linear-gradient-taro
v1.0.1
Published
linear gradient fro taro
Downloads
96
Readme
Linear Gradient Taro
linear gradient fro taro, reference react-native-linear-gradient & react-native-web-linear-gradient add web and miniprogram support. the documentation modified from project react-native-linear-gradient.
Table of Contents
Installation
Using Yarn
yarn add linear-gradient-taroUsing npm
npm install linear-gradient-taro --saveWith React Native >= 0.60
Run npx pod-install
Simple
The following code will produce something like this:
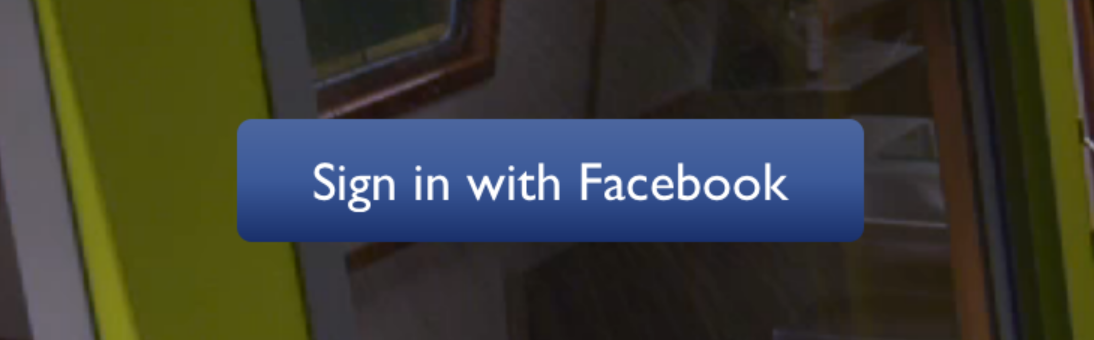
import LinearGradient from 'linear-gradient-taro';
// Within your render function
<LinearGradient colors={['#4c669f', '#3b5998', '#192f6a']}>
<Text>
Sign in with Facebook
</Text>
</LinearGradient>Horizontal gradient
Using the styles from above, set start and end like this to make the gradient go from left to right, instead of from top to bottom:
<LinearGradient start={{x: 0, y: 0}} end={{x: 1, y: 0}} colors={['#4c669f', '#3b5998', '#192f6a']}>
<Text>
Sign in with Facebook
</Text>
</LinearGradient>Animated Gradient
Check out Examples/AnimatedGradient (git clone this project, cd into it, npm install, open in Xcode and run) to see how this is done:
This gif was created using licecap - a great piece of free OSS
Transparent Gradient
The use of transparent color will most likely not lead to the expected result. transparent is actually a transparent black color (rgba(0, 0, 0, 0)). If you need a gradient in which the color is "fading", you need to have the same color with changing alpha channel. Example:
// RGBA
<LinearGradient colors={['rgba(255, 255, 255, 0)', 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 1)']} {...otherGradientProps} />
// Hex
<LinearGradient colors={['#FFFFFF00', '#FFFFFF']} {...otherGradientProps} />Props
In addition to regular View props, you can also provide additional props to customize your gradient look:
colors
An array of at least two color values that represent gradient colors. Example: ['red', 'blue'] sets gradient from red to blue.
start
An optional object of the following type: { x: number, y: number }. Coordinates declare the position that the gradient starts at, as a fraction of the overall size of the gradient, starting from the top left corner. Example: { x: 0.1, y: 0.1 } means that the gradient will start 10% from the top and 10% from the left.
end
Same as start, but for the end of the gradient.
locations
An optional array of numbers defining the location of each gradient color stop, mapping to the color with the same index in colors prop. Example: [0.1, 0.75, 1] means that first color will take 0% - 10%, second color will take 10% - 75% and finally third color will occupy 75% - 100%.
<LinearGradient
start={{x: 0.0, y: 0.25}} end={{x: 0.5, y: 1.0}}
locations={[0,0.5,0.6]}
colors={['#4c669f', '#3b5998', '#192f6a']}
>
<Text>
Sign in with Facebook
</Text>
</LinearGradient>
useAngle / angle / angleCenter
You may want to achieve an angled gradient effect, similar to those in image editors like Photoshop. One issue is that you have to calculate the angle based on the view's size, which only happens asynchronously and will cause unwanted flickr.
In order to do that correctly you can set { useAngle: true, angle: 45, angleCenter: { x: 0.5, y: 0.5} }, to achieve a gradient with a 45 degrees angle, with its center positioned in the view's exact center.
useAngle is used to turn on/off angle based calculation (as opposed to start/end).
angle is the angle in degrees.
angleCenter is the center point of the angle (will control the weight and stretch of the gradient like it does in photoshop.
