npm-check-updates-resolutions
v16.14.12
Published
Find newer versions of dependencies than what your package.json allows
Downloads
80
Maintainers
Readme
npm-check-updates
npm-check-updates upgrades your package.json dependencies to the latest versions, ignoring specified versions.
- maintains existing semantic versioning policies, i.e.
"react": "^16.0.4"to"react": "^18.2.0". - only modifies package.json file. Run
npm installto update your installed packages and package-lock.json. - sensible defaults, but highly customizable
- CLI and module usage
- compatible with:
npm,yarn,pnpm,deno,bun
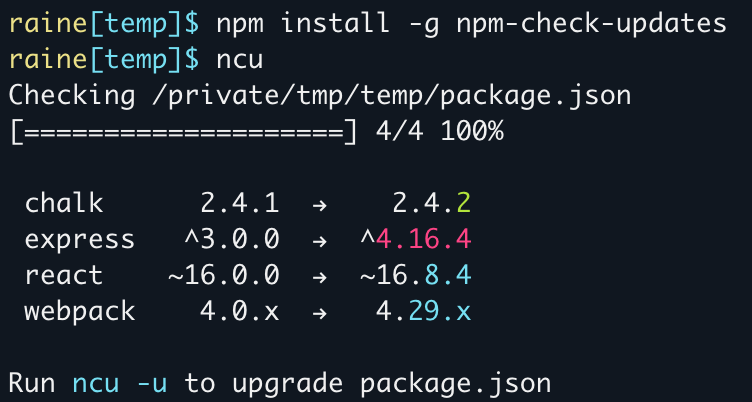
- Red = major upgrade (and all major version zero)
- Cyan = minor upgrade
- Green = patch upgrade
Installation
Install globally:
npm install -g npm-check-updatesOr run with npx:
npx npm-check-updatesUsage
Check the latest versions of all project dependencies:
$ ncu
Checking package.json
[====================] 5/5 100%
eslint 7.32.0 → 8.0.0
prettier ^2.7.1 → ^3.0.0
svelte ^3.48.0 → ^3.51.0
typescript >3.0.0 → >4.0.0
untildify <4.0.0 → ^4.0.0
webpack 4.x → 5.x
Run ncu -u to upgrade package.jsonUpgrade a project's package file:
Make sure your package file is in version control and all changes have been committed. This will overwrite your package file.
$ ncu -u
Upgrading package.json
[====================] 1/1 100%
express 4.12.x → 4.13.x
Run npm install to install new versions.
$ npm install # update installed packages and package-lock.jsonCheck global packages:
ncu -gInteractive Mode
Choose which packages to update in interactive mode:
ncu --interactive
ncu -i
Combine with --format group for a truly luxe experience:

Filter packages
Filter packages using the --filter option or adding additional cli arguments. You can exclude specific packages with the --reject option or prefixing a filter with !. Supports strings, wildcards, globs, comma-or-space-delimited lists, and regular expressions:
# upgrade only mocha
ncu mocha
ncu -f mocha
ncu --filter mocha
# upgrade packages that start with "react-"
ncu react-*
ncu "/^react-.*$/"
# upgrade everything except nodemon
ncu \!nodemon
ncu -x nodemon
ncu --reject nodemon
# upgrade only chalk, mocha, and react
ncu chalk mocha react
ncu chalk, mocha, react
ncu -f "chalk mocha react"
# upgrade packages that do not start with "react-".
ncu \!react-*
ncu '/^(?!react-).*$/' # mac/linux
ncu "/^(?!react-).*$/" # windowsHow dependency updates are determined
- Direct dependencies are updated to the latest stable version:
2.0.1→2.2.01.2→1.30.1.0→1.0.1
- Range operators are preserved and the version is updated:
^1.2.0→^2.0.01.x→2.x>0.2.0→>0.3.0
- "Less than" is replaced with a wildcard:
<2.0.0→^3.0.01.0.0 < 2.0.0→^3.0.0
- "Any version" is preserved:
*→*
- Prerelease and deprecated versions are ignored by default.
- Use
--preto include prerelease versions (e.g.alpha,beta,build1235) - Use
--deprecatedto include deprecated versions
- Use
- With
--target minor, only update patch and minor:0.1.0→0.2.1
- With
--target patch, only update patch:0.1.0→0.1.2
- With
--target @next, update to the version published on thenexttag:0.1.0->0.1.1-next.1
Options
Options are merged with the following precedence:
- CLI
- Local Config File
- Project Config File
- User Config File
Options that take no arguments can be negated by prefixing them with --no-, e.g. --no-peer.
Advanced Options
Some options have advanced usage, or allow per-package values by specifying a function in your .ncurc.js file.
Run ncu --help [OPTION] to view advanced help for a specific option, or see below:
doctor
Usage:
ncu --doctor
ncu --no-doctor
ncu -dIteratively installs upgrades and runs tests to identify breaking upgrades. Reverts broken upgrades and updates package.json with working upgrades.
