moodle-webservice
v1.8.1
Published
Moodle Web Service API client with intellisense and typechecking
Downloads
38
Readme
TypeScript Moodle API client for Node.js
A simple and developer friendly TypeScript module to perform Web Service (API) calls to the Moodle site.
Getting started
Install the module
npm install moodle-webserviceGet site info (using Promised callbacks)
import MoodleApi, { MoodleClient } from "moodle-webservice";
const moodle = MoodleApi({
baseUrl: "https://moodle.example.com", //<-- Put your Moodle URL here
token: "exppsBdQwLvNwYRoAuaiBO5j0aWTzxU6", //<-- Put your token here
});
moodle.core.webservice //<-- with intellisense and type checking
.getSiteInfo()
.then((res) => console.log(res)) //<-- Response of type IMoodleSiteInfo
.catch((err) => console.error(err.message));Get course contents (using async-await approach)
import MoodleApi from 'moodle-webservice';
const moodle = MoodleApi({ ... });
async function main() {
try {
const sections =
await moodle.core.course.getContents({courseid: 1234});//<-- returns IMoodleCourseSection[]
//Response data
console.log(sections[0].name);
/*
Introduction
*/
}
catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
}
main();if a token param is provided, it will override the token supplied when instantiating the api
import MoodleApi, { MoodleClient } from "moodle-webservice";
const moodle = MoodleApi({
baseUrl: "https://moodle.example.com",
token: "exppsBdQwLvNwYRoAuaiBO5j0aWTzxU6",
});
moodle.core.webservice
.getSiteInfo({ token: "37512512c24112b1235cc123f821bd27cd" }) //<-- This token will be used instead
.then((res) => console.log(res))
.catch((err) => console.error(err.message));
moodle.config.token = "37512512c24112b1235cc123f821bd27cd"; //<-- You can also do this.
//..many function calls with the same token above.Intellisense + Typechecking
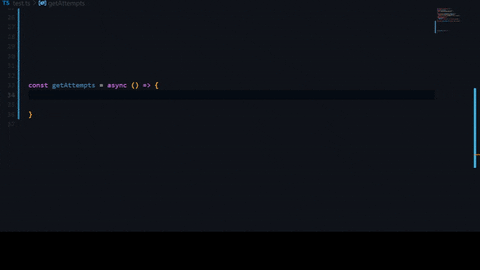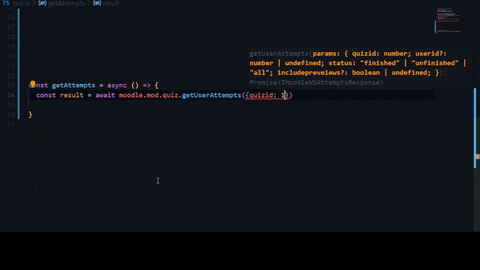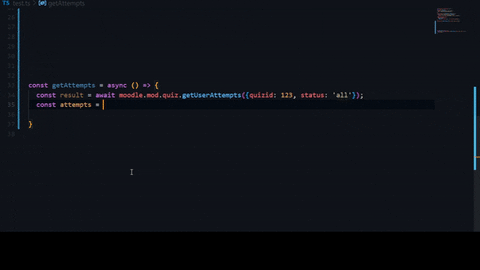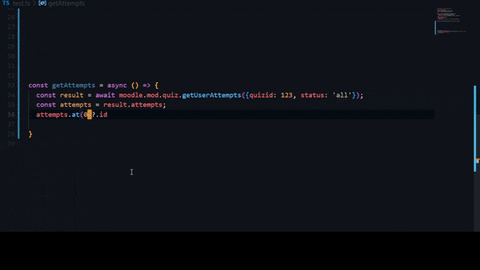
Getting your api token.
if you don't immediately have your token to pass to the api you can import MoodleClient directly and use the authenticate method to get one.
