native_math
v2.1.1
Published
NATIVE MATH: A tiny math library for node.js, deno.js & JavaScript on browser
Downloads
37
Maintainers
Readme
NATIVE MATH
NATIVE MATH: A tiny math library for node.js, deno, bun & JavaScript on browser
Installation
npm install native_math
yarn add native_math
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/native_math/index.js"></script>
Some solutions provided by native math library
// JavaScript
0.1 + 0.2 = 0.30000000000000004 // 0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3 returns false
0.2 + 0.7 = 0.8999999999999999 // 0.2 + 0.7 === 0.9 returns false
0.7 - 0.2 = 0.49999999999999994 // 0.7 - 0.2 === 0.5 returns false
0.1 * 0.2 = 0.020000000000000004 // 0.1 * 0.2 === 0.02 returns false
0.3 / 0.1 = 2.9999999999999996 // 0.3 / 0.1 === 3 returns false
1.2 % 0.5 = 0.19999999999999996 // 1.2 / 0.5 === 0.2 returns false
// NATIVE MATH library
nm.add(0.1, 0.2) = 0.3 // nm.add(0.1, 0.2) === 0.3 returns true
nm.add(0.2, 0.7) = 0.9 // nm.add(0.2, 0.7) === 0.9 returns true
nm.subt(0.7, 0.2) = 0.5 // nm.subt(0.7, 0.2) === 0.5 returns true
nm.mult(0.1, 0.2) = 0.02 // nm.mult(0.1, 0.2) === 0.02 returns true
nm.divi(0.3, 0.1) = 3 // nm.divi(0.3, 0.1) === 3 returns true
nm.rem(1.2, 0.5) = 0.2 // nm.rem(1.2, 0.5) === 0.2 returns true<!-- html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>NATIVE MATH</title>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/index.js"></script>-->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/native_math/index.min.js"></script>
<!-- This link is the latest mini version ☝ -->
</head>
<body>
<script>
let myNumber = 0.1;
const myCube = nm.cube(myNumber);
// nm.cube(0.1) returns 0.001
console.log(`(${myNumber})^3 returns ${myCube} in native math library`);
// Math.pow(0.1, 3) or (0.1 * 0.1 * 0.1) returns 0.0010000000000000002
console.log(`(${myNumber})^3 returns ${Math.pow(myNumber, 3)} in JavaScript`);
</script>
</body>
</html>// Next JS
// index.js
// npm install native_math
import nm from 'native_math';
import React from 'react';
const Home = () => {
const price = 4.5 / 3;
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>{nm.add([1,8], 1).[1]}</li>
<li>{nm.fix(1, 2)}</li>
<li>{nm.fix(nm.phi,2)}</li>
<li>{nm.stn('8.00')}</li>
<li>{nm.zeros(2,2)}</li>
<li>{nm.zeros(2.1,2)}</li>
<li>{nm.zeros(2.1440000000,2)}</li>
<li>{nm.zeros(2.1440000000,5)}</li>
<li>${nm.zeros(price,2)}</li>
<li>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://www.npmjs.com/package/native_math"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn NATIVE MATH Library
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default Home;// React JS
// App.js
// npm install native_math
import { divi, zeros, stn, nts } from 'native_math';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
function App() {
const price = divi(4.2, 3);
const priceWithFormat = zeros(price, 2);
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<p>
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</p>
<a className="App-link" href="https://reactjs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">
Learn React
</a>
<br />
<a className="App-link" href="https://www.npmjs.com/package/native_math" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">
Learn NATIVE MATH Library
</a>
<h2>
<p>${nts(0.0)}</p>
Free ${zeros(stn('0.00'), 2)} <strike>${priceWithFormat}</strike>
</h2>
<small>Type: {typeof priceWithFormat}</small>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;// Node JS
// index.js
// npm install native_math
// import nm from 'native_math';
// console.log(nm.sin.deg(nm.range(0, 90, 30)));
// Or
import { sin, range } from 'native_math';
console.log(sin.deg(range(0, 90, 30)));Examples
Use
console.log()to output the result.console.log(nm.abs(-3.6)); // 3.6
const nm = require(`native_math`);
nm.abs(-3.6); // 3.6
nm.subt(2, 5); // -3
nm.sqr(2) + nm.sqrt(4); // 6
nm.sqr(4) + nm.sqrt(4) / nm.pi; // 16.63661977236758
nm.e; // 2.718281828459045
nm.exp(1); // 2.718281828459045
nm.exp(-1); // 0.367879441171442
nm.exp(nm.pi / 3); // 2.849653908226361
nm.log(10); // 2.302585092994046
nm.ln2; // 0.693147180559945
nm.ln10; // 2.302585092994046
nm.log2e; // 1.442695040888963
nm.log10e; // 0.434294481903252
nm.log1p(5); // 1.791759469228055
nm.log(mnjs.e); // 1
nm.hypot(4); // 4
nm.hypot([4]); // 4
nm.hypot(3, 4); // 5
nm.hypot([3, 4]); // 5
nm.hypot(4, 2, 4); // 6
nm.hypot([4, 2, 4]); // 6
nm.hypot([-3, -4]); // 5
nm.hypot(-3, -4); // 5
nm.hypot([-4]); // 4
nm.hypot(-4); // 4
nm.sqrt(nm.add(nm.sqr(6), nm.sqr(8))) === nm.hypot(6, 8); // true
nm.hypot([-3, -4], 1); // Error: NATIVE MATH ERROR No. 01 : 05
mnjs.hypot([-3, -4], [1]); // Error: NATIVE MATH ERROR No. 01 : 05
mnjs.hypot([-3, -4, '1']); // Error: NATIVE MATH ERROR No. 01 : 05
nm.fix(2.718281828459045, 2); // 2.72
nm.inv(10); // 0.1
nm.ceil(1.1); // 2
nm.ceil(-1.1); // -1
nm.ceil([-0.2, 0, 0.2]); // [-0, 0, 1]
nm.max(1, 10, 3, -2); // 10
nm.max([1, 10, 3, -2]); // 10
nm.max(1, 10, 3, ''); // Error: NATIVE MATHnm ERROR No. 01 : 05
nm.min(5, 1, -3.2, 0.5, 3); // -3.2
nm.min([5, 1, -3.2, 0.5, 3]); // -3.2
nm.min(); // Error: NATIVE MATHnm ERROR No. 01 : 05
nm.min([]); // Error: NATIVE MATHnm ERROR No. 01 : 05: This function accepts numeric arguments or one numeric array argument. (num1, num2, ..., num) => {} or ([num1, num2, ..., num]) => {}
nm.pow(2, 4); // 16
nm.pow(2, -2.5); // 0.176776695296637
nm.cbrt(8); // 2
nm.nrt(0.0001, 4); // 0.1
