kinematics-js
v1.0.8
Published
A forward and inverse kinematics package for a basic 6 axis robotic arm.
Downloads
55
Maintainers
Readme
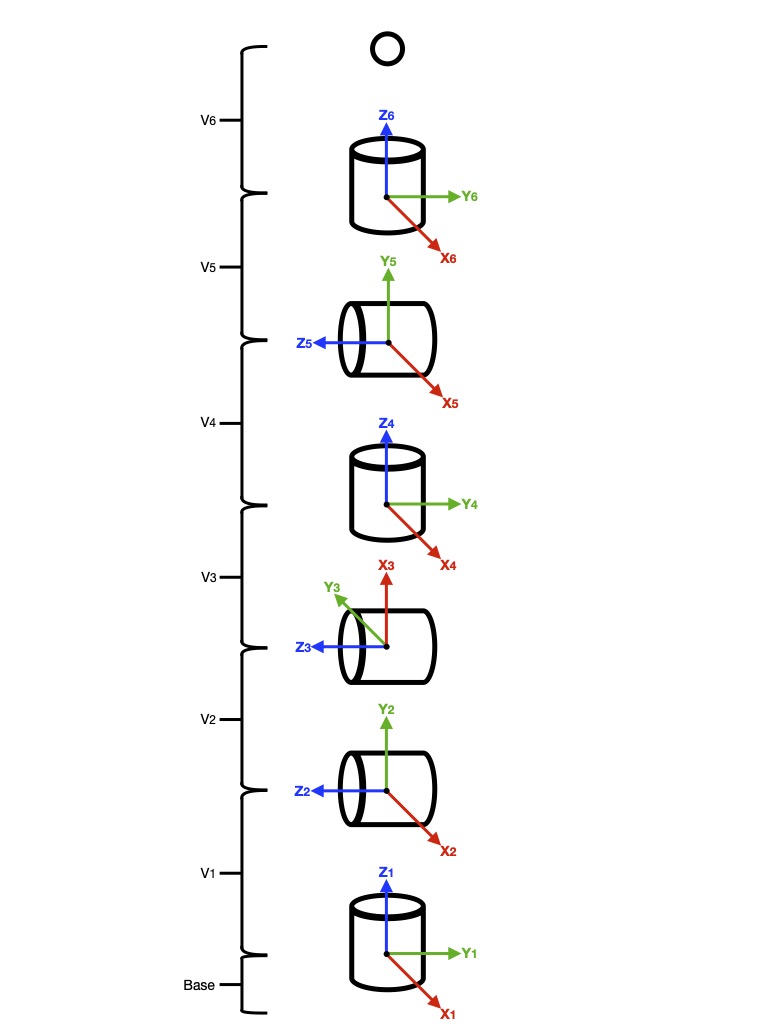
Kinematics.js
A forward and inverse kinematics package for a basic 6 axis robotic arm.
Inverse
import { inverse } from 'kinematics-js';
inverse(5, 0, 11, 0, 0, 0, {
base: 1,
v1: 2.5,
v2: 3,
v3: 2.5,
v4: 2.5,
v5: 2.5,
v6: 2,
});| Parameter | Description | | --------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | x | x cartesian coordinate in the three dimensional space relative to the base frame | | y | y cartesian coordinate in the three dimensional space relative to the base frame | | z | z cartesian coordinate in the three dimensional space relative to the base frame | | r1 | euler angle 1, the rotation around the z1 axis of the end effector | | r2 | euler angle 2, the rotation around the x axis of the end effector | | r3 | euler angle 3, the rotation around the z2 axis of the end effector | | config | robot configuration see table below |