Add -u to execute (modifies your package file, lock file, and node_modules)
To be more precise:
- Runs
npm installandnpm testto ensure tests are currently passing. - Runs
ncu -uto optimistically upgrade all dependencies. - If tests pass, hurray!
- If tests fail, restores package file and lock file.
- For each dependency, install upgrade and run tests.
- Prints broken upgrades with test error.
- Saves working upgrades to package.json.
Additional options:
Example:
$ ncu --doctor -u
Running tests before upgrading
npm install
npm run test
Upgrading all dependencies and re-running tests
ncu -u
npm install
npm run test
Tests failed
Identifying broken dependencies
npm install
npm install --no-save [email protected]
npm run test
✓ react 15.0.0 → 16.0.0
npm install --no-save [email protected]
npm run test
✗ react-redux 6.0.0 → 7.0.0
/projects/myproject/test.js:13
throw new Error('Test failed!')
^
npm install --no-save [email protected]
npm run test
✓ react-dnd 10.0.0 → 11.1.3
Saving partially upgraded package.jsonfilter
Usage:
ncu --filter [p]
ncu -f [p]Include only package names matching the given string, wildcard, glob, comma-or-space-delimited list, /regex/, or predicate function.
The predicate function is only available in .ncurc.js or when importing npm-check-updates as a module, not on the command line.
/**
@param name The name of the dependency.
@param semver A parsed Semver array of the upgraded version.
(See: https://git.coolaj86.com/coolaj86/semver-utils.js#semverutils-parse-semverstring)
@returns True if the package should be included, false if it should be excluded.
*/
filterFunction: (name, semver) => {
if (name.startsWith('@myorg/')) {
return false
}
return true
}filterResults
Filters out upgrades based on a user provided function.
filterResults runs after new versions are fetched, in contrast to filter and filterVersion, which run before. This allows you to filter out upgrades with filterResults based on how the version has changed (e.g. a major version change).
Only available in .ncurc.js or when importing npm-check-updates as a module.
/** Filter out non-major version updates.
@param {string} packageName The name of the dependency.
@param {string} current Current version declaration (may be a range).
@param {SemVer[]} currentSemver Current version declaration in semantic versioning format (may be a range).
@param {string} upgraded Upgraded version.
@param {SemVer} upgradedSemver Upgraded version in semantic versioning format.
@returns {boolean} Return true if the upgrade should be kept, otherwise it will be ignored.
*/
filterResults: (packageName, { current, currentSemver, upgraded, upgradedSemver }) => {
const currentMajor = parseInt(currentSemver[0]?.major, 10)
const upgradedMajor = parseInt(upgradedSemver?.major, 10)
if (currentMajor && upgradedMajor) {
return currentMajor < upgradedMajor
}
return true
}For the SemVer type definition, see: https://git.coolaj86.com/coolaj86/semver-utils.js#semverutils-parse-semverstring
filterVersion
Usage:
ncu --filterVersion [p]Include only versions matching the given string, wildcard, glob, comma-or-space-delimited list, /regex/, or predicate function.
The predicate function is only available in .ncurc.js or when importing npm-check-updates as a module, not on the command line. This function is an alias for the filter option function.
/**
@param name The name of the dependency.
@param semver A parsed Semver array of the upgraded version.
(See: https://git.coolaj86.com/coolaj86/semver-utils.js#semverutils-parse-semverstring)
@returns True if the package should be included, false if it should be excluded.
*/
filterVersionFunction: (name, semver) => {
if (name.startsWith('@myorg/') && parseInt(semver[0]?.major) > 5) {
return false
}
return true
}format
Usage:
ncu --format [value]Modify the output formatting or show additional information. Specify one or more comma-delimited values.
groupFunction
Customize how packages are divided into groups when using --format group.
Only available in .ncurc.js or when importing npm-check-updates as a module, not on the command line.
/**
@param name The name of the dependency.
@param defaultGroup The predefined group name which will be used by default.
@param currentSpec The current version range in your package.json.
@param upgradedSpec The upgraded version range that will be written to your package.json.
@param upgradedVersion The upgraded version number returned by the registry.
@returns A predefined group name ('major' | 'minor' | 'patch' | 'majorVersionZero' | 'none') or a custom string to create your own group.
*/
groupFunction: (name, defaultGroup, currentSpec, upgradedSpec, upgradedVersion) => {
if (name === 'typescript' && defaultGroup === 'minor') {
return 'major'
}
if (name.startsWith('@myorg/')) {
return 'My Org'
}
return defaultGroup
}install
Usage:
ncu --install [value]Default: prompt
Control the auto-install behavior.
packageManager
Usage:
ncu --packageManager [s]
ncu -p [s]Specifies the package manager to use when looking up versions.
peer
Usage:
ncu --peer
ncu --no-peerCheck peer dependencies of installed packages and filter updates to compatible versions.
