http-request-mock
v2.0.2
Published
Intercept & mock http requests issued by XMLHttpRequest, fetch, nodejs https/http module, axios, jquery, superagent, ky, node-fetch, request, got or any other request libraries by intercepting XMLHttpRequest, fetch and nodejs native requests in low level.
Downloads
189,631
Maintainers
Keywords
Readme
English | 中文
http-request-mock 
Full documentation: https://huturen.github.io/http-request-mock-docs/
A quick demo: https://huturen.github.io/http-request-mock-docs/plain-html/
A CURD demo: https://huturen.github.io/http-request-mock-curd/
It mocks http requests issued by axios, jquery, superagent, node-fetch, got, (… you name it) by intercepting XMLHttpRequest, fetch, and nodejs native HTTP/HTTPS module requests at the low level.
- XMLHttpRequest
- fetch
- https.request, https.get (nodejs native https request)
- http.request, http.get (nodejs native http request)
- wx.request (for mini program in Wechat)
Because of the low-level interception, any 3th-party request libraries that based on the above requests can also be supported, such as:
axios, jquery, superagent, ky, node-fetch, got, request ...
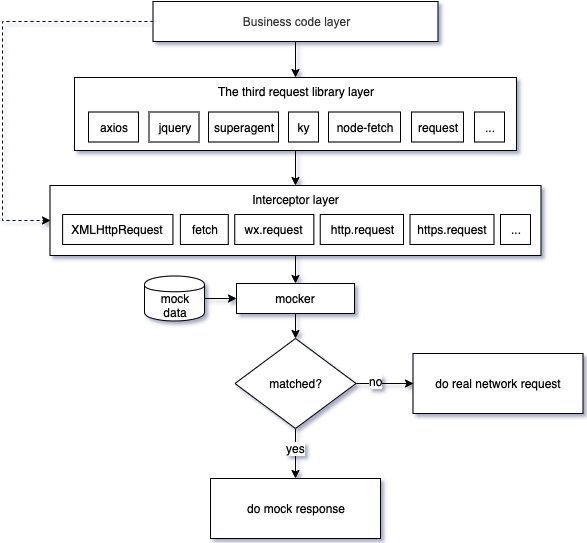
It differs from the other mocking libraries in that it provides a webpack plugin and command line tool to separate mock data from your business code. It's a truly non-hacking mocking library. You never have to hack into your business code to mock something ever again after a one-time configuration.
A simple integration case with vue3:
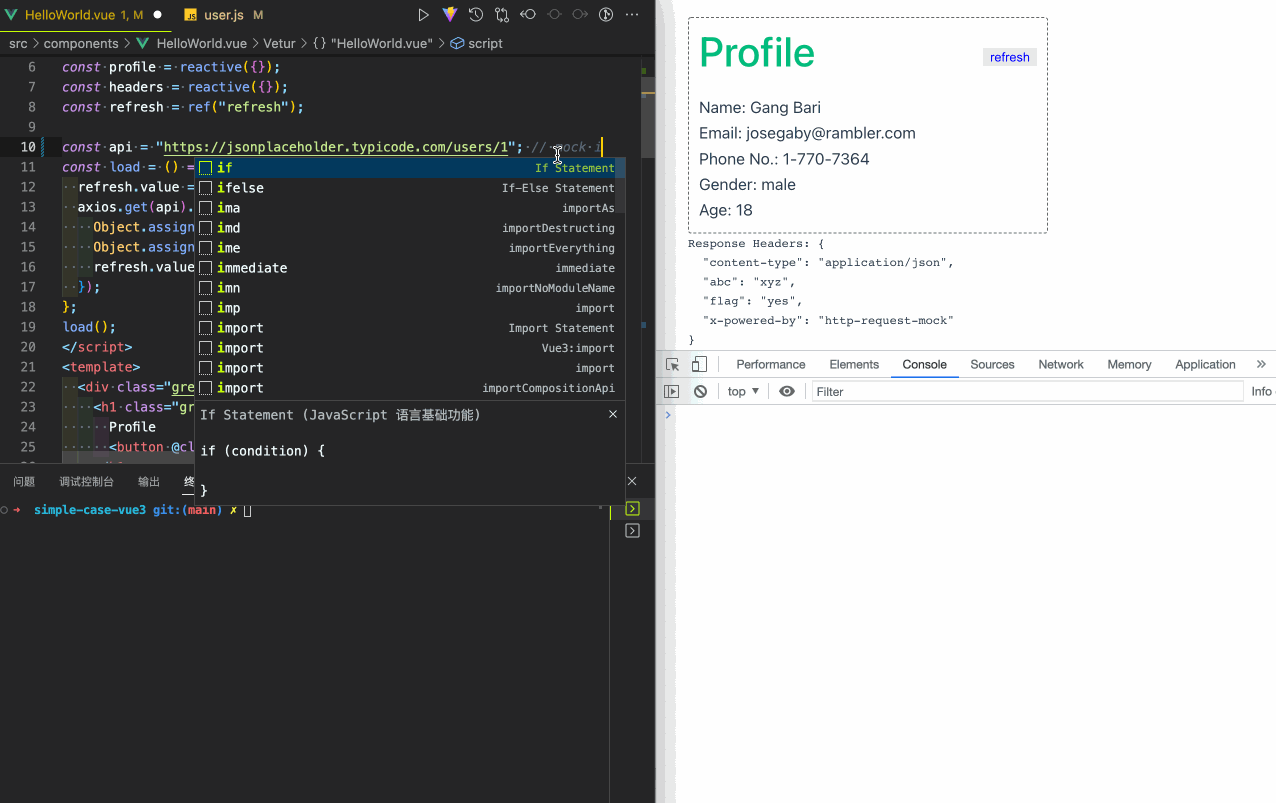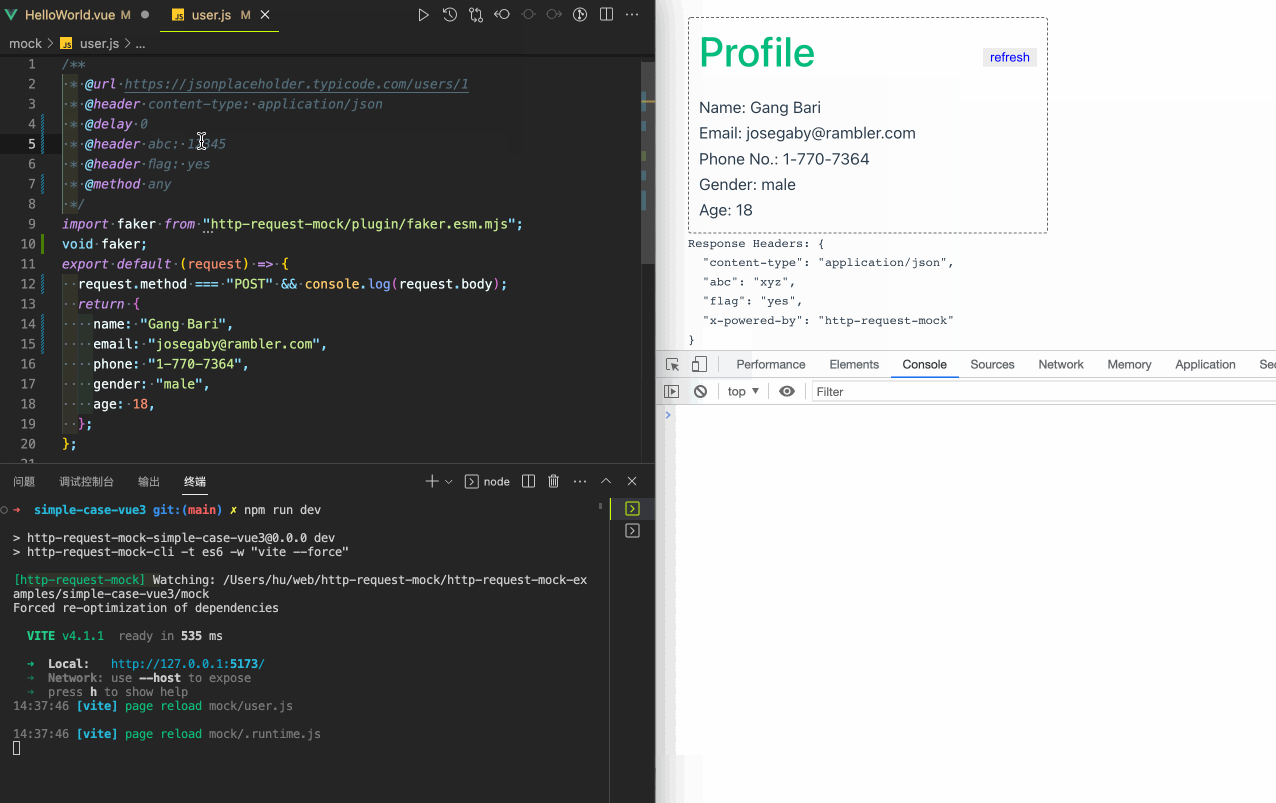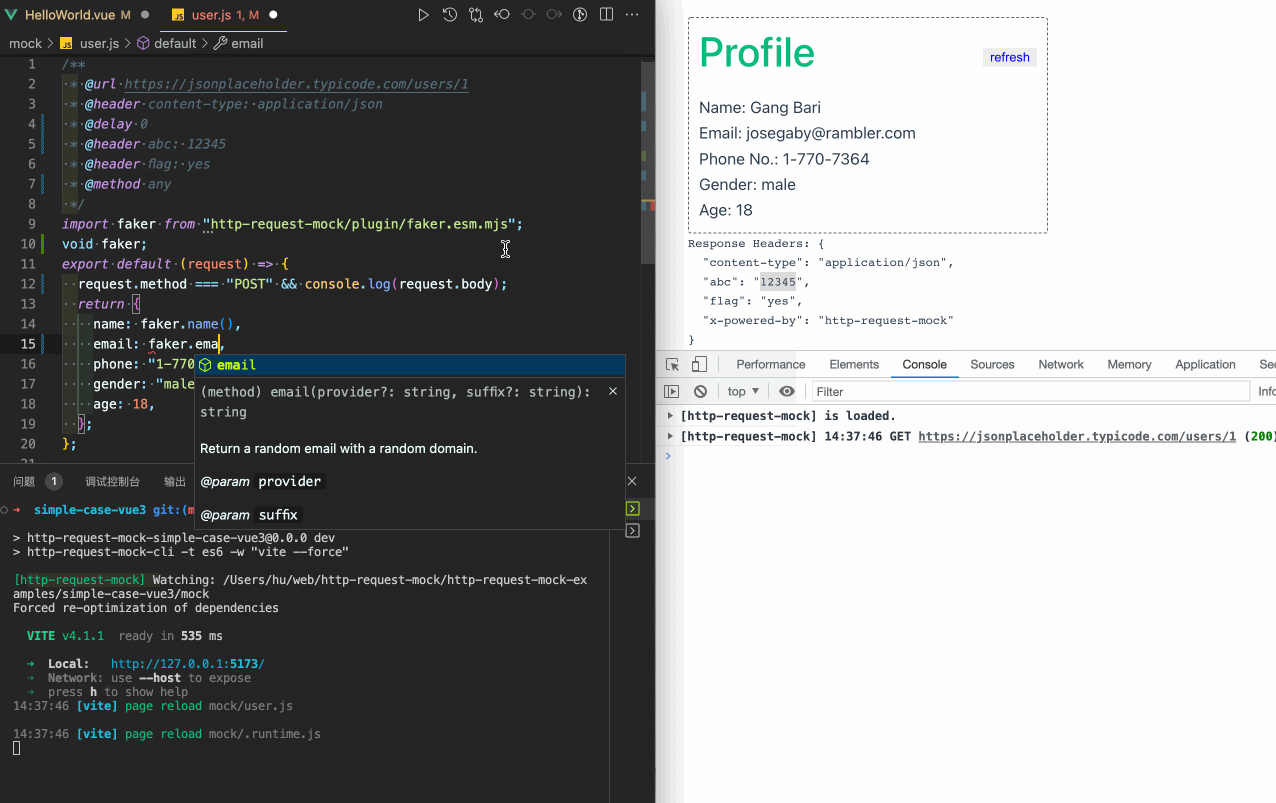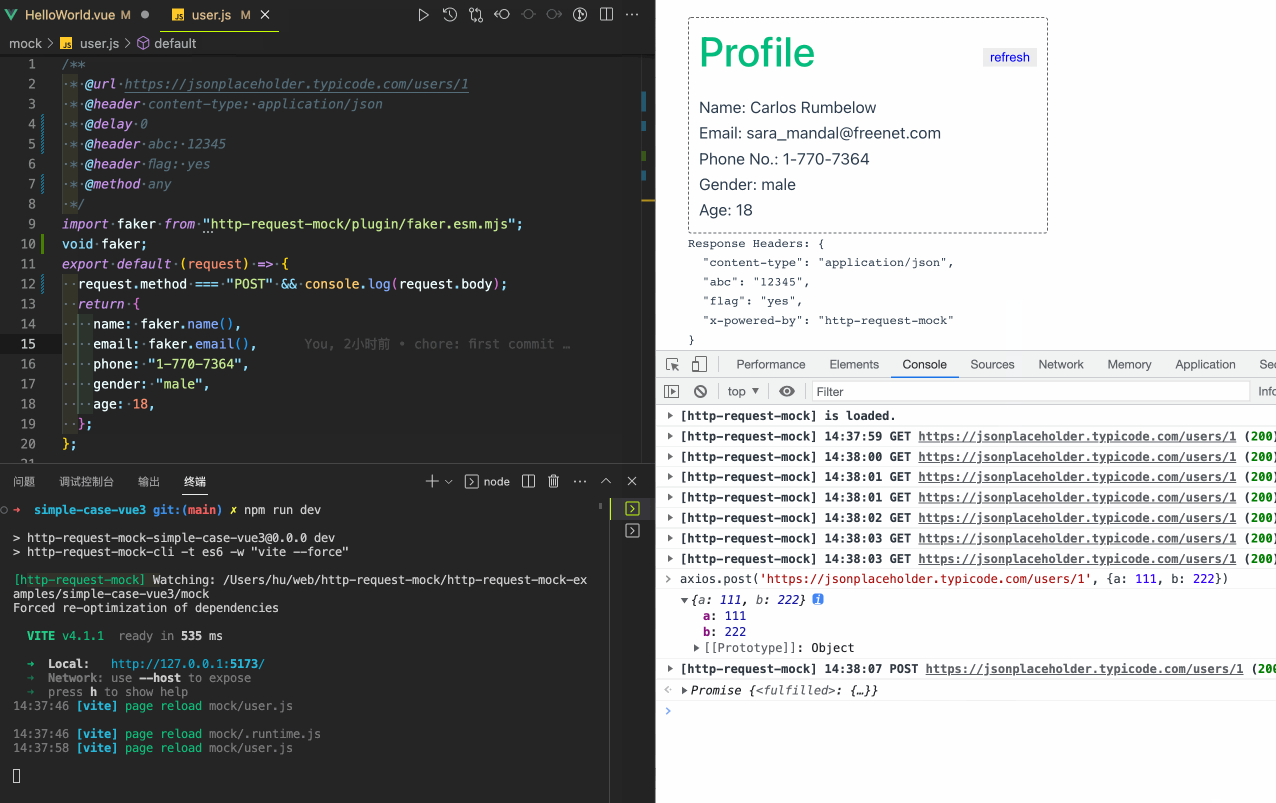 Get the source code of the above case. More integration cases.
Get the source code of the above case. More integration cases.
Table of Contents
- Introduction And Motivation
- Features
- Installation
- Examples
- Integration
- Command Line Tool Options
- API
- Unit test
- Mock data file
- FAQ
- License
Introduction And Motivation
http-request-mock is an http request mocking library that lets you develop, build and test as normal even when
backend APIs are down or not ready yet. It supplies a new way to prototype your web application.