nm.nrt(Infinity, Infinity); // 1
nm.nrt(Infinity, Infinity) === nm.pow(Infinity, 1 / Infinity); // true
nm.tau; // 6.283185307179586
nm.sin(1); // 0.841470984807897
nm.sin.rad(1); // 0.841470984807897
nm.sin(1) === nm.sin.rad(1); // true
nm.dtr(30); // 0.523598775598299
nm.sin.deg(30); // 0.5
nm.sin.deg(30) === nm.sin(mnjs.dtr(30)); // true
nm.cos.deg(60); // 0.5
nm.cos(0); // 1
nm.cos.rad(0); // 1
nm.cos(1) === nm.cos.rad(1); // true
nm.tan.deg(45); // 1
nm.tan(0.5); // 0.54630248984379
nm.tan(0.5) === nm.tan.rad(0.5); // true
nm.tan.deg(90); // -Infinity
1 / nm.sin.deg(30); // 2
nm.csc.deg(30)(
// 2
1 / nm.cos.deg(60)
) === nm.sec.deg(60); // true
console.log(nm.sec.deg(60))(
// 2
1 / nm.tan.deg(45)
) === nm.cot.deg(45); // true
nm.cot.deg(45); // 1
nm.cot.deg(0); // Infinity
nm.acsc(mnjs.csc(0.67)); // 0.67
nm.asec.rad(1) === nm.asec(1); // true
nm.stn('123'); // 123
nm.nts(123); // "123"
/***** Matrices *****/
nm.range(1, 10, 1); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ]
nm.range(1, 10); // [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ]
nm.range(10, 1, 1); // [ 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 ]
nm.range(10, 1); // [ 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 ]
nm.range(1, 5, 0.5); // [ 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5 ]
nm.range(1, 0, 0.2); // [ 1, 0.8, 0.6, 0.4, 0.2, 0 ]
nm.range(10, 1, 2); // [ 10, 8, 6, 4, 2 ]
nm.range(-20, 1, 0); // Error: NATIVE MATH ERROR No. 02 : 01: The step parameter should not be:
// 1/ null
// 2/ equal or less than zero.
// 3/ greater than the absolute difference between the first and second parameter
nm.monolist(1, 5); // [ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 ]
nm.monolist(0.5, 3); // [ 0.5, 0.5, 0.5 ]
nm.monolist(0, 5); // [ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
nm.monolist(-0.5, 3); // [ -0.5, -0.5, -0.5 ]
nm.monolist(-1, 5); // [ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 ]
nm.monolist(5, 1.1); // RangeError: Invalid array length
// Most of the NATIVE MATH functions return a number or an array of numbers
const myArray = nm.range(0, 90, 30);
const errArray = [0, 30, '60', 90];
myArray; // [ 0, 30, 60, 90 ]
errArray; // [ 0, 30, '60', 90 ]
nm.cube(myArray); // [ 0, 27000, 216000, 729000 ]
nm.sin.deg(myArray[1]); // 0.5
nm.sin.deg(myArray); // [ 0, 0.5, 0.866025403784439, 1 ]
nm.abs(errArray); // Error: NATIVE MATHnm ERROR No. 01: This function accepting either a number or an array.
// In the case of an array, all of its elements must be numbers.
nm.dtr(myArray); // [ 0, 0.523598775598299, 1.047197551196598, 1.570796326794897 ]
// Note the result may change in some functions depending on the position of the arguments
nm.add(2, 2); // 4
nm.add([0, 2], [4, 8]); // [ 4, 10 ]
nm.add([4, 8], [0, 2]); // [ 4, 10 ]
nm.add(2, [1, 2]); // [ 3, 4 ]
nm.add([1, 2], 2); // [ 3, 4 ]
nm.subt(2, [1, 2]); // [ 1, 0 ]
nm.subt([1, 2], 2); // [ -1, 0 ]
nm.subt([0, 2], [4, 8]); // [ -4, -6 ]
nm.subt([4, 8], [0, 2]); // [ 4, 6 ]
nm.mult(2, [1, 2]); // [ 2, 4 ]
nm.mult([1, 2], 2); // [ 2, 4 ]
nm.divi(2, [1, 2]); // [ 2, 1 ]
nm.divi([1, 2], 2); // [ 0.5, 1 ]
nm.divi([0, 2], [4, 8]); // [ 0, 0.25 ]
nm.divi([4, 8], [0, 2]); // [ Infinity, 4 ]
nm.add([2], [1, 2]); // Error: NATIVE MATH ERROR No. 01 : 03: This function accepting two arguments of numbers, arrays, or one of them must be a number, and the other must be an array; In the case of arrays, all elements must be a number, the length of arrays must be equal
nm.pow(4, [1, 2, 3]); // [ 4, 16, 64 ]
nm.pow([1, 2, 3], 4); // [ 1, 16, 81 ]
nm.nrt(8, [1, 2, 3]); // [ 8, 2.82842712474619, 2 ]
nm.nrt([1, 2, 3], 8); // [ 1, 1.090507732665258, 1.147202690439877 ]
nm.nrt([1, 3], [3, 1]); // [ 1, 3 ]
nm.nrt([3, 1], [1, 3]); // [ 3, 1 ]
nm.mult(0.2, [5, 10, 15]); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
nm.mult(0.2, nm.range(5, 15, 5)); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
nm.mult([0.2, 0.2, 0.2], [5, 10, 15]); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
nm.mult(nm.monolist(0.2, 3), [5, 10, 15]); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
nm.mult(0.2, [5, 10, 15])[1] === nm.mult(nm.monolist(0.2, 3), [5, 10, 15])[1]; // true
nm.imul(0xffffffff, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]); // [ -1, -2, -3, -4, -5 ]
nm.rib(100000, 999999); // returns random integer between two values, inclusive min and max value
// Remember that:
// 0 / 0 = NaN, NaN / NaN = NaN, Infinity / Infinity = NaN, Infinity / NaN = NaN
// NaN / Infinity = NaN, 0 / NaN = NaN, NaN / 0 = Nan
// 0 / Infinity = 0, Infinity / 0 = Infinity
// Infinity === Infinity returns true. Infinity is equal to itself
// Infinity > Infinity, return false
// NaN === NaN, NaN > NaN, NaN < NaN, returns false
// Infinity === NaN, Infinity > NaN, Infinity < NaN, returns false
// The change function replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x = y
// The change and change.isEqual functions are the same
// nm.change(x=1, y=1, z=0)
nm.change(1, 1, 0) === mnjs.change.isEqual(1, 1, 0); // returns true
nm.change(1, 1, 0); // returns 0
nm.change(1, NaN, 0); // returns 1
nm.change(Infinity, Infinity, 0); // returns 0
nm.change([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], NaN, 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, Infinity]
// where [0 = old value, NaN = old value, 1 = old value, Infinity = old value], nothing changed!
