node-red-contrib-json-logic
v2.0.1
Published
Node-RED node utlizing json-logic rules & operations.
Downloads
31
Maintainers
Readme
node-red-contrib-json-logic
This is a Node-RED node for working with JsonLogic rules and operations in your flow.
Installation ⚡
To install the node execute the following command inside the .node-red directory:
npm install node-red-contrib-json-logicLogic Node 🖖
The logic node utilizes the json-logic-engine which makes it easy to write safe instructions for evaluating and operating on json data. These instructions can be persisted into a database, and shared between the front-end and back-end. This works very similar to having access control lists for the data traversing through your flow, if the node is set to rule mode, or applying custom logic to your json data, if the node is set to operator mode.
Using the Logic Node 🔧
The logic node provides two modes of usage:
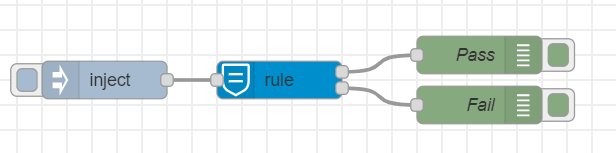
Rule Mode
This mode is used to apply a rule on the data given, the node evaluates the rule against the
msg.payload, forwarding themsgobject accordingly to thepassorfailoutputs. Rules defined must be logical operations and in json format:Check here for more info on logical operations.
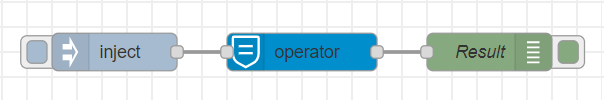
Operator Mode
This mode is used to perform custom logic operations when a
msg.payloadis inbound, the node evaluates the operation, adding it to themsg.resultfield.Check here for more info on math operations.
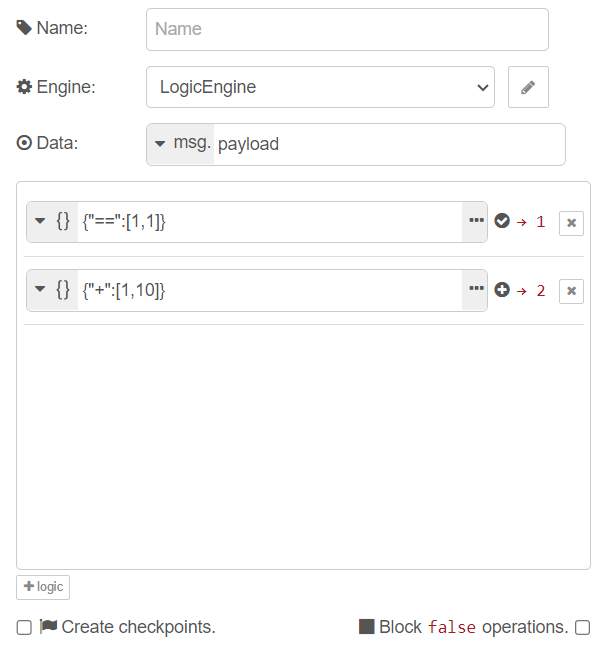
Configuring the Logic Engine ⚙️
The config node is implemented to share the engine instance between logic nodes. This way your logic and switcher nodes can access the same Logic Engine instance across your flows for the rules and operations they perform.
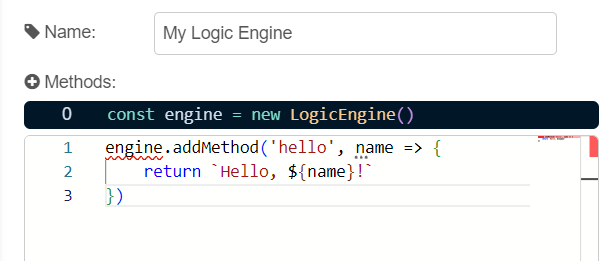
Adding Methods 🔩
The configuration node allows you to set the name (optional) and allows you to add new methods to the Logic Engine. The editor inside the config node gives you access to an engine variable that contains the instance of the Logic Engine.
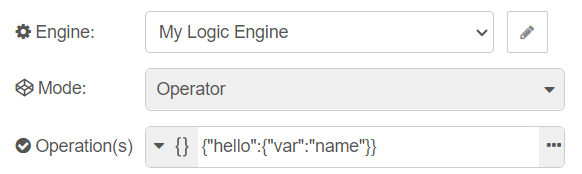
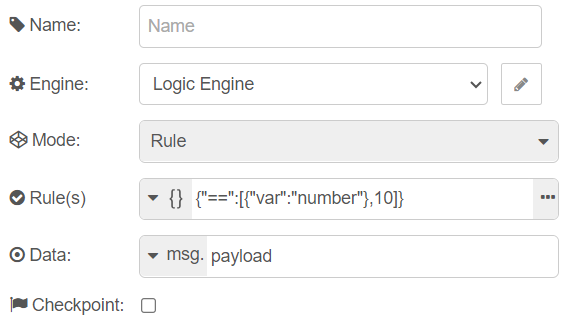
Setting the Rules 📑
The rules used by the logic node must be in JSON format and they can be set by editing the Rule(s) property on the logic node's edit dialog window. There are also other options to set the rules/operation using the type field and choosing from the dropdown (json ,msg ,flow ,global ,env,).
