hue.ts
v0.6.0
Published
A powerful library to interact with the Hue API
Downloads
22
Readme
⚠️ Library is under construction and may not work as expected
About
hue.ts is a node module that allows you to easily interact with the hue API (V2).
- Object-oriented
- Written in TypeScript
- Future 100%-coverage of the hue API (v2)
Installation
⚠️ Hue bridge version 1948086000 or newer is required: You can find your bridge's version in the hue app, Settings -> My Hue system -> Select your bridge -> Software
npm install hue.tsExample usage
This examples goal is to create a new zone, and adding a scene to this zone.
npm install hue.tsBefore connecting to your hue bridge, its ip address and an application key are required. The ip address can be found in the Hue app at Settings -> My hue system -> Select your bridge -> IP After, an application key can be acquired by the following method:
- Open your browser and go to
https://<bridge ip address>/debug/clip.html - Next fill in the options below: URL: /api BODY: {"devicetype":"some-random-name"}
- Press the POST button
- Go click the button on your Hue bridge
- Press the POST button again
- You should now see something like
{ success: { username: 'some-key' } }
For more information on retrieving this key visit: https://developers.meethue.com/develop/hue-api-v2/getting-started/
import { Hue, ArcheType, SceneAction } from 'hue.ts';
// Create new Hue, with the ip address and application key
const hue = new Hue({
connection: {
ip: 'some-ip',
applicationKey: 'some-key',
},
});
// Listen to the 'ready' event, which is emitted when the socket has connected and cached all resources
hue.on('ready', async () => {
// Get the lights we want in the new zone
const light1 = hue.lights.cache.find((light) => light.name == 'Demo Light 1')!;
const light2 = hue.lights.cache.find((light) => light.name == 'Demo Light 2')!;
// Create the zone
await hue.zones.create({
name: 'Demo',
archeType: ArcheType.ManCave,
children: [light1.id, light2.id],
});
});
// Listen to the 'zoneAdd' event, emitted on creation of a new zone
hue.on('zoneAdd', async (zone) => {
// Ignore if the zone is not the one created above
if (zone.name !== 'Demo') return;
// Find the lights belonging to the zone again, in this case these will be Demo Light 1 & Demo Light 2
const lights = hue.lights.cache.filter((light) => zone.childIds.includes(light.id));
// Make the actions
const actions = lights.map((light) => {
const action: SceneAction = {
id: light.id,
on: true,
};
// Check if the light can do dimming, and if so, set the brightness of the light to 50%
if (light.isCapableOfDimming()) action.brightness = 50;
// Check if the light can display color, and if so, set the color to #eb403
if (light.isCapableOfColor()) action.color = fromHex('#eb403');
return action;
});
// Create the scene
await zone.createScene({
name: 'Awesome scene',
actions,
});
});
// Listen to the sceneAdd event, emitted on creation of a new scene
hue.on('sceneAdd', async (scene) => {
// Ignore if not the scene just created above
if (scene.name !== 'Awesome scene') return;
// Recall the scene
await scene.recall();
});Colors
Colors... get more complicated. The hue system uses the C.I.E. color representation. This representation is a 2D-colored diagram.
This also means, to get a color of this diagram, a coordinate (position on the horizontal and vertical axes) is needed.
A color is therefor represented as { x: number; y: number }. Where x is the horizontal placement and y the vertical.
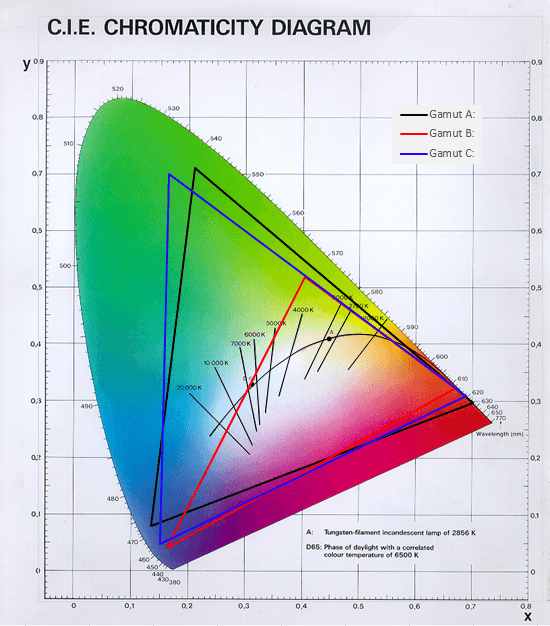
As this is a sort of 'non-standard' color representation, utility functions are provided to convert a rgb/hex value to C.I.E.
const xy = fromHex('#eb4034');
await light.setColor(xy);const xy = fromRGB({
red: 235,
green: 64,
blue: 52,
});
await light.setColor(xy);const hex = toHex(light.color);const rgb = toRGB(light.color);As also visible in the C.I.E. above, defined by the triangles, there is a limit to what the light is able to display. Because of that, there might be a difference of your input and the color of the light. In order to calculate the color the light is currently showing, the following method can be used.
const xy = light.colorToRange(light.color);
const hex = toHex(xy);Links
Help
For questions or issues, please open an issue on our github page.