nm.change([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], Infinity, 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, 0]
// where [0 = old value, NaN = old value, 1 = old value, 0 = new value ], only Infinity value replaced with 0
// The change.isNotEqual function replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x is not equal to y
// nm.change.isNotEqual(x=1, y=1, z=0)
nm.change.isEqual(1, 1, 0) !== nm.change.isNotEqual(1, 1, 0); // returns true
nm.change.isNotEqual(1, 1, 0); // returns 1, where 1 is the old value of x
nm.change.isNotEqual(1, NaN, 0); // returns 0, where 0 is the new value of x
nm.change.isNotEqual(Infinity, Infinity, 0); // returns Infinity
nm.change.isNotEqual([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], NaN, 0); // returns [0, 0, 0, 0]
// where [0 = new value, 0 = new value, 0 = new value, 0 = new value], all elements changed with new values!
nm.change.isNotEqual([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], Infinity, 0); // returns [0, 0, 0, Infinity]
// where [0 = new value, 0 = new value, 0 = new value, Infinity = old value ], all elements replaced with 0 except Infinity
nm.change.isGreater([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], NaN, 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, Infinity]
nm.change.isLess([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], NaN, 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, Infinity]
nm.change.isGreaterOrEqual([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], Infinity, 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, 0]
// where orEqual is true (Infinity replaced by 0)
nm.change.isLessOrEqual([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], Infinity, 0); // returns [0, NaN, 0, 0]
// change.isFiniteNum(x, y) or change.isFiniteNum(xArray, y)
nm.change.isFiniteNum([0, NaN, 1, Infinity], Infinity); // returns [Infinity, NaN, Infinity, Infinity]
// where [Infinity = new value, NaN = old value, Infinity = new value, Infinity = old value]
nm.change.isInfinity([-Infinity, NaN, 1, Infinity], 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, 0] (change ±Infinity)
nm.change.isPlusInfinity([-Infinity, NaN, 1, Infinity], 0); // returns [-Infinity, NaN, 1, 0]
nm.change.isMinusInfinity([-Infinity, NaN, 1, Infinity], 0); // returns [0, NaN, 1, Infinity]
nm.change.isNAN([-Infinity, NaN, 1, Infinity], 0); // returns [-Infinity, 0, 1, Infinity]
// Fermat number
nm.fermat(-1) or nm.fermat(1.2) // returns error