The original intention of making this library was to find a mocking library to decouple from backend. However, we can't find a library that meets our requirements. Some libraries have occupied the most readable names, but they provide weak functionalities or even no longer provide any updates .
There are some problems you may encounter when using the other mocking libraries:
- You may have to hack your source code to mock something and revert it back to restore normal after mocking.
- You may involve complex setups, such as all kinds of proxies, http servers.
- Not all in one, some library only for
XMLHttpRequest, some library only forfetch. - No updates, hard to set up and a lot of bugs.
Features
- Business-code-unaware: Does not interfere with code writing. Keep your code unaware of whether something is mocked or not.
- Interceptor: It can be used as an interceptor. You can decide how to handle requests.
- All in one: XMLHttpRequest, fetch, https.get, http.get, https.request, http.request, and wx.request.
- More 3rd-party libraries support: It supports axios, jquery, superagent, ky, node-fetch, got, (you name it).
- Unit test capability: It can be worked in jest, mocha, and ava environments.
- Dynamic mocking: Dynamically resolve response based on request query, payloads...
- Flexible route matching: Supports RegExp matching and partial string matching.
- Delaying mocking: Support for simulating network latency.
- Fake data: Easy to generate massive amounts of fake data.
- Complete unit tests: It has complete unit tests including the 3th-party request libraries.
- Remote: Support for using remote mock data, where you can dynamically modify the data returned from the remote.
Installation
NPM:
npm install --save-dev http-request-mock
// using ES6 modules
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
// using CommonJS modules
const HttpRequestMock = require('http-request-mock');CDN:
The UMD build is also available on unpkg:
<!-- unpkg -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/http-request-mock/http-request-mock.js"></script>You can find the library on window.HttpRequestMock.
Examples
Usage
To mock an http request, just call a mock method or http verb method(get,post,put,patch,delete).
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
mocker.mock({
url: 'www.api.com/some-api' // or RegExp: /.*\/some-api$/
method: 'get', // get, post, put, patch or delete
delay: 0,
status: 200,
headers: { // respone headers
'content-type': 'application/json',
'some-header': 'value',
},
body: 'some response data'
});
// or using http verb method:
mocker.get('www.api.com/some-api', 'some response data');Static response
// mock configuration:
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
mocker.get('https://www.api.com/text-response', '<html>mock response content</html>');
mocker.post('https://www.api.com/json-response', { ret: 0, msg: 'ok' });
// issue some requests:
...
const text = await axios.get('https://www.api.com/text-response');
const json = await axios.post('https://www.api.com/json-response', null, { responseType: 'json' });
console.log(text); // <html>mock response content</html>
console.log(json); // { ret: 0, msg: 'ok' }
...Dynamic response
You can export a function instead of an object to resolve a dynamic response, so as to simulate a complex business logic in the real world.
// mock configuration:
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
let times = 0;
// requestInfo: please refer to < RequestInfo > in src/types.ts
mocker.get('https://www.api.com/dynamic-response', (requestInfo) => {
times = times + 1;
return { times: 'times: ' + times, url: requestInfo.url };
});
// Note: the contents of url and times fields are different between the two requests below:
...
const res1 = await axios({ url: 'https://www.api.com/dynamic-response?a=1', responseType: 'json' });
const res2 = await axios({ url: 'https://www.api.com/dynamic-response?b=2', responseType: 'json' });
console.log(res1); // { times: 'times: 1', url: 'https://www.api.com/dynamic-response?a=1' }
console.log(res2); // { times: 'times: 2', url: 'https://www.api.com/dynamic-response?b=2' }
...Delay
// configuration
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
mocker.mock({
url: 'https://some.api.com/name',
method: 'get',
delay: 3000 // the response will be resolved in 3 seconds
});
// issue a request:
let time = Date.now();
axios.get('https://some.api.com/name').then(() => {
console.log(Date.now() - time); // >= 3000
});HTTP status
// configuration
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
mocker.mock({
url: 'www.api.com/status404',
status: 404,
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json',
'some-header': 'header-value',
}
});
// issue a request:
// Note: axios will throw an error when meets a 404 response
axios.get('https://www.api.com/status404').catch(err => {
console.log(err.message); // Request failed with status code 404
console.log(err.response.status); // 404
console.log(err.response.headers['some-header']); // header-value
});Disable a mock item
For more details, please refer to experiment/disable.js.