import MoodleApi, { MoodleClient } from "moodle-webservice";
const YOUR_WEBSITE_URL = "https://moodle.example.com";
//No token provided beforehand
const moodle = MoodleApi({
baseUrl: YOUR_WEBSITE_URL, //<-- Put your Moodle URL here
});
async function main() {
try {
//result type of IMoodleWSAuthResponse
const { token } = await MoodleClient.authenticate({
baseUrl: YOUR_WEBSITE_URL,
credentials: { username: "AwesomeJohn", password: "SmartPa33word" },
});
moodle.config.token = token;
const { fullname: firstName } = await moodle.core.webservice.getSiteInfo();
/*
logs:
John Smith
*/
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
}
main();Helper classes
The moodle webservice has some caveats here and there such as how when getting an attempt
moodle doesn't send you all the raw question data, instead some is raw data while other is
the rendered HTML question element.
moodle-webservice aims to solve that by providing a number of helper classes such as MoodleAttempt , these are abstract classes that have a number of functions that aim to solve
these issues.
import MoodleApi, { MoodleAttempt } from "moodle-webservice";
const moodle = MoodleApi({
baseUrl: "https://moodle.example.com",
token: "375208h132h1222h20h202b823b227cd",
});
moodle.mod.quiz.getAttemptReview({ attemptid: 3665103 }).then((res) => {
const questions = res.questions; //<-- of type IMoodleQuestion[].
//IMoodleQuestion does not contain the actual question text or choices.
questions[0].text; //<-- Error no such property on questions
const parsedReview = MoodleAttempt.parse(res);
const parsedQuestions = parsedReview.questions; //<-- of type IMoodleParsedQuestion[].
//IMoodleParsedQuestion contains additional data such as the name, instance number, and choices
console.log(parsedQuestions[0].text);
//Output: "The muscles of facial expression are supplied by the ____ nerve."
});or parse a single question
import MoodleApi, { MoodleQuestion } from "moodle-webservice";
const moodle = MoodleApi({
baseUrl: "https://moodle.example.com",
token: "375208h132h1222h20h202b823b227cd",
});
moodle.mod.quiz.getAttemptReview({ attemptid: 3665103 }).then((res) => {
const questions = res.questions; //<-- of type IMoodleQuestion[].
//IMoodleQuestion does not contain the actual question text or choices.
questions[0].text; //<-- Error no such property on questions
//IMoodleParsedQuestion contains additional data such as the name, instance number and choices
const parsedQuestion = MoodleQuestion.parse(questions[0]); //<-- of type IMoodleParsedQuestion.
console.log(parsedQuestion.text);
//Output: "The muscles of facial expression are supplied by the ____ nerve."
});JSON to form data
Moodle has a peculiar way of specifying request parameters. Parameters can either be sent in URL query string or POST form body.
Thus a JSON object needs to be converted to form data
{
"users": [
{
"firstname": "Foo",
"lastname": "Bar",
"username": "foo",
"password": "FooBar123!",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
]
}As Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
users[0][firstname]=Foo&users[0][lastname]=Bar&users[0][username]=foo&users[0][password]=FooBar123%21&users[0][email]=foo%40email.comTo perform the conversion in the code invoke the flatten function
import { MoodleClient } from "moodle-webservice";
const form = MoodleClient.flatten({
users: [
{
firstname: "Foo",
lastname: "Bar",
username: "foo",
password: "FooBar123!",
email: "[email protected]",
},
],
});
console.log(form); //users[0][firstname]=Foo&users[0][lastname]=Bar...However, there is no need to invoke the function outside the code as anything passed as data parameter to api functions is automatically flattened and formatted in the right way.
List of functions
Offical list of functions can be found at Web service API functions
The following table represents mapping between JavaScript function names and Moodle Web Service function names.
| JS function | API function | Description | | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------- | | auth.email.getSignupSettings(data) | auth_email_get_signup_settings | Get the signup required settings and profile fields. | | auth.email.signupUser(data) | auth_email_signup_user | Adds a new user (pendingto be confirmed) in the site. | | core.user.createUsers(data) | core_user_create_users | Create users - admin function | | core.webservice.getSiteInfo(data) | core_webservice_get_site_info | Return some site info / user info / list web service functions | | Read more... | | |
Note that the data argument is not always required and can be omitted.
Note regarding types
Due to poor moodle webservice function documentation not all functions have definite parameter types
and instead have IMoodleWSParams as its parameter type and any as its return type.
I've added types for the most important functions first, and I'll keep adding more as I go, contact me if you want to add types for a function that you know about.
