" button text or value.
router.button("buy*", ...) // match to all button values or texts that start with "buy".
router.button("(buy|cancel)", ...) // only match to "buy" or "cancel" button text or value.
router.button("buy {product}", ...) // match to "buy iphone", "buy macbook", etc.5. Grouping Route
Route can also be grouped if the callback or the second parameter is not set.
router.middleware([AuthMiddleware, 'change settings']).group(() => {
// Code block below is only executed if AuthMiddleware function returns true.
router.keyword("Change payment to (cash|transfer)", [PaymentController, 'changePayment'])
router.button("Change profile", [ProfileController, 'changeProfile'])
})
router.state("loggedIn").group(() => {
// Code block below is only executed if user state equals to "loggedIn".
router.keyword("View my balance", [BalanceController, 'viewBalance'])
router.button("View my profile", [ProfileController, 'viewProfile'])
})# Controller
1. Own method
Controller method can be an async/sync function.
The first parameter is
Requestobject and the rest is route parameter.The return value is the response message of bot. It can be
stringorResponseobject.If you want the bot respond more than one message, you can make the return value as
Array.Example:
introduction(request, firstName, lastName) { return `Hello ${firstName} ${lastName}` } pingTwoTimes(request) { return ["Ping 1", "Ping 2"] } async downloadYoutube(request) { const url = request.text const youtube = await download(url) return [ Response.video.fromBuffer(youtube.video), youtube.title ] }
2. reply(response)
The
replymethod is used to reply to the user's message.The parameter can be
string,Response,Array of string,Array of Response, orArray of Response or string.Example:
async convertToMp3(request) { await this.reply("Please wait...") await this.reply(Response.image.fromURL("...")) const url = request.text const mp3 = await toMp3(url) return Response.audio.fromBuffer(mp3) }
3. send(number, response)
The
sendmethod is used to send message to the another user.The first parameter is recipient WhatsApp number.
The second parameter can be
string,Response,Array of string,Array of Response, orArray of Response or string.Example:
async sendConfirm(request) { const message = request.text await this.send("6289876543210", [ message, Response.image.fromURL("...") ]) return "Confirmed" }
4. getMedia()
The
getMediamethod is used to get any media sent by user.The return of this method is
Promise<Buffer>Example:
async uploadReceipt(request) { const receipt = await this.getMedia() await this.send("6289876543210", Response.image.fromBuffer(receipt)) return "Uploaded" }
5. setState(state)
The
setStatemethod is used to set current user state.The parameter is state
string.Example:
async login(request) { const key = request.text const isAllowed = await checkKey(key) if (isAllowed) { await this.setState("loggedIn") return "You are logged in" } return "Invalid key" }
6. deleteState()
The
deleteStatemethod is used to delete the current user state.Example:
async logout(request) { await this.deleteState() return "Logged out" }
# Request
Request is an object that contains information from the user's message. Example:
{
id: '3EB00744EB342283C522', // Message ID
key: ..., // Message key object
text: "Hello", // Message text or caption
button: ..., // { text: "Button text", value: "Button value or ID" }
jid: "[email protected]", // User's JID
number: "6281234567890", // User's WhatsApp number
name: "Muhammad Qadri", // User's name
state: "MyState", // Current user's state
stateObject: ..., // User's state object
type: ..., // 'image' | 'video' | 'document' | 'sticker'
message: ..., // Message object
document: ..., // Document message object
image: ..., // Video message object
sticker: ..., // Sticker message object
contact: ..., // Contact message object
route: ... // Current route object
}# Response
1. Text Response
Response.text.fromString("Assalamu'alaikum brother")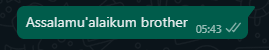
2. Image Response
Response.image.fromBuffer(imageBuffer, "caption")
Response.image.fromURL("https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/WhatsApp.svg/2044px-WhatsApp.svg.png", "caption")
3. Video Response
Response.video.fromBuffer(videoBuffer, "caption")
Response.video.fromStream(videoStream, "caption")
Response.video.fromURL("http://techslides.com/demos/sample-videos/small.mp4", "caption")
4. Audio Response
Response.audio.fromBuffer(webpBuffer)
Response.audio.fromURL("https://download.quranicaudio.com/quran/wadee_hammadi_al-yamani/001.mp3")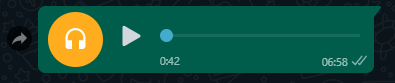
5. Sticker Response
Response.sticker.fromBuffer(webpBuffer)
Response.sticker.fromURL("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mqad21/pepesan-assets/main/sticker.webp")
6. Button Response
Response.button.fromArrayOfString(["yes", "cancel"], "Content", "Footer")
Response.button.fromArrayOfObject([{text: "yes", value: "1"}, {text:"no", value: "0"}], "Content", "Footer")
# Middleware
Middleware is an async/sync function that return
BooleanorResponsevalueThe first parameter is
Requestobject.The second parameter is
nextfunction.The rest is route parameter.
Example:
(request, next, action) => { if (request.number !== "6281234567890") { let errorMessage = "You are not allowed" if (action) errorMessage += ` to ${action}` return errorMessage } return next() }
# Global Variable
1. sock
Access to WASocket object anywhere after initiate the Pepesan class.
2. db
Access to Database object anywhere after initiate the Pepesan class.