nm.fermat(0) // returns 3
nm.fermat([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) // returns [5, 17, 257, ..., 1.3407807929942597e+154, Infinity]Demo Projects
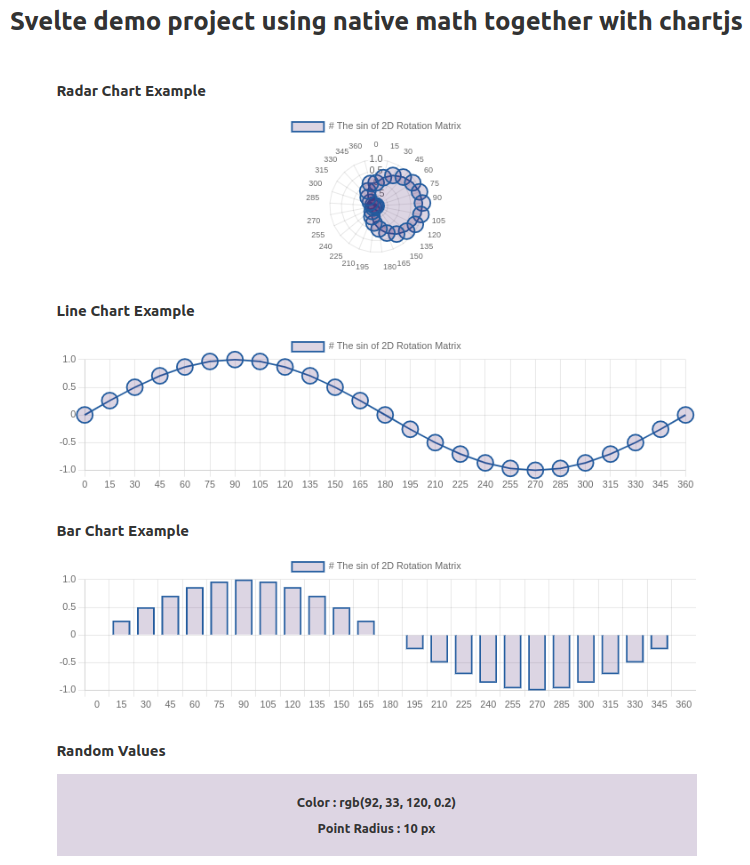
Svelte Demo Project [https://svelte-native-math-chartjs.vercel.app]
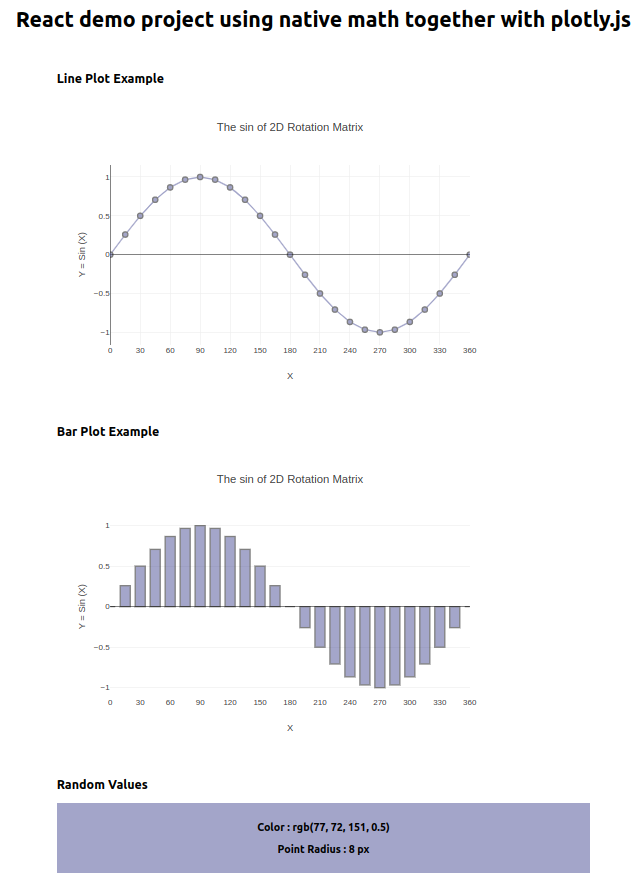
React Demo Project [https://react-native-math-plotlyjs.vercel.app]
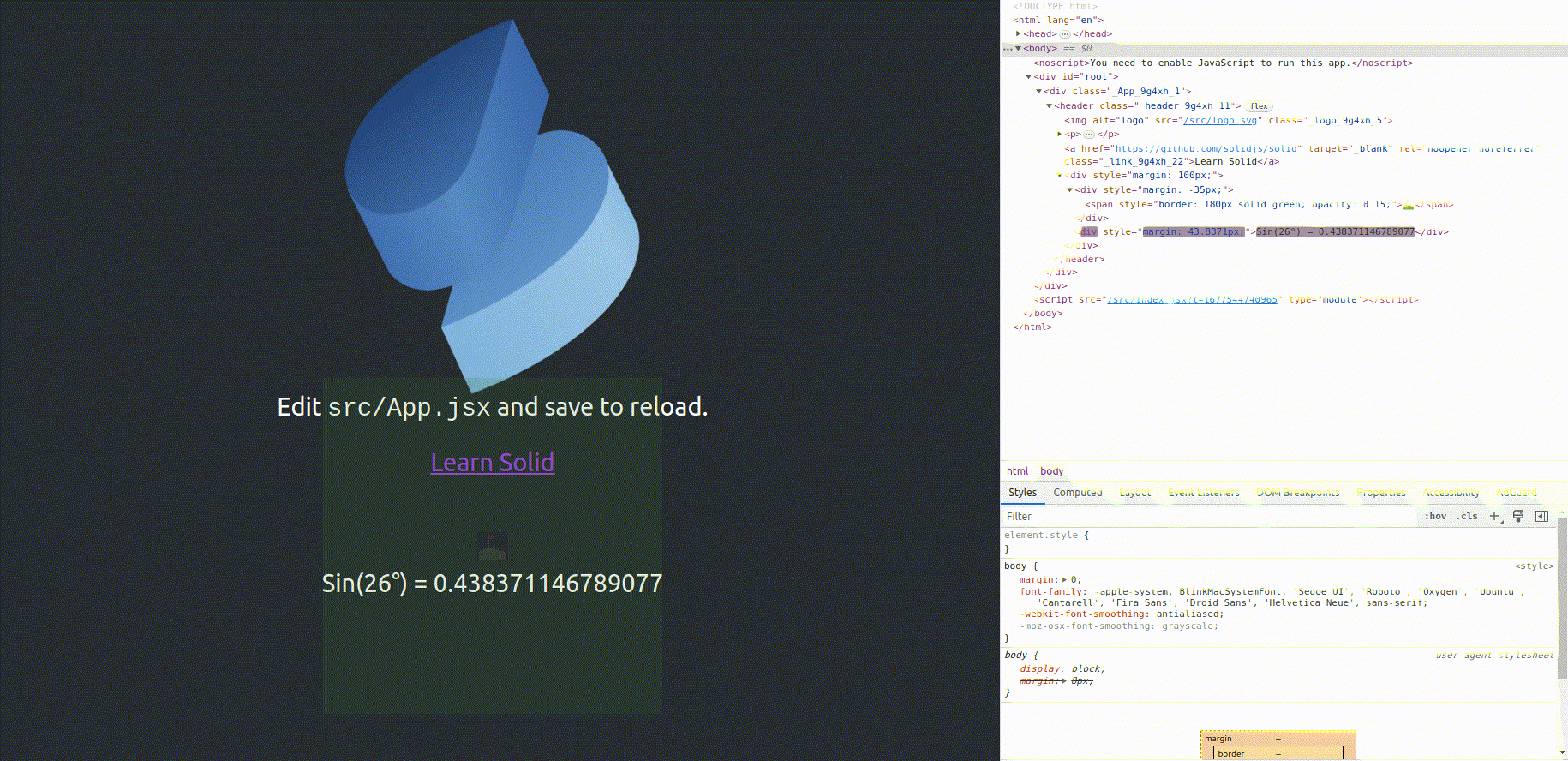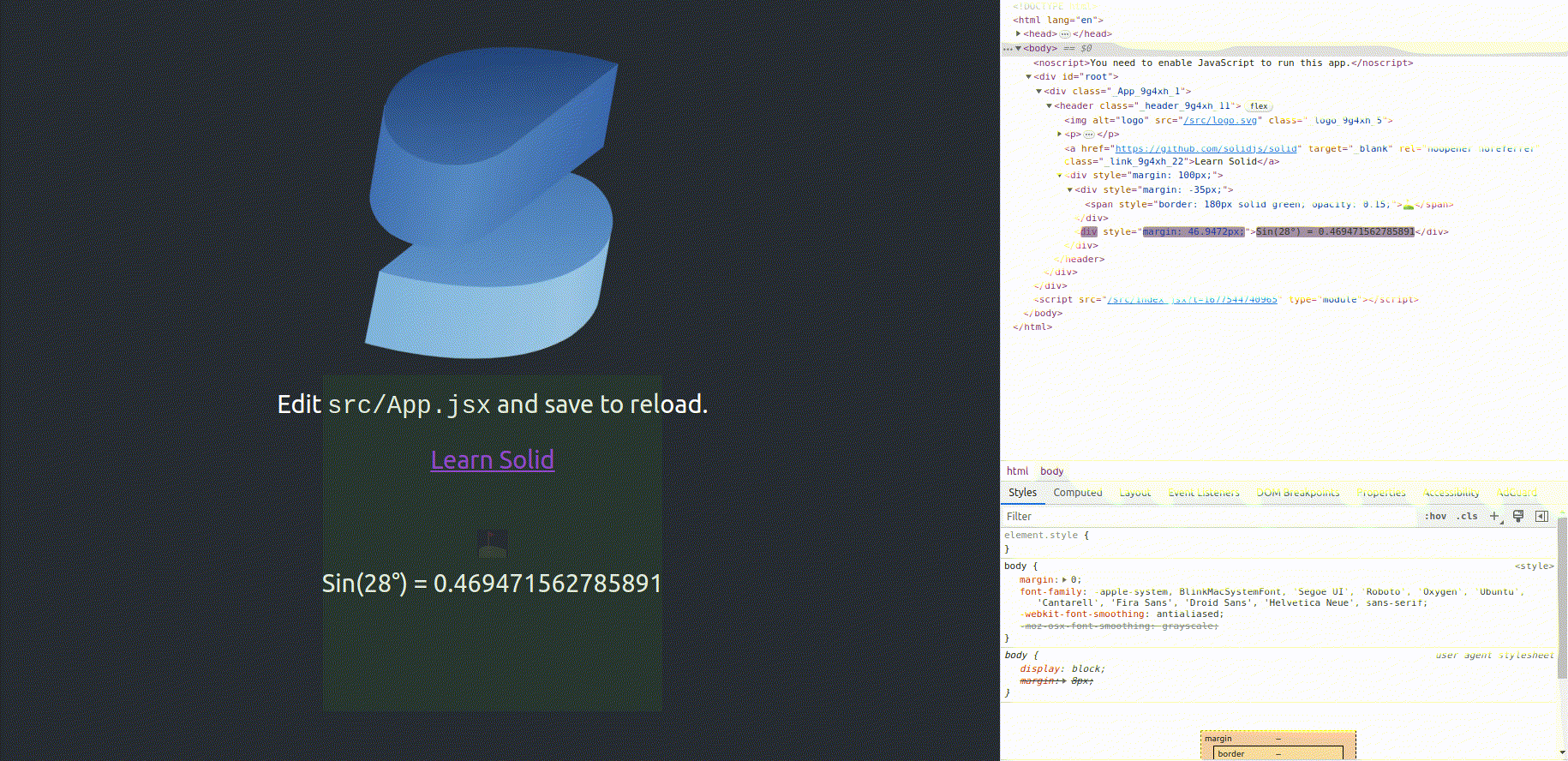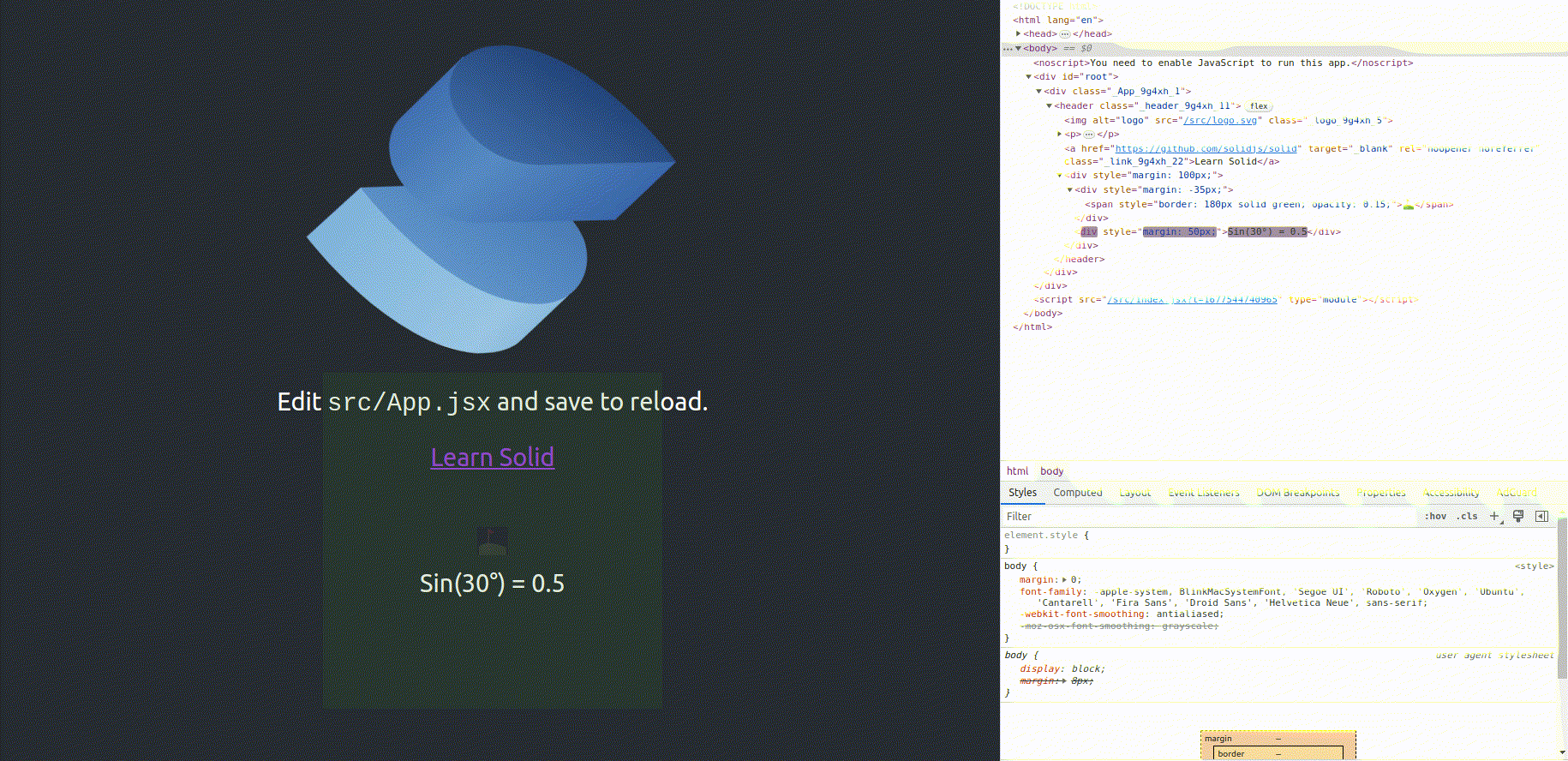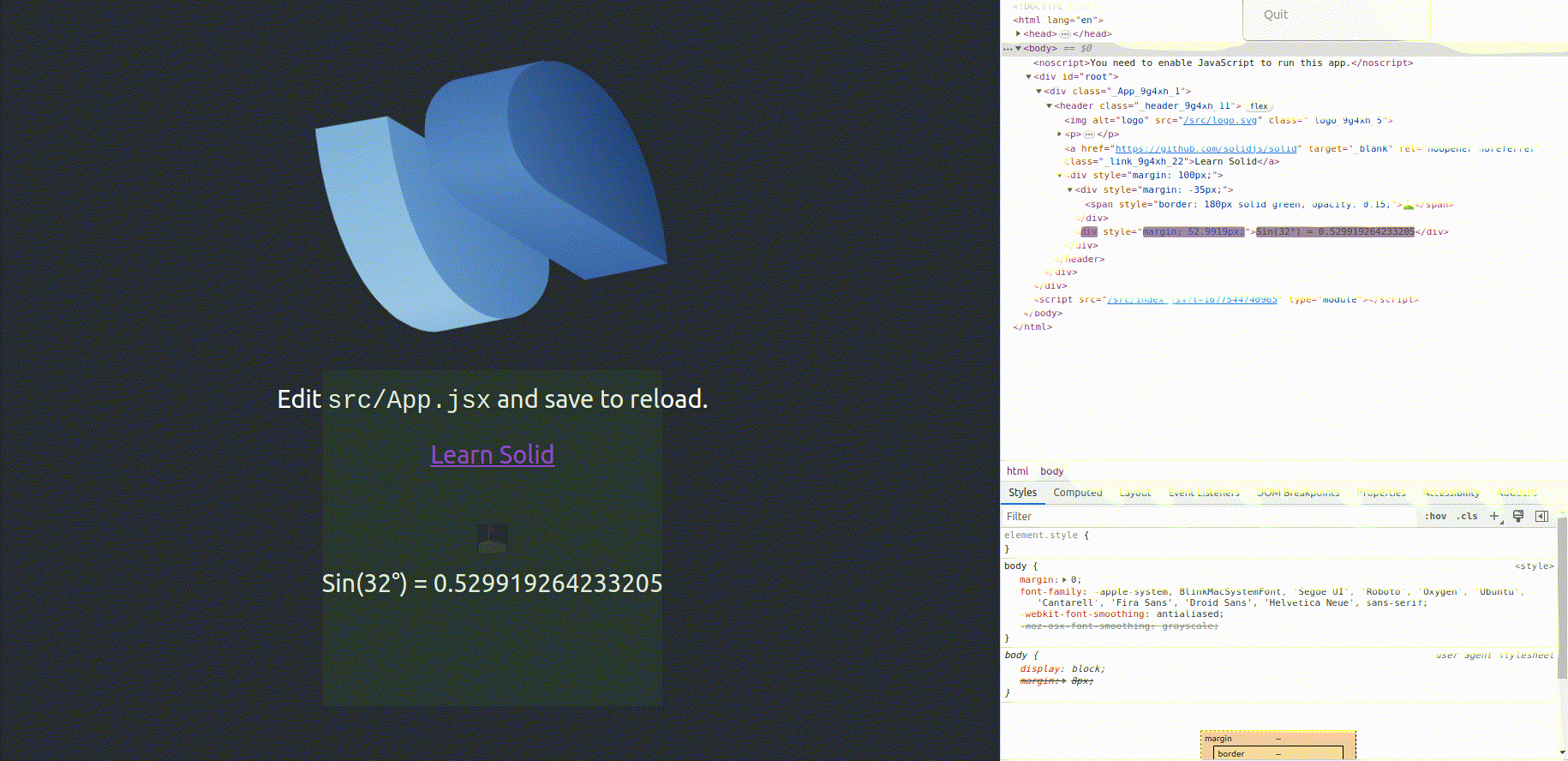
Solid.js Demo Project [https://reactive-sine-function.vercel.app]
NATIVE MATH Object Keys
| Key | Definition | Value | | :---------------------- | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | abs | The absolute value of a number | function: abs(num) | | add | Addition | function: add(num1, num2) | | acos | Inverse cosine (in radians) | function: acos(num) | | acos.rad | Inverse cosine (in radians) | function: acos.rad(num) | | acos.deg | Inverse cosine (in degrees) | function: acos.deg(num) | | acosh | Inverse hyperbolic cosine (in radians) | function: acosh(num) | | acosh.rad | Inverse hyperbolic cosine (in radians) | function: acosh.rad(num) | | acosh.deg | Inverse hyperbolic cosine (in degrees) | function: acosh.deg(num) | | acot | Inverse cotangent (in radians) | function: acot(num) | | acot.rad | Inverse cotangent (in radians) | function: acot.rad(num) | | acot.deg | Inverse cotangent (in degrees) | function: acot.deg(num) | | acoth | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent (in radians) | function: acoth(num) | | acoth.rad | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent (in radians) | function: acoth.rad(num) | | acoth.deg | Inverse hyperbolic cotangent (in degrees) | function: acoth.deg(num) | | acsc | Inverse cosecant (in radians) | function: acsc(num) | | acsc.rad | Inverse cosecant (in radians) | function: acsc.rad(num) | | acsc.deg | Inverse cosecant (in degrees) | function: acsc.deg(num) | | acsch | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant (in radians) | function: acsch(num) | | acsch.rad | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant (in radians) | function: acsch.rad(num) | | acsch.deg | Inverse hyperbolic cosecant (in degrees) | function: acsch.deg(num) | | asec | Inverse secant (in radians) | function: asec(num) | | asec.rad | Inverse secant (in radians) | function: asec.rad(num) | | asec.deg | Inverse secant (in degrees) | function: asec.deg(num) | | asech | Inverse hyperbolic secant (in radians) | function: asech(num) | | asech.rad | Inverse hyperbolic secant (in radians) | function: asech.rad(num) | | asech.deg | Inverse hyperbolic secant (in degrees) | function: asech.deg(num) | | asin | Inverse sine (in radians) | function: asin(num) | | asin.rad | Inverse sine (in radians) | function: asin.rad(num) | | asin.deg | Inverse sine (in degrees) | function: asin.deg(num) | | asinh | Inverse hyperbolic sine (in radians) | function: asinh(num) | | asinh.rad | Inverse hyperbolic sine (in radians) | function: asinh.rad(num) | | asinh.deg | Inverse hyperbolic sine (in degrees) | function: asinh.deg(num) | | atan | Inverse tangen (in radians) | function: atan(num) | | atan.rad | Inverse tangen (in radians) | function: atan.rad(num) | | atan.deg | Inverse tangen (in degrees) | function: atan.deg(num) | | atanh | Inverse hyperbolic tangen (in radians) | function: atanh(num) | | atanh.rad | Inverse hyperbolic tangen (in radians) | function: atanh.rad(num) | | atanh.deg | Inverse hyperbolic tangen (in degrees) | function: atanh.deg(num) | | ceil | The ceil function returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to a number | function: ceil(num) | | change | The change function replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x = y | function: change(x, y, z) | | change.isEqual | The change.isEqual function replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x = y | function: change.isEqual(x, y, z) | | change.isNotEqual | The change.isNotEqual replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x is not equal to y | function: change.isNotEqual(x, y, z) | | change.isGreater | The change.isGreater replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x is greater than y | function: change.isGreater(x, y, z) | | change.isLess | The change.isLess replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x is less than y | function: change.isLess(x, y, z) | | change.isGreaterOrEqual | The change.isGreaterOrEqual replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x is greater than or equal to y | function: change.isGreaterOrEqua(x, y, z) | | change.isLessOrEqual | The change.isLess replace x (number or numeric array element) with z if x is less than y | function: change.isLessOrEqual(x, y, z) | | change.isFiniteNum | The change.isFiniteNum replace x (number or numeric array element) with y if x is finite | function: change.isFiniteNum(x,y) | | change.isInfinity | The change.isInfinity replace x (number or numeric array element) with y if x is infinity | function: change.isInfinity(x,y) | | change.isPlusInfinity | The change.isPlusInfinity replace x (number or numeric array element) with y if x is plus infinity | function: change.isPlusInfinity(x,y) | | change.isMinusInfinity | The change.isMinusInfinity replace x (number or numeric array element) with y if x is minus infinity | function: change.isMinusInfinity(x,y) | | change.isNAN | The change.isNAN replace x (number or numeric array element) with y if x is NAN | function: change.isNAN(x,y) | | cos | Cosine (in radians) | function: cos(angleRadians) | | cos.rad | Cosine (in radians) | function: cos.rad(angleRadians) | | cos.deg | Cosine (in degrees) | function: cos.deg(angleDegrees) | | cosh | Hyperbolic cosine (in radians) | function: cosh(angleRadians) | | cosh.rad | Hyperbolic cosine (in radians) | function: cosh.rad(angleRadians) | | cosh.deg | Hyperbolic cosine (in degrees) | function: cosh.deg(angleDegrees) | | csc | cosecant (or cosec) | function: csc(angleRadians) | | csc.rad | cosecant (or cosec) | function: csc.rad(angleRadians) | | csc.deg | Cosecant (in degrees) | function: csc.deg(angleDegrees) | | csch | Hyperbolic cosecant (or cosec) | function: csch(angleRadians) | | csch.rad | Hyperbolic cosecant (or cosec) | function: csch.rad(angleRadians) | | csch.deg | Hyperbolic cosecant (in degrees) | function: csch.deg(angleDegrees) | | cube | Cube (n)^3 | function: cube(num) | | cbrt | Cube Root | function: cbrt(num) | | cot | Cotangent (or cotan or cotg or ctg or ctn). (in radians) | function: cot(angleRadians) | | cot.rad | Cotangent (or cotan or cotg or ctg or ctn). (in radians) | function: cot.rad(angleRadians) | | cot.deg | Cotangent (in degrees) | function: cot.deg(angleDegrees) | | coth | Hyperbolic cotangent (or cotan or cotg or ctg or ctn). (in radians) | function: coth(angleRadians) | | coth.rad | Hyperbolic cotangent (or cotan or cotg or ctg or ctn). (in radians) | function: coth.rad(angleRadians) | | coth.deg | Hyperbolic cotangent (in degrees) | function: coth.deg(angleDegrees) | | dtr | Degrees to Radians conversion | function: dtr(angleDegrees). Result in radians | | divi | Division | function: divi(numerator, denominator) | | e | The Number e (Euler's number) | number: 2.718281828459045 | | exp | The power of e (Euler's number) | function: exp(power) | | expm1 | The expm1 function returns e^x - 1, where x is the argument, and e the base of the natural logarithms | function: expm1(power) | | fermat | The fermat function accepting a non-negative integer | function: fermat(num) | | fix | Fix to the certain decimal point | function: fix(num, point) | | floor | The floor function returns the largest integer less than or equal to a given number | function: floor(num) | | fround | The fround function returns the nearest 32-bit single precision float representation of a Number | function: fround(num) | | hypot | The square root of the sum of squares | function: hypot(num1, num2, ..., num) or function: hypot([num1, num2, ..., num]) | | imul | The imul function returns the result of the C-like 32-bit multiplication of the two parameters | function: imul(num1, num2) | | inv | The inverse of a number | function: inv(num) | | ln2 | The natural logarithm of 2 | number: 0.693147180559945 | | ln10 | The natural logarithm of 10 | number: 2.302585092994046 | | log | The Natural logarithm (base e) of a number | function: log(x) is equivalent to ln(x) in mathematics | | log1p | The natural logarithm (base e) of 1 + a number | function: log1p(x) | | log2 | The base 2 logarithm of a number | function: log2(x) | | log10 | The base 10 logarithm of a number | function: log10(x) | | log2e | The base 2 logarithm of E | number: 1.4426950408889634 | | log10e | The base 10 logarithm of E | number: 0.434294481903252 | | max | Max function returns the largest-valued number | function: max(num1, num2, ..., num) or max(array of numbers) | | min | Min function returns the lowest-valued number | function: min(num1, num2, ..., num) or min(array of numbers) | | monolist | The monolist function returns an array of numbers of equal values, specifying the element's value and the size of the array. | function: monolist(value, size). It returns an array | | mult | Multiplication | function: mult(num1, num2) | | nrt | N Root | function: nrt(num, root), when root=n={1,2,..} | | nts | Number to String conversion | function: nts(num). Result as string | | pi | The Number pi (π) | number: 3.141592653589793 | | phi | The Golden Ratio (Phi) | number: 1.618033988749895 | | pow | power | function: pow(num, power) | | range | The range function returns a sequence of numbers, starting from start value by default, and increments or decrements by step value, and stops before or in specified end value. | function: range(start, end, step). It returns an array | | rem | The remainder function (%) returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division, after one number is divided by