Example:
The following example demonstrates how --peer works, and how it uses peer dependencies from upgraded modules.
The package ncu-test-peer-update has two versions published:
- 1.0.0 has peer dependency
"ncu-test-return-version": "1.0.x" - 1.1.0 has peer dependency
"ncu-test-return-version": "1.1.x"
Our test app has the following dependencies:
"ncu-test-peer-update": "1.0.0",
"ncu-test-return-version": "1.0.0"The latest versions of these packages are:
"ncu-test-peer-update": "1.1.0",
"ncu-test-return-version": "2.0.0"With --peer:
ncu upgrades packages to the highest version that still adheres to the peer dependency constraints:
ncu-test-peer-update 1.0.0 → 1.1.0
ncu-test-return-version 1.0.0 → 1.1.0Without --peer:
As a comparison: without using the --peer option, ncu will suggest the latest versions, ignoring peer dependencies:
ncu-test-peer-update 1.0.0 → 1.1.0
ncu-test-return-version 1.0.0 → 2.0.0registryType
Usage:
ncu --registryType [type]Specify whether --registry refers to a full npm registry or a simple JSON file.
Example:
// local file
$ ncu --registryType json --registry ./registry.json
// url
$ ncu --registryType json --registry https://api.mydomain/registry.json
// you can omit --registryType when the registry ends in .json
$ ncu --registry ./registry.json
$ ncu --registry https://api.mydomain/registry.jsonregistry.json:
{
"prettier": "2.7.1",
"typescript": "4.7.4"
}reject
Usage:
ncu --reject [p]
ncu -x [p]The inverse of --filter. Exclude package names matching the given string, wildcard, glob, comma-or-space-delimited list, /regex/, or predicate function.
The predicate function is only available in .ncurc.js or when importing npm-check-updates as a module, not on the command line.
/**
@param name The name of the dependency.
@param semver A parsed Semver array of the upgraded version.
(See: https://git.coolaj86.com/coolaj86/semver-utils.js#semverutils-parse-semverstring)
@returns True if the package should be excluded, false if it should be included.
*/
rejectFunction: (name, semver) => {
if (name.startsWith('@myorg/')) {
return true
}
return false
}rejectVersion
Usage:
ncu --rejectVersion [p]The inverse of --filterVersion. Exclude versions matching the given string, wildcard, glob, comma-or-space-delimited list, /regex/, or predicate function.
The predicate function is only available in .ncurc.js or when importing npm-check-updates as a module, not on the command line. This function is an alias for the reject option function.
/**
@param name The name of the dependency.
@param semver A parsed Semver array of the upgraded version.
(See: https://git.coolaj86.com/coolaj86/semver-utils.js#semverutils-parse-semverstring)
@returns True if the package should be excluded, false if it should be included.
*/
filterVersionFunction: (name, semver) => {
if (name.startsWith('@myorg/') && parseInt(semver[0]?.major) > 5) {
return true
}
return false
}target
Usage:
ncu --target [value]
ncu -t [value]Determines the version to upgrade to. (default: "latest")
You can also specify a custom function in your .ncurc.js file, or when importing npm-check-updates as a module:
/** Upgrade major version zero to the next minor version, and everything else to latest.
@param name The name of the dependency.
@param semver A parsed Semver object of the upgraded version.
(See: https://git.coolaj86.com/coolaj86/semver-utils.js#semverutils-parse-semverstring)
@returns One of the valid target values (specified in the table above).
*/
target: (name, semver) => {
if (parseInt(semver[0]?.major) === '0') return 'minor'
return 'latest'
}Config File
Use a .ncurc.{json,yml,js,cjs} file to specify configuration information.
You can specify the file name and path using --configFileName and --configFilePath
command line options.
For example, .ncurc.json:
{
"upgrade": true,
"filter": "svelte",
"reject": ["@types/estree", "ts-node"]
}If you write .ncurc config files using json or yaml, you can add the JSON Schema to your IDE settings for completions.
e.g. for VS Code:
"json.schemas": [
{
"fileMatch": [
".ncurc",
".ncurc.json",
],
"url": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/raineorshine/npm-check-updates/main/src/types/RunOptions.json"
}
],
"yaml.schemas": {
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/raineorshine/npm-check-updates/main/src/types/RunOptions.json": [
".ncurc.yml",
]
},Module/Programmatic Usage
npm-check-updates can be imported as a module:
import ncu from 'npm-check-updates'
const upgraded = await ncu.run({
// Pass any cli option
packageFile: '../package.json',
upgrade: true,
// Defaults:
// jsonUpgraded: true,
// silent: true,
})
console.log(upgraded) // { "mypackage": "^2.0.0", ... }Contributing
Contributions are happily accepted. I respond to all PR's and can offer guidance on where to make changes. For contributing tips see CONTRIBUTING.md.
Problems?
File an issue. Please search existing issues first.