// configuration
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
const mockItem = mocker.mock({
url: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1',
method: 'any',
body: {mock: 'some response data'}
});
(async () => {
const res1 = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1');
console.log('res1:', res1.data); // it'll resolve a response from mocking.
mockItem.disable = 'yes';
const res2 = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1');
console.log('res2:', res2.data); // it'll resolve a response from real network request.
})();
// res1: { mock: 'some response data' }
// res2: { userId: 1, id: 1, title: 'delectus aut autem', completed: false }Limited number of mocking
For more details, please refer to experiment/times.js:
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup();
mocker.mock({
url: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1',
method: 'any',
times: 2,
body: {mock: 'some response data'}
});
(async () => {
let i = 0;
await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1').then(res => {
console.log(++i, 'res:', res.data);
});
await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1').then(res => {
console.log(++i, 'res:', res.data);
});
await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1').then(res => {
console.log(++i, 'res:', res.data);
});
})();
// 1 res: { mock: 'some response data' }
// 2 res: { mock: 'some response data' }
// 3 res: { userId: 1, id: 1, title: 'delectus aut autem', completed: false }Request information
mocker.mock({
url: 'https://www.api.com/reqinfo',
response(requestInfo) {
return requestInfo;
}
});
axios.post('https://www.api.com/reqinfo?abc=123', {xyz: 456}, {responseType: 'json'}).then(res => {
console.log('info:', res.data);
});
// output may look like below:
// info: {
// "url": "https://www.api.com/reqinfo?abc=123",
// "method": "POST",
// "query": {
// "abc": "123"
// },
// "headers": {
// "Accept": "application/json, text/plain, */*",
// "Content-Type": "application/json;charset=utf-8"
// },
// "body": {
// "xyz": 456
// }
// }Interceptor
You can intercept a request, do something, then make the original call and capture the response and do something again. For more detailed discussions about the interceptor, please refer to this issue.
// mock case
mocker.mock({
url: '//jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/',
response: async function(requestInfo) {
// 1. intercept a request, do something (here, output the original request information)
console.log('original request info: ', requestInfo);
// 2. then make the original call and capture the response
const res = await requestInfo.doOriginalCall();
// 3. and do something again.
console.log('original response:', res);
return { code: 0, msg: 'ok', data: res.responseJson };
}
});
// issue a request
axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/photos/1').then(res => console.log(res.data));Integration
In a bare-bones example, you just import http-request-mock into your application
entry file(such as: src/main.js) and configure your mock datas there.
Take a Vue project as an example:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock'
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setup()
mocker.get('https://some.api.com/some-path', ...)
mocker.post('https://some.api.com/other-path', ...)
...
}
createApp(App).mount('#app')It may be ok in a small project, however, for a large web application, it may have lots of APIs to be mocked. You may need frequently change the entry file when adding/deleting/updating a mock data. There will be a day that you'll get a mess as the project grows.
In order to solve the problem above, we provide a webpack plugin and command tool to integrate your project. In this way, the mock data file can be separated from the entry to reduce the burden of managing this entry file.
Integration By Webpack plugin
You can set it up by the steps below:
- Run
npx http-request-mock-cli -i. It'll initialize some samples in your mock directory. - Configure
HttpRequestMockWebpackPluginin your webpack configurations, which looks like below.
const path = require('path');
// The webpack plugin will parse mock files under the mock directory and generate a mock
// configuration entry file named `.runtime.js`, then inject it into the your application entry file.
const HttpRequestMockWebpackPlugin = require('http-request-mock/plugin/webpack.js');
module.exports = {
// ...
plugins: [
new HttpRequestMockWebpackPlugin(
enable: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development', // activate/deactivate
entry: /src\/main\.js$/, // web application entry
dir: path.resolve(__dirname, 'mock/'), // mock directory
),
]
// ...