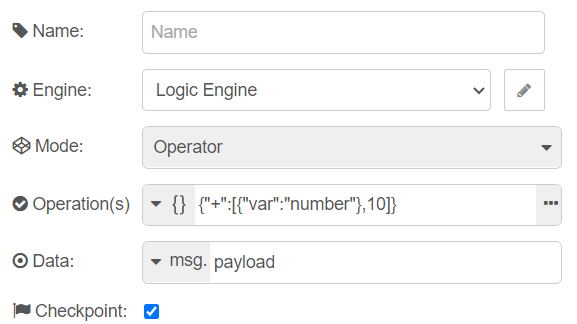
Same is true when using the logic node in the operator mode. The Rule(s) property transforms to Operation(s) property and a non logical operation is expected in the input field.
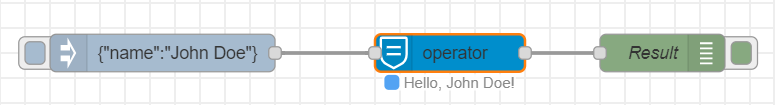
Switcher Node 🧪
The switcher node utilizes the json-logic-engine to evaluate multiple operations on the data target object. The node can act as a complex data switch, if given rules to evaluate, or as on-the-fly operator for incoming data. Similarly to the logic node, the switcher node can be configured with a Logic Engine instance, the target data to inject to the engine and a list of operations to perform to those target data.
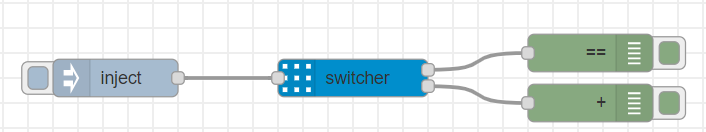
Using the Switcher Node 🔧
In the switcher, each new logic operation will create a new output for the node that will be used to send the operation result in the msg.result property. The node forwards any msg properties as received, but it will change the result and checkpoints (if enabled) properties of the msg. You can configure the node to append a checkpoint report to the msg object and also block the forwarding of an output if it has evaluated to a false (i.e. used a logic operation).
Check please? 🧾
In the edit dialog of the both nodes you can enable the Checkpoint property, this sets the node to append a checkpoint event to the msg.checkpoints array about the logical rule or operation performed.
In the logic node, you can optionally can add a message on the checkpoint event in the input shown:
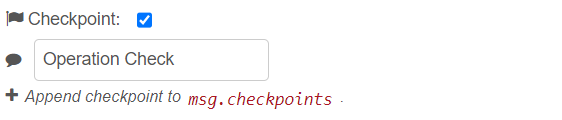
- Operator Mode with Checkpoint:
{
"_msgid":"2a7c3f3134e4ed25",
"payload":{
"number":10
},
"checkpoints":[
{
"id": "5d24464cdecdd106",
"engine": "6d021524792f5088",
"mode":"operator",
"operator":{
"+":[
{
"var":"number"
},
10
]
},
"data":"msg.payload",
"result":20,
"message":"Operation Check",
"timestamp":"Mon Oct 23 2023 17:34:36 GMT+0300 (Eastern European Summer Time)"
}
]
}- Rule Mode with Checkpoint:
{
"_msgid":"6649bef2e8755413",
"payload":{
"number":10
},
"checkpoints":[
{
"id":"b66841c73ecb0ff4",
"engine":"54d129555b731d34",
"mode":"rule",
"rule":{
"==":[
{
"var":"number"
},
10
]
},
"data":"msg.payload",
"result":true,
"timestamp":"Tue Oct 24 2023 00:30:40 GMT+0300 (Eastern European Summer Time)"
}
]
}
- Switcher with Checkpoint:
{
"result":true,
"_msgid":"5cbb1a22e67286c2",
"payload":{
"name":"John",
"five":5,
"ten":10,
"object":{
"first":{
"second":{
"value":17
}
}
}
},
"checkpoints":[
{
"operation":{
"==":[1,1]
},
"result":true,
"id":"41a8322123bc809a",
"engine":"54d129555b731d34",
"data":"msg.payload",
"timestamp":"Tue Nov 14 2023 23:11:53 GMT+0200 (Eastern European Standard Time)"
}
]}The msg.checkpoints is an array that keeps track of the rule(s) / operation(s) performed, the evaluated result, the node's id, mode and engine id, an optional message and a timestamp for the checkpoint event. Each logic and switcher node can be configured to append checkpoint event information about the rule(s) /operation(s) done and will push these events into the msg.checkpoints array.