forma-video-player
v1.0.1
Published
A react native video player packaged with controls that can be customized
Downloads
14
Maintainers
Readme
Forma Video Player
Complete video player solution for react-native-video
Customizable
Extensible
Installation
Requires react-native-video ^2.0.0 to be installed
yarn add forma-video-playerexoplayer
We recommend using exoplayer with react-native-video. It is capable of playing streaming video and has overall better performance than the default player. Follow these instructions for installation.
Default Player
import {Player} from 'forma-video-player'
const videoProps = {
name: 'Big Buck Bunny',
source: {
uri: 'https://archive.org/download/BigBuckBunny_328/BigBuckBunny_512kb.mp4'
}
}
...
render() {
return (
<View style={{flex: 1}}>
<Player videoProps={videoProps} />
</View>
)
}
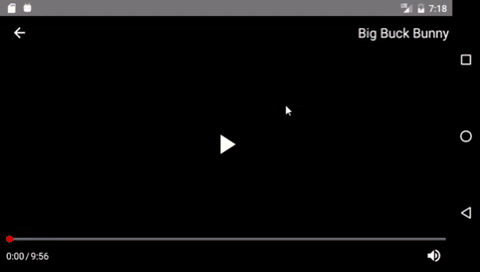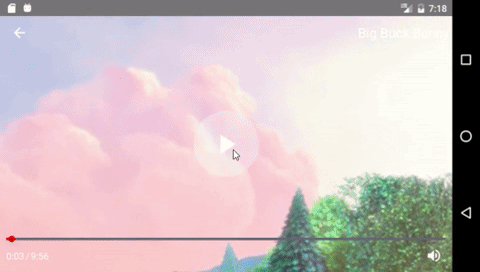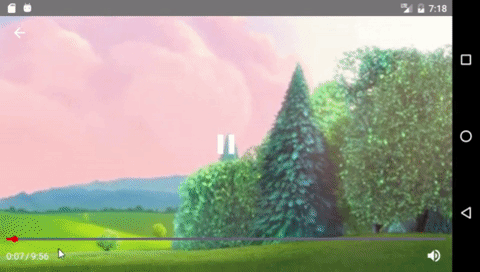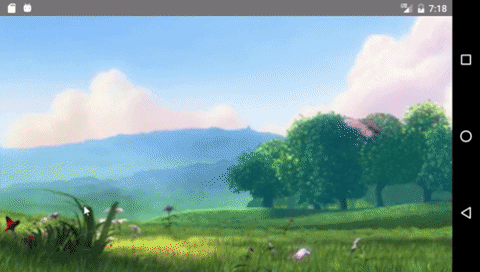
Components
Layout Components
Controls
Back
Mute
Play
PlayerTime
ProgressBar
Title
Add your own Custom Controls
Player
import {Player} from 'forma-video-player'
<Player
videoProps=Required object
back=function
styles=object
theme=object
layout=object
integrateRedux=boolean
/>Props
videoProps (Required object): These are the same props accepted by react-native-video's Video component, with two exceptions:
Prop | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- name | string | If a Title control is included in the layout, the name will be displayed there. | null style | object | This property will not be passed to the Video component. The Video component fills its parent container by default. | n/a
The rest of the props are passed to the Video component normally. Some defaults differ from react-native-video.
We recommend that you only use these properties to set initial values. Updating these properties will trigger a render of the entire Player tree. Instead, you should use a Control Component or make your own Custom Control to change the player state.
Prop | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- source | Required object {uri=string} | Can be a URL or a local file | null rate | number | 0 is paused, 1 is normal | 1.0 volume | number | 0 is muted, 1 is normal | 1.0 muted | boolean | Mutes the audio entirely | false paused | boolean | Pauses playback entirely | true resizeMode | string | How the video fills the player. One of 'contain', 'cover', 'stretch' | 'contain' repeat | boolean | Automatically repeat after ending | false playInBackground | boolean | Audio continues to play when app entering background | false playWhenInactive | boolean | [iOS] Video continues to play when control or notification center are shown | false ignoreSilentSwitch | string | [iOS] 'ignore' or 'obey' - When 'ignore', audio will still play with the iOS hard silent switch set to silent. When 'obey', audio will toggle with the switch. When not specified, will inherit audio settings as usual | 'ignore' progressUpdateInterval | number | [iOS] Interval to fire onProgress | 250 onLoadStart | function | Callback when video starts to load | null onLoad | function | Callback when video loads | null onProgress | function | Callback every ~250ms with currentTime | null onEnd | function | Callback when playback finishes | null onError | function | Callback when video cannot be loaded | null onBuffer | function | Callback when remote video is buffering | null onTimedMetadata | function | Callback when the stream receives some metadata | null
back (function): This function will be called by the Back control when it is pressed. The function can do anything, but it is intended to transition your navigation state backwards. Useful for full screen players. If this prop is not provided, the Back button will not be displayed.