};- In your package.json, set a command named
mock-devto start a mock development:
"scripts": {
"dev": "npm run start",
"mock-dev": "NODE_ENV=development npm run start"
},Webpack Plugin options
| Option | Required | Description | | :----- | :---- | :---- | | entry | yes | Application entry file, must be a Regexp object | | dir | yes | Mock directory | | enable | no | Whether or not to enable this plugin, default: true | | watch | no | A callback that is triggered when a mock data file is changed | | proxyMode | no | Proxy mode. Valid values: marked |
Integration By Command Line Tool
An alternative way to integrate with your project is using CLI. You can set it up by the steps below:
- Run
npx http-request-mock-cli -j src/xxx.jsto inject mock configuration file into the specified entry which may look like below:
import '../mock/.runtime.js'
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// ...
createApp(App).mount('#app')- In your package.json, set a command named
mock-devto start a mock development:
"scripts": {
"serve": "vue-cli-service serve",
"mock-dev": "http-request-mock-cli -w \"vue-cli-service serve\"",
},The command passed into http-request-mock-cli -w must be quoted with double quotes.
Note:
If -e --environment is not specified, mock function will be enabled by NODE_ENV=development.
Or, you can specify another environment variable, such as: -e MOCK=yes.
Command Line Tool Options
npx http-request-mock-cli -h:
Usage: npx http-request-mock-cli [options]
Description: http-request-mock command line tool at version 1.6.8.
Glossary: [.runtime.js] A runtime mock configuration entry file.
Example:
npx http-request-mock-cli -i
Options:
-d, --directory [directory] The mock directory relative to the working directory. (default: "mock")
-e, --environment [variable-pair] Enable mock function by environment variable for .runtime.js.
(default: "NODE_ENV=development")
-i, --init Initialize some samples & a .runtime.js in the mock directory.
-w, --watch [command] Watch mock directory & update .runtime.js. If the [command] is specified,
ths specified command will be executed together with watching.
-j, --inject <app-entry-file> Inject .runtime.js into the specified entry relative to the working directory.
-t, --type [module-type] The module type of .runtime.js.
Possible values are: es6(alias of ESM), cjs(alias of commonjs).
(default: "cjs")
--index [index-entry] Index entry, automatic detection by default.
Possible values are: src/index.js, http-request-mock.js and http-request-mock.esm.mjs.
[src/index.js] for commonJS
[http-request-mock.js] for UMD
[http-request-mock.pure.js] An alternative version without faker and cache plugins for UMD.
[http-request-mock.esm.mjs] for ESM
[http-request-mock.pure.esm.mjs] An alternative version without faker and cache plugins for ESM.
-p, --proxy [mode] Proxy mode. In proxy mode, http-request-mock will start
a proxy server which receives incoming requests on localhost.
The mock files will be run in a nodejs environment.
This feature is designed for browser, so do not use it in a nodjs project.
Note: proxy mode is still under experimental stage, only for experts.
[matched] All requests matched by @url will be proxied to a proxy server. (default: "none")
-h, --help output usage informationAPI
For HttpRequestMock
setup() : Mocker:
Auto detect request environment and set up request mock.
setupForWx() : Mocker:
Set up request mock for wx.request.
setupForXhr() : Mocker:
Set up request mock for XMLHttpRequest.
setupForFetch() : Mocker:
Set up request mock for fetch.
setupForNode() : Mocker:
Set up request mock for http.get, https.get, http.request and https.request in nodejs envrioment.
setupForUnitTest() : Mocker:
Set up request mock for unit test.
enable() : Mocker:
Enable mock function temporarily.
disable() : Mocker:
Disable mock function temporarily.