| Key | required | Description | | ---- | -------- | ------------------------------------------- | | base | no | height of the base | | v1 | yes | length between joint 1 and 2 | | v2 | yes | length between joint 2 and 3 | | v3 | yes | length between joint 3 and 4 | | v4 | yes | length between joint 4 and 5 | | v5 | yes | length between joint 5 and 6 | | v6 | yes | length between joint 6 and the end effector |
Examples:
// First define a config for the robot
const config == {
v1: 2.5,
v2: 3,
v3: 2.5,
v4: 2.5,
v5: 2.5,
v6: 2,
};
/**
* |
* [ ]
* |
* ( )
* |
* [ ]
* |
* ( )
* |
* ( )
* |
* [ ]
*/
inverse(0, 0, 15, 0, 0, 0, config)
// ==> [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
/**
* [ ]
* |
* ( ) -- [ ] -- ( )
* |
* ( )
* |
* [ ]
*/
inverse(5, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0, config)
// ==> [0, 0, -Math.PI / 2, 0, Math.PI / 2, 0 ]
/**
* [ ]
* |
* ( ) -- [ ] -- ( )
* |
* ( )
* |
* [ ]
*/
inverse(5, 0, 11, 0, 0, 0, { ...config, base: 1 })
// ==> [0, 0, -Math.PI / 2, 0, Math.PI / 2, 0 ]Forward
import { forward } from 'kinematics-js';
forward(0, 0, -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI, -Math.PI / 2, 0, {
v1: 2.5,
v2: 3,
v3: 2.5,
v4: 2.5,
v5: 2.5,
v6: 2,
});
// ==>
// [-1, 0, 0, 5],
// [0, -1, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 1, 10],
// [0, 0, 0, 1],
//
