gamepads
v1.2.2
Published
A library providing a standardaized way of handling gamepads and gamepad events.
Downloads
70
Maintainers
Readme
HTML5 Gamepad API Enhancements
Gamepads.js is a JavaScript module for tracking Gamepads and events pertaining to their usage. Gamepads.js also offers an optional gamepad icons extension containing button images, available on GitHub or on npm as gamepad-icons.
Why use this library instead of the built-in Gamepad API?
The existing Gamepad standard lacks support for button/joystick events, and gamepadconnected/gamepaddisconnected events do not work consistently across browsers. This module seeks to offer a standard event-handling implementation that works across multiple browsers.
Installation
Via npm
npm install gamepadsimport Gamepads from 'gamepads';Via script tag
Include the script hosted on jsDelivr CDN or download it and include it on your page.
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/FThompson/gamepads.js@1.2.2/gamepads.min.js'></script>Usage
The gamepads.js script exposes the Gamepads object that takes care of event polling and tracking which gamepads are currently connected. You can add event handlers to this object to track when a gamepad is connected or disconnected.
// Start polling
Gamepads.start();
// Add event listeners
Gamepads.addEventListener('connect', e => {
console.log('Gamepad connected');
console.log(e.gamepad);
});
Gamepads.addEventListener('disconnect', e => {
console.log('Gamepad disconnected');
console.log(e.gamepad);
});These examples print the gamepad instances related to each connect or disconnect event. You can add event handlers to these gamepad objects to track gamepad events:
buttonpressfires when a button is pressed and passes the buttonindexto event handlers.buttonreleasefires when a button is released and passes the buttonindexto event handlers.buttonvaluechangefires when a button value changes and passes the buttonindexandvalueto event handlers. This value will typically be0or1except in the case of an axis button like a trigger, which can have a value between0and1.axischangefires when a gamepad axis changes and passes the axisindexandvalueto event handlers.joystickmovefires when a joystick moves and passes the axesindicesandvaluesto event handlers each as two-item arrays. To use this event, you must pass a two-length array of axis indices to the third parameter ofaddEventListenercorresponding to the horizontal and vertical axis indices. Joystick axis values go from-1(left/top) to1(right/bottom). This library applies a0.10deadzone by default, and this value is subtracted from the absolute minimum and maximum joystick axis values to smooth out values in the deadzone.
Gamepads.addEventListener('connect', e => {
console.log('Gamepad connected');
console.log(e.gamepad);
e.gamepad.addEventListener('buttonpress', e => console.log(e));
e.gamepad.addEventListener('buttonrelease', e => console.log(e));
e.gamepad.addEventListener('joystickmove', e => console.log(e), [0, 1]);
});In this example, the [0, 1] parameter in the joystickmove event handler corresponds to the axis indices of the left joystick on the standard gamepad mapping.
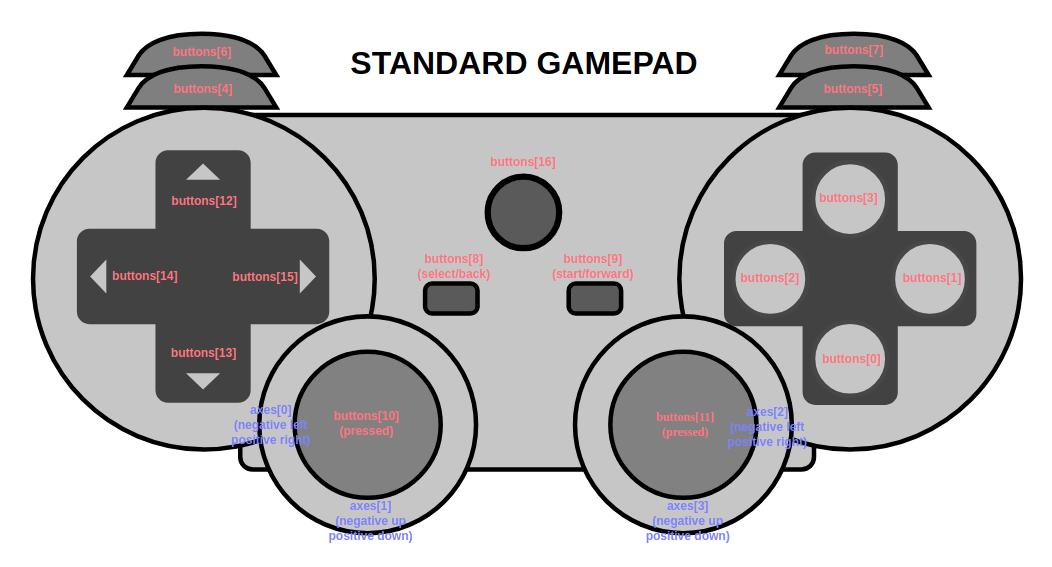
You can query a gamepad to determine if it follows the standard gamepad mapping using gamepad.mapping. This value will either be "standard" or "".