For Mocker
setMockData(mockConfigData: MockConfigData)
Set global mock data configuration.
reset()
Reset global mock data configuration.
mock(mockItem: MockItemInfo)
Check specified mock item & add it to global mock data configuration.
interface MockItemInfo {
url: RegExp | string;
method?: HttpVerb; // GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE or HEAD
headers?: Header, // response headers
delay?: number;
disable?: Disable; // yes or no
times?: number;
body?: any; // response body
status?: number; // http status code
};get(url: RegExp | String, body: any, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP GET request.
interface MockItemExt {
headers?: Header, // response headers
disable?: Disable; // yes or no
delay?: number;
times?: number;
status?: number; // http status code
};post(url: RegExp | String, body: any, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP POST request.
put(url: RegExp | String, body: any, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP PUT request.
patch(url: RegExp | String, body: any, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP PATCH request.
delete(url: RegExp | String, body: any, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP DELETE request.
head(url: RegExp | String, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP HEAD request.
any(url: RegExp | String, body: any, opts: MockItemExt)
Make a mock item that matches an HTTP GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE or HEAD request.
Unit test
http-request-mock comes with built-in unit test capability and can be used in jest and mocha environments.
An example of jest:
import axios from 'axios';
import xhrAdapter from 'axios/lib/adapters/xhr';
import HttpRequestMock from 'http-request-mock';
axios.defaults.adapter = xhrAdapter;
const mocker = HttpRequestMock.setupForUnitTest('xhr');
mocker.get('https://your.api.com/path', function() {
return { abc: 123 };
});
it('should match object`', async () => {
const res = await axios.get('https://your.api.com/path');
expect(res.data).toMatchObject({abc: 123});
});Mock data file
/**
* Note: Only the first comments block will be parsed.
*
* The url to be mocked.
* Both string and RegExp(which begins and ends with # or /) are supported.
* RegExp example: #.*\/getUserInfo.*#
* @url https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1
*
* The request method to be mocked.
* One of http verb method get, post, put, patch, delete, head.
* Default: any
* @method any
*
* Response http status to be mocked.
* Default: 200
* @status 200
*
* Response http headers to be mocked.
* It can be set repeatedly.
* @headers content-type: application/json
*
* Request headers, request headers, only available for @remote tag
* It can be set repeatedly.
* @remoteRequestHeaders content-type: application/json
*
* Simulate network latency in milliseconds.
* Default: 0
* @delay 100
*
* Limited number of mocking.
* It'll do a real network request after specified number of mocking.
* Default: Infinity
* @times 5
*
* Whether or not to enable this mock item.
* 'yes' for real network request, 'no' for mock request.
* Default: no
* @disable no
*
* Remote mock data.
* In browser, the specified remote url must conform to the cross-domain specification.
* @remote https://remote.api.com/some/mock/data
*/
// Response body to be mocked.
// It supports to export an object, function, async function, sting or any other types.
// If a function is specified, the function accepts an argument with request information.
module.exports = (requestInfo) => {
return 'Your response data';
};FAQ
1. Cannot assign to read only property 'exports' of object '#' at Module.eval
Solution 1: You can avoid this issue by setting sourceType: unambiguous in your babel config file:
{ // babel.config.js or .babelrc.js
"presets": [...],
"plugins": [...],
sourceType: 'unambiguous'
}
Solution 2: set [type] option to es6. Note: es6 can't work with proxy mode, don't use es6 and proxy mode together.
a. If you are using cli to set up your http-request-mock:
http-request-mock-cli -t es6 -w "vue-cli-service serve"
b. If you are using webpack to set up your http-request-mock:
new HttpRequestMockPlugin({
...
type: 'cjs',
...
}),2. TypeError: webpack_require.r is not a function
Solution:
Change `require('http-request-mock')` to `require('http-request-mock/http-request-mock.js')`,
or change `import('http-request-mock')` to `import('http-request-mock/http-request-mock.js')` if you are using es6.Integration Cases:
Integration with vue by webpack plugin: Codesandbox, Github
Integration with vue by webpack CLI: Codesandbox, Github
Integration with react: Codesandbox, Github
Integration with nodejs: Codesandbox, Github
Integration with webpack-dev-server: Codesandbox, Github
A CURD demo (http-request-mock + vite + vue3 + ES2015+ + TypeScript): Website, Github
Unit test: Codesandbox, Github
License
http-request-mock is licensed under the MIT license.


