node-sort-counting
v2.0.1
Published
Counting sort is a sorting technique based on keys between a specific range. It works by counting the number of objects having distinct key values (kind of hashing). Then doing some arithmetic to calculate the position of each object in the output sequenc
Downloads
14
Readme
Algorithm-Sort-Counting
About Counting Sort
Counting sort is a sorting technique based on keys between a specific range. It works by counting the number of objects having distinct key values (kind of hashing). Then doing some arithmetic to calculate the position of each object in the output sequence.
* Counting sort algorithm !
* Class Sorting algorithm
* Data structure Array
* Worst-case performance O(n+k)
* Best-case performance O(n+k)
* Average performance O(n+k)
* Worst-case space complexity
* where n is the number of elements in input array and k is the range of input.
* size of the input array.
* Note: if k is greater than log(n) then an n*log(n) algorithm would be a
* better fit. In reality we can always change the radix to make k
* less than log(n).
*
* Author: Pooya HatamiInstallation
If you are using a browser, you can download node-sort-counting.js from GitHub or just bellow hotlink to it:
<script src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pooyahatami/Algorithm-Sort-Counting/master/node-sort-counting.js"></script>If you are using node, you can install node-sort-counting with npm.
npm install node-sort-countingUsage :
var nodesort = require('./node-sort-counting');
var displaymode = "No"; //"Yes"; // "Yes" for more details of algorithm progress
...
nodesort(inputArray, displaymode, function(err,sortRef) {
if (err) {
// TODO error handeling
}
else {
var result = sortRef.countingSort(inputArray);
// TODO output
}
});Ruls :
- Sort Array of integers between 0 and rangeMax
- Array's element could not be negative.
- Returns error mesage if not found valid input.
- Turn On details of Algorithms progress useing : displaymode = "Yes"
var displaymode = "No"; //"Yes";Example
var nodesort = require('./node-sort-counting');
var displaymode = "No"; //"Yes"; // "Yes" for more details of algorithm progress
var base = 10;
var arrin00 = [20, 8 , -11, 12, 22 , 9 , 10 ];
var arrin01 = [20, 8 , 48, 120, 220 , 390 , 1000 ];
var arrin02 = [20, 8 , 480 , 120, 220 , 390 , 1000 ];
var arrin03 = [1120, 800 , 480 , 120, 20 , 390 , 1000 ];
var arrin04 = ['g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's', 'f', 'o',
'r', 'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's'];
var arrin05 = [1, 3, 7, 25, 12, 9, 8,
121, 221, 10, 18, 29, 49];
var arrin06 = [1, 3, -7, 25, 12, 9, 8,
121, 221, -10, 18, 29, 49];
var arrin07 = [1, 3, 7000000000000000000, 25, 12, 9, 8,
121, 221, 100000000000000000000000000 , 18, 290000000000000000000, 49];
var arrin08 = [1, 3, 75432, 25, 12, 9, 8,
121, 221, 976562 , 18, 299999, 49];
var arrin09 = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434 , 0.611 , 0.621 ];
var arrin10 = [1,342, 14,293 , 0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434 , 0.611 , 0.621 ];
var arrin11 = [5, 8 , 11, 12, 2 , 9 , 10 , 4 , 11, 10, 12, 7, 9 ];
var arrin12 = "";
//var arrin13 = [A7,02,22,77,37,15,00,40,B00,75,04,05,07,75,52,12,50,77,71,D07]; //base16
var arrin14 = [1001,101010,11,10,01,111,100,1000,11100,10110,101,100010,0111,101,11111,1000001,1,0,111,11010]; //base 2
var arrin15 = [7,2,22,77,37,15,10770,740,70,75,04,5,107,75,52,12,50,177,71,207]; //base 8
function solveSorting(inputArray) {
var arr_original = inputArray.toString() ;
var sortedArray = inputArray;
nodesort(inputArray, displaymode, function(err,sortRef) {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
}
else {
var result = sortRef.countingSort(inputArray);
console.log("Success attempt to sort array \r\n \t ["+arr_original+" ] \r\n and result is : \r\n \t [ "
+ result + " ]" );
sortedArray = result;
}
console.log("----------------------------------------------------------");
});
return sortedArray;
};
solveSorting(arrin01);
solveSorting(arrin00);
solveSorting(arrin03);
solveSorting(arrin11);
solveSorting(arrin12);
solveSorting(arrin14);
solveSorting(arrin15);Let us understand it with the help of an example.