The gamepads.js script includes an object containing the standard gamepad mapping, StandardMapping, with indices split up into Button and Axis objects. You can use these index values in gamepad event handlers to identify which buttons the user is interacting with.
const xboxYIndex = StandardMapping.Button.BUTTON_TOP; // 3
const dpadUpIndex = StandardMapping.Button.D_PAD_UP; // 12
const leftStickIndices = StandardMapping.Axis.JOYSTICK_LEFT; // [0, 1]Notice that the standard mapping object contains joystick index pairs you can use to specify which joystick you want to add an event handler to.
e.gamepad.addEventListener('joystickmove', e => console.log(e), StandardMapping.Axis.JOYSTICK_LEFT);Live Example
You can view a live example here or browse the /examples directory. In the linked example, button images should appear when you press buttons and the two dots should mirror your gamepad joystick positions. The examples folder also contains a similar example created with React. Be sure to read the following Compatibility section if the code does not behave as expected.
Compatibility
The HTML5 Gamepad API backing gamepads.js is a relatively new API and various browser and gamepad configurations may perform differently, causing bugs such as non-responsive gamepads or non-standard mappings on standard gamepads. If a gamepad is not detected immediately, try pressing buttons or unplugging it and plugging it back in. If you are using a PS3 or PS4 gamepad, you may need to install DS4Windows, a program that emulates an Xbox 360 controller.
See a browser compatibility table here. Note that Microsoft Edge captures gamepad events for browser navigation so you will not be able to use buttons like the Xbox gamepad's B button without causing the browser to go back a page.
Contributing
If you have a browser/gamepad configuration that does not work with this library, please open an issue or a pull request.
API Reference
GamepadHandler object
GamepadsA GamepadHandler singleton is exposed as Gamepads. This object takes care of polling the HTML5 API for gamepads and tracking which gamepads are currently connected. Call Gamepads.start() to begin polling.
Methods
Gamepads.addEventListener(type, callback)Adds an event listener to the page's gamepad handler.
Event listeners are called in order of most recently added.
Event types
event 'connect': GamepadConnectionEventFires when a gamepad is connected or accessed for the first time (if already physically connected).
event 'disconnect': GamepadConnectionEventFires when a gamepad is disconnected.
Gamepads.removeEventListener(type, callback)Removes an event listener from the page's gamepad handler.
Gamepads.start()Begins polling and updating available Gamepads at the screen frame rate.
Gamepads.poll()Polls and updates all available Gamepads. You may call this manually (via setInterval for example) if you need the module to update gamepads at a different rate than the screen frame rate.
Gamepads.stop()Pauses polling and updating of gamepads. May be resumed by start().
Properties
Gamepads.gamepadsThe map of all connected Gamepad objects { index: gamepad }.
Gamepads.pausedRead-only property indicating whether or not polling is paused.
Gamepads.supportedRead-only property indicating whether or not the current browser supports the gamepads API.
Gamepad object
Retrieve Gamepad instances via GamepadHandler's connect/disconnect events or GamepadHandler.gamepads.
Methods
gamepad.addEventListener(type, callback[, index])Adds an event listener to this gamepad. If index is supplied, the listener will apply only to events for the button at that index; otherwise (default value -1) the listener will apply to all buttons or axes. In the case of 'joystickmove' events, a two-item array must be passed to index to handle two-axis joysticks.