another (called the modulus of the operation) | function: rem(num1, num2) | | rib | The rib function returns a random integer between two values, inclusive min and max value | function: rib(min, max) | | round | The round function returns the value of a number rounded to the nearest integer | function: round(num) | | rtd | Radians to Degrees conversion | function: rtd(angleRadians). Result in degrees | | sec | Secant (in radians) | function: sec(angleRadians) | | sec.rad | Secant (in radians) | function: sec.rad(angleRadians) | | sec.deg | Secant (in degrees) | function: sec.deg(angleDegrees) | | sech | Hyperbolic secant (in radians) | function: sech(angleRadians) | | sech.rad | Hyperbolic secant (in radians) | function: sech.rad(angleRadians) | | sech.deg | Hyperbolic secant (in degrees) | function: sech.deg(angleDegrees) | | sign | The sign function (+, -) | function: sign(num). It returns -1, -0, 0, 1 | | sin | Sine (in radians) | function: sin(angleRadians) | | sin.rad | Sine (in radians) | function: sin.rad(angleRadians) | | sin.deg | Sine (in degrees) | function: sin.deg(angleDegrees) | | sinh | Hyperbolic sine (in radians) | function: sinh(angleRadians) | | sinh.rad | Hyperbolic sine (in radians) | function: sinh.rad(angleRadians) | | sinh.deg | Hyperbolic sine (in degrees) | function: sinh.deg(angleDegrees) | | sqr | Square | function: sqr(num) | | sqrt | Square Root | function: sqrt(num) | | stn | String to Number conversion | function: stn(str). Result as number | | subt | Subtraction | function: subt(num1, num2) | | sum | The Sum Function, Also Called The Reducer Function. The final result of running the sum function across all elements of the array is a single value. The first argument should be one (numeric or empty) array and the second should be a number. | function: sum(Array, number) or sum(Array), number=0 | | tan | Tangent (in radians) | function: tan(angleRadians) | | tan.rad | Tangent (in radians) | function: tan.rad(angleRadians) | | tan.deg | Tangen (in degrees) | function: tan.deg(angleDegrees) | | tanh | Hyperbolic tangent (in radians) | function: tanh(angleRadians) | | tanh.rad | Hyperbolic tangent (in radians) | function: tanh.rad(angleRadians) | | tanh.deg | Hyperbolic tangent (in degrees) | function: tanh.deg(angleDegrees) | | tau | The tau constant (2 x pi) | number: 6.283185307179586 | | trunc | Returns the integer part of a number | function: trunc(num) | | zeros | Add .00 to number | function: zeros(num, point). Result as string |