For simplicity, consider the data in the range 0 to 9.
Input data: 1, 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 2
1) Take a count array to store the count of each unique object.
Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Count: 0 2 2 0 1 1 0 1 0 0
2) Modify the count array such that each element at each index
stores the sum of previous counts.
Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Count: 0 2 4 4 5 6 6 7 7 7
The modified count array indicates the position of each object in
the output sequence.
3) Output each object from the input sequence followed by
decreasing its count by 1.
Process the input data: 1, 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 2. Position of 1 is 2.
Put data 1 at index 2 in output. Decrease count by 1 to place
next data 1 at an index 1 smaller than this index.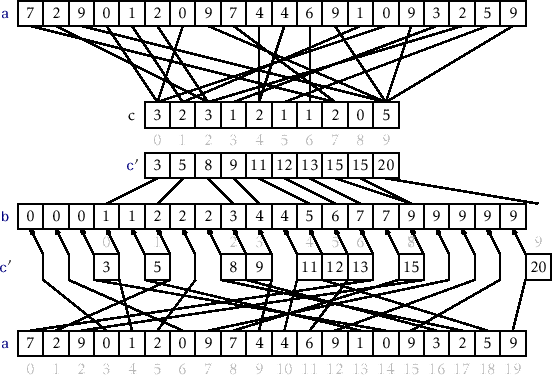
Following is C implementation of counting sort.
C/C++JavaPython
// C Program for counting sort
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define RANGE 255
// The main function that sort the given string arr[] in
// alphabatical order
void countSort(char arr[])
{
// The output character array that will have sorted arr
char output[strlen(arr)];
// Create a count array to store count of inidividul
// characters and initialize count array as 0
int count[RANGE + 1], i;
memset(count, 0, sizeof(count));
// Store count of each character
for(i = 0; arr[i]; ++i)
++count[arr[i]];
// Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
// position of this character in output array
for (i = 1; i <= RANGE; ++i)
count[i] += count[i-1];
// Build the output character array
for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i)
{
output[count[arr[i]]-1] = arr[i];
--count[arr[i]];
}
// Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now
// contains sorted characters
for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
char arr[] = "geeksforgeeks";//"applepp";
countSort(arr);
printf("Sorted character array is %s\n", arr);
return 0;
}Following is Java implementation of counting sort.
// Java implementation of Counting Sort
class CountingSort
{
void sort(char arr[])
{
int n = arr.length;
// The output character array that will have sorted arr
char output[] = new char[n];
// Create a count array to store count of inidividul
// characters and initialize count array as 0
int count[] = new int[256];
for (int i=0; i<256; ++i)
count[i] = 0;
// store count of each character
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i)
++count[arr[i]];
// Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
// position of this character in output array
for (int i=1; i<=255; ++i)
count[i] += count[i-1];
// Build the output character array
for (int i = 0; i<n; ++i)
{
output[count[arr[i]]-1] = arr[i];
--count[arr[i]];
}
// Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now
// contains sorted characters
for (int i = 0; i<n; ++i)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
CountingSort ob = new CountingSort();
char arr[] = {'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's', 'f', 'o',
'r', 'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's'
};
ob.sort(arr);
System.out.print("Sorted character array is ");
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; ++i)
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Following is Python implementation of counting sort.
# Python program for counting sort
# The main function that sort the given string arr[] in
# alphabetical order
def countSort(arr):
# The output character array that will have sorted arr
output = [0 for i in range(256)]
# Create a count array to store count of inidividul
# characters and initialize count array as 0
count = [0 for i in range(256)]
# For storing the resulting answer since the
# string is immutable
ans = ["" for _ in arr]
# Store count of each character
for i in arr:
count[ord(i)] += 1
# Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
# position of this character in output array
for i in range(256):
count[i] += count[i-1]
# Build the output character array
for i in range(len(arr)):
output[count[ord(arr[i])]-1] = arr[i]
count[ord(arr[i])] -= 1
# Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now
# contains sorted characters
for i in range(len(arr)):
ans[i] = output[i]
return ans
# Driver program to test above function
arr = "geeksforgeeks"
ans = countSort(arr)
print "Sorted character array is %s" %("".join(ans))
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar SinghOutput:
Sorted character array is eeeefggkkorss
Other Sorting Algorithms :
- Selection Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- Heap Sort
- QuickSort
- Counting Sort
- Bucket Sort
- ShellSort
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Counting_sort
- http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/counting-sort

