oauth-jwt-server
v1.0.6
Published
Symple oAuth2 Server for Nodejs && Expressjs with jwt tokens
Downloads
33
Readme
oauth-jwt-server
Complete, compliant and well tested module for implementing an OAuth2 server with JWT(JSON Web Token) token in Node.js.
The oauth-jwt-server module is officially supported wrappers available for popular HTTP server framework Express
Install
$ npm install oauth-jwt-serverUsage
var express = require('express')
//Get oAuth Server Reference
const { Server } = require('oauth-jwt-server');
/*The use of jwt-simple and moment is only illustrative, you can choose the method that is most considered pertinent,
in this case it is used to simulate the generation of the server token (identification of client requests for the rest api)*/
const jwt = require('jwt-simple');
const moment = require('moment');
let oAuthServer = Server(config);
var app = express();
//Cookie parser for oAuth Server Identification Access
app.use(oAuthServer.CookieParser);
//endpoint to manage the User Session
app.get('/auth/login', function(req, res){
//Set de reference user cookie for oAuth identification access
oAuthServer.SetCookie(res, "1234");
res.status(200).jsonp('ok');
});
/*In OAuth, the client requests access to resources controlled by the resource owner
and hosted by the resource server and is issued a different set of credentials than
those of the resource owner. Instead of using the resource owner's credentials to access protected resources,
the client obtains an access token--a string denoting a specific scope, lifetime,
and other access attributes. Access tokens are issued to third-party clients by an
authorization server with the approval of the resource owner. */
app.get('/auth/authorization', oAuthServer.Authorization);
/*Requesting tokens with a grant
JWT bearer assertion -- a signed JSON Web Token (JWT), issued by a third-party token service (STS) or issued by the client itself, to obtain an access and / or ID token.
*/
app.get('/auth/token', oAuthServer.Token);
app.listen(80);config params
let config = {
/*Jwt Config for authorization code*/
jwt: {
authCode: {
secretPassword: 'RIJJQuDtUa7ksfSTcHGyNkZhN29snfTC',
exp: 35,
algorithm: 'HS512',
unit: "days"
}
},
/*oauth cookie config for aurhorization access*/
cookie: {
name: "SSID_OAUTH",
secretPassword : "thebest",
conf: {
httpOnly: true, // to disable accessing cookie via client side js
secure: true, // to force https (if you use it)
maxAge: 1000000000, // ttl in ms (remove this option and cookie will die when browser is closed)
signed: true // if you use the secret with cookieParser
}
},
/*reference to the function that returns the configuration of oauth clients registered in your system,
it must return a list with the following parameters*/
getAuthClients: ()=>{
//Get de oauth client list
return [{
id: "l2mp/a5NDlMw1b9wQvIgg==",
name: "Market Place",
redirect_uri: "https://external/auth",
secretPassword: "secret"
}];
},
/*each rest api uses a unique identification to generate the access authorization (jwt),
this function allows assigning any type of token once the authorization has been processed*/
getTokenServer: ()=>{
//Example for jwt token
var payload = {
sub: "1234",
iat: moment().unix(),
exp: moment().add(1, "days").unix(),
};
return jwt.encode(payload, "secretPassword", "HS512");
}
};Getting started
Your own rest api must store the information of the clients that will be able to connect via oAuth, this point is scalable to any persistence implementation you have, the getAuthClients method of the configuration object guarantees that you can assign the oAuth clients regardless of their own implementation.
There are five ways to get started:
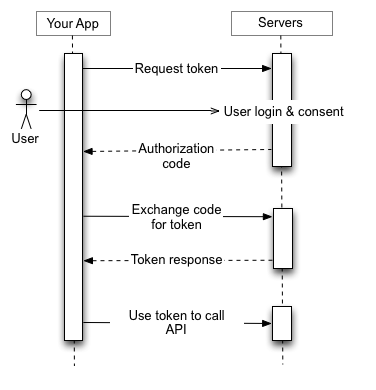
The client application (External) requests authorization to access a user's resources in a given service. Example: The external application will have a mock endpoint like /auth/myserver This endpoint should do a redirect to https://myserver/api/v1/Authorization?Client_id=&redirect_uri=
Where client_id: Client identification code given to the external site by the oauth server redirect_uri: redirect uri set as callback to get authorization code
curl 'https://myserver/api/v1/Authorization?Client_id=123456&redirect_uri=https://external/endpoint' -i -X GETIf the platform authorizes this request, the application receives an authorization grant. If the authorization of point 1 is correct, the server generates a one-time authorization code (JWT Valid for 1 minute), which is sent to the previously configured redirect_uri.
Example:
external/auth/response?code=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJzdWIiOnsiaWQiOiJsMm1wL2E1TkRsTXcxYjl3UXYrSWdnPT0iLCJzY2hlbWFJZCI6IjEifSwiaWF0IjoxNTUyNjI1NTIzLCJleHAiOjE1NTI2MjU1ODN9.8HDGPZ4-25WJNkEdz8P7fqW4_z2g9H8MHMFJCILP7PM1nz0sWRo8z8dCYsWKVhsQ7UTtI08ngDfbTkQSbX0qYQThe external application requests an access token from the API authorization server presenting its identity and the permission previously granted. Through an http server to server request, the external application performs a get to the endpoint https://myserver/api/v1/auth/token Sending as part of the header the following data: code: authorization code returned by the server in point 2. Secret_pass: Secret key given to the external client to access the server client_id: unique user id granted to the external client for access to the server. ⚡
Example:
GET /auth/token HTTP/1.1 Host: https://myserver/api/v1 code: eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJsMm1wL2E1TkRsTXcxYjl3UXZJZ2c9PSIsImlhdCI6MTYzMzEyNjg2NiwiZXhwIjoxNjM2MTUwODY2fQ.LZ0g2_F3icTMRrECp8MUcg9HRsYt_-Li1lsS1hpqr1OsxsZX2nz1R8ZaCPagSWp43pz7uIcxZvhCqfnd85MMEg secret_pass: secret client_id: l2mp/a5NDlMw1b9wQvIgg== Content-Type: application/json Content-Length: 100120If the identity of the client application is correctly recognized by the service, and the authorization grant is valid, the authorization server issues an access token (jwt) to the application. With this the authorization has been completed. Server response at point 3 is {access_token: “123.123.123”}
The application requests a resource from the resource server (API) and presents the corresponding access token in the request header through the key x-access-token
This step depends on how your rest api is implemented, for this case there is the getTokenServer method of the server configuration object oAuth
Features
- Supports
authorization_code,client_credentials,refresh_tokenandpasswordgrant, as well as extension grants - Can be used with promises, Node-style callbacks, ES6 generators and async/await
- Fully RFC 6749 and RFC 6750 compliant.
Jwt Algorithms
By default the algorithm to encode is HS256.
The supported algorithms for encoding and decoding are HS256, HS384, HS512 and RS256.