// The return value gives you the rotation matrix and also the cartesian location which you can get below
// const x = res[0][3];
// const y = res[1][3];
// const z = res[2][3];| Parameter | Description | | --------- | ----------------------------------- | | theta1 | angle of joint j1 in radians | | theta2 | angle of joint j2 in radians | | theta3 | angle of joint j3 in radians | | theta4 | angle of joint j4 in radians | | theta5 | angle of joint j5 in radians | | theta6 | angle of joint j6 in radians | | config | robot configuration see table below |
| Key | required | Description | | ---- | -------- | ------------------------------------------- | | base | no | height of the base | | v1 | yes | length between joint 1 and 2 | | v2 | yes | length between joint 2 and 3 | | v3 | yes | length between joint 3 and 4 | | v4 | yes | length between joint 4 and 5 | | v5 | yes | length between joint 5 and 6 | | v6 | yes | length between joint 6 and the end effector |
Live Demo
See the kinematics in action here
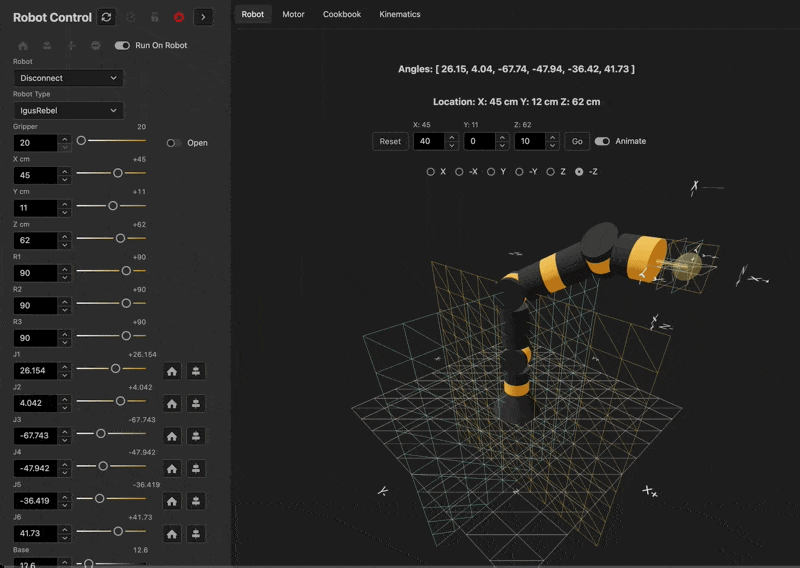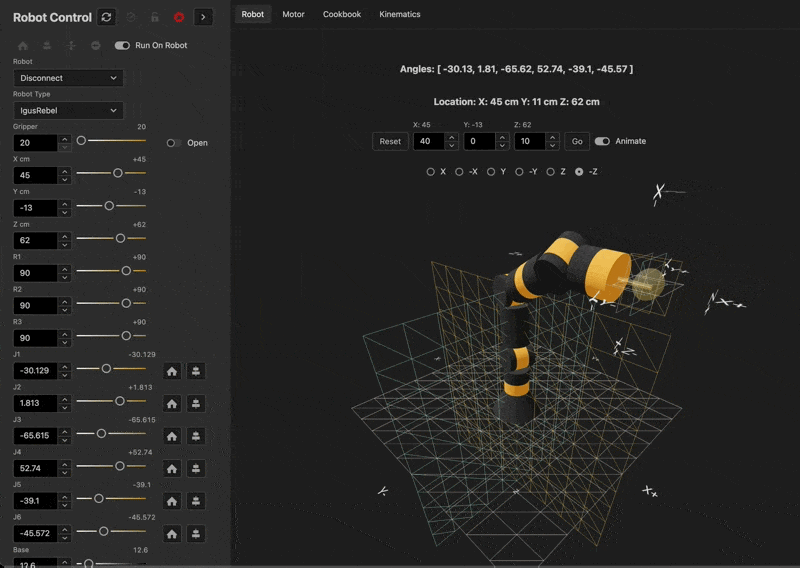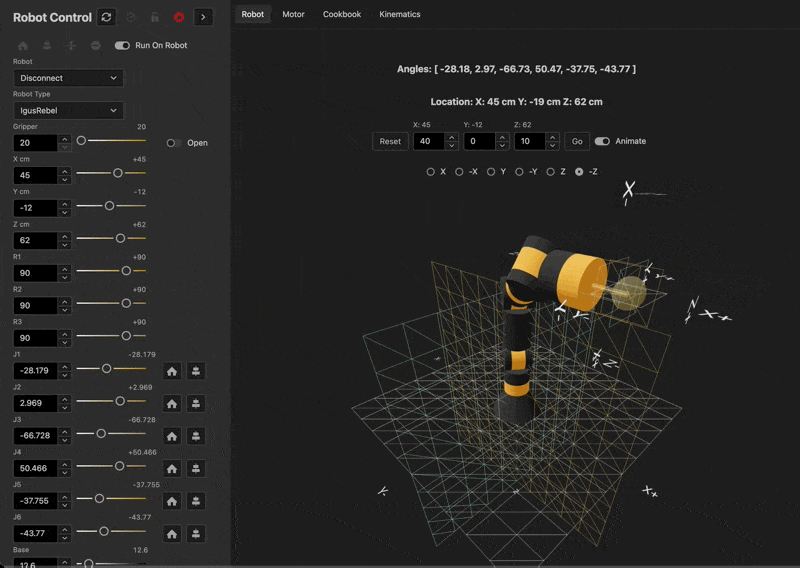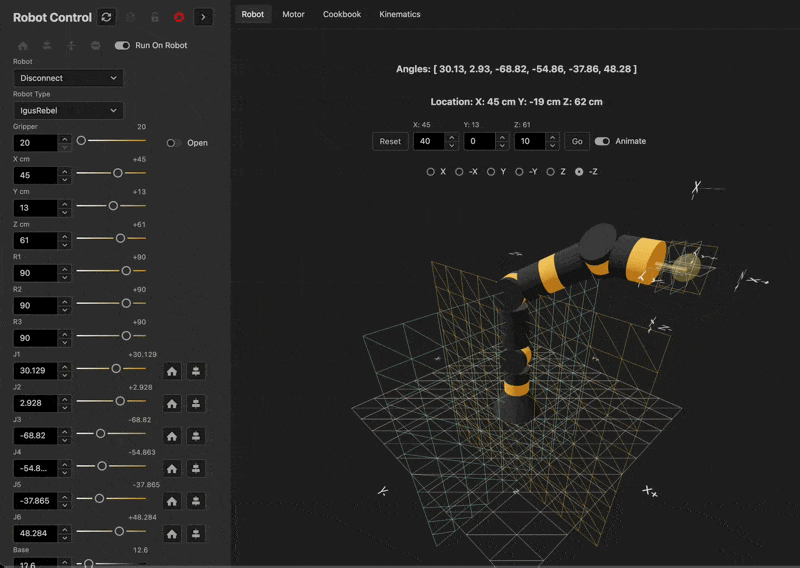
Kinematics Diagram