Indexed event listeners are called before unindexed event listeners. After that, event listeners are called in order of most recently added.
Event types
type 'buttonpress': GamepadValueEventFires when a button is pressed and passes the button
indexto the callback.type 'buttonrelease': GamepadValueEventFires when a button is released and passes the button
indexto the callback.type 'buttonvaluechange': GamepadValueEventFires when a button changes and passes the button
indexandvalueto the callback. This value will typically be0or1except in the case of an axis button like a trigger.type 'axischange': GamepadValueEventFires when a gamepad axis changes and passes the axis
indexandvalueto the callback. If a deadzone was specified for this axis viagamepad.setAxisDeadzone, the deadzone will be subtracted from the value to create a smoother feel.type 'joystickmove': GamepadJoystickEventFires when a joystick moves outside of the gamepad's deadzone and passes the axis indices (
horizontalIndex,verticalIndex) and axis values (horizontalValue,verticalValue). Values have the deadzone subtracted from them to create a smoother feel. To use this event, users must specify inaddEventListenerthe pair of axis indices corresponding to the joystick's axes.
gamepad.removeEventListener(type, callback[, index])Removes an event listener from this gamepad. If index is supplied, the listener will only be removed from the button at that index. In the case of 'joystickmove' events, a two-item array must be passed to index to handle two-axis joysticks.
gamepad.addJoystickEventListener(type, callback, horizontalIndex, verticalIndex)Convenience method for adding joystick event listeners.
gamepad.removeJoystickEventListener(type, callback, horizontalIndex, verticalIndex)Convenience method for removing joystick event listeners.
gamepad.update()Updates this gamepad's values and fires events if necessary.
gamepad.getButton(index)Gets the button at the given index, in form { pressed: true/false, value: x }.
gamepad.getAxis(index)Gets the floating point value of the axis at the given index.
gamepad.isConnected()Checks if this gamepad is connected.
gamepad.getMapping()Gets this gamepad's mapping from the internal gamepad object. This value will only be 'standard' or '' at time of writing.
gamepad.setAxisDeadzone(index, deadzone)Specifies a deadzone to be used for an axis on this gamepad. Joystick axis deadzones should be set with the gamepad.joystickDeadzone property. Must be set to range [0, 1).
gamepad.getAxisDeadzone(index)Get the deadzone specified for the axis at index, or undefined if none specified.
Properties
gamepad.joystickDeadzoneThe joystick deadzone to apply. Defaults to 0.10. Must be set to range [0, 1).
Event Objects
_GamepadEventclass. Underscore in name used to avoid collision with DOM's built-inGamepadEvent.gamepadThe gamepad for which the event occured.
typeThe event type.
consume()Consumes the event to avoid calling additional listeners.
isConsumed()Checks if the event is consumed.
GamepadConnectionEventclass extends_GamepadEvent.Represents a gamepad connection or disconnection.
GamepadValueEventclass extends_GamepadEvent.Represents a gamepad button or axis value change.
indexThe index of the button or axis.
valueThe value of the button or axis.
GamepadJoystickEventclass extends_GamepadEvent.Represents a gamepad joystick change.
horizontalIndexThe index of the horizontal axis.
verticalIndexThe index of the vertical axis.
horizontalValueThe value of the horizontal axis.
verticalValueThe value of the vertical axis.
StandardMapping dictionary
A dictionary object containing button/axis index values for the standard gamepad mapping. Use StandardMapping.Button for buttons and StandardMapping.Axis for axes.
TODO
- Improve browser compatibility.
- Additional button image icon mapping and testing the untested mappings.
- Haptic Actuator support. Currently an experimental API internally, so a different implementation may be required per browser engine.
- Better joystick support. Maybe rewrite
GamepadJoystickEventto have horizontal/vertical specifiers for each axis index/value. Maybe define a Joystick object which would automatically populated by any recognized/user-defined mapping (e.g.StandardMappingfor standard gamepads).
Own a gamepad?
With so many possible configurations of gamepads, browsers, and operating systems out there, I need help to verify support for various gamepad configurations. Please open issues or pull requests if you find any problems with this module or have any suggestions towards improving support.