styles (object): Define styles for the player, grouped by component name. See the Styles section for more details.
theme (object): A convenient way to define styles for multiple components at once. See the Themes section for more details.
layout (object): Override the default layout for the player. See the Layout section for more details.
integrateRedux (boolean): Use an existing store for the player redux state. You must also integrate the player reducer into your store if you do this by using createReducer(). See Redux Integration for more info.
Layout
By default, the player is laid out on a grid consisting of a Header, Body and Footer, each of which is divided into a Left, Middle, and Right ControlGroup
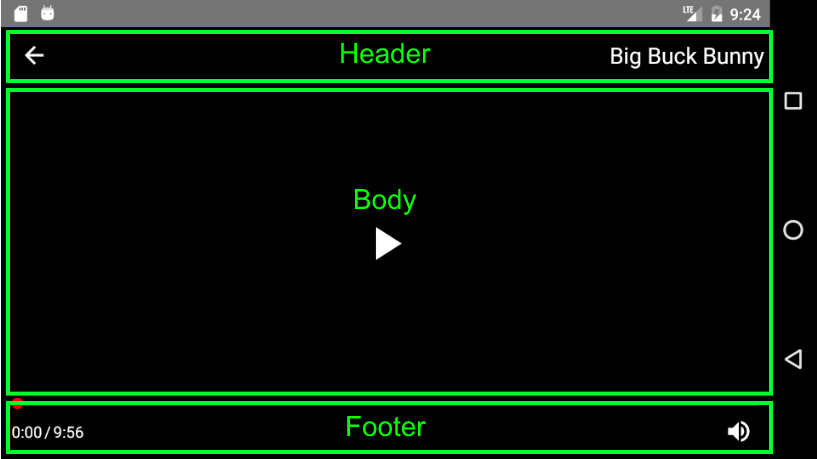
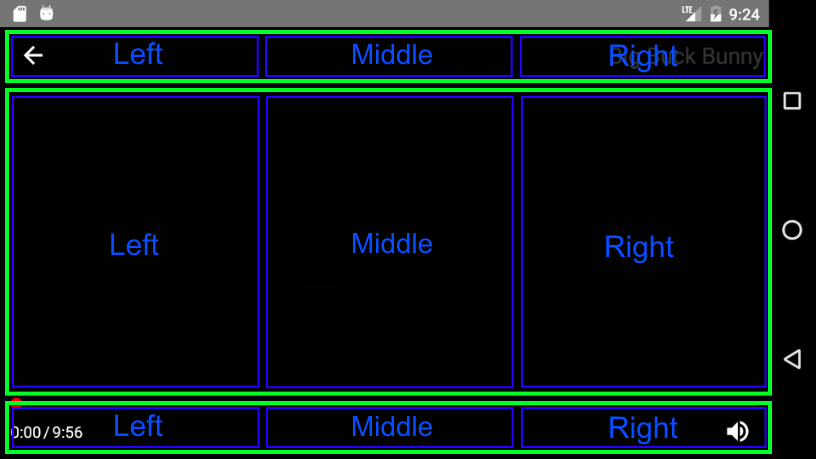
Default Layout
{
Header: <Header layout={{
Left: <ControlGroup layout={[<Back />]} />,
Center: <ControlGroup layout={[]} />,
Right: <ControlGroup layout={[<Title />]} />,
}} />,
Body: <Header layout={{
Left: <ControlGroup layout={[]} />,
Center: <ControlGroup layout={[<Play />]} />,
Right: <ControlGroup layout={[]} />,
}} />,
Footer: <Header layout={{
Left: <ControlGroup layout={[<PlayerTime />]} />,
Center: <ControlGroup layout={[]} />,
Right: <ControlGroup layout={[<Mute />]} />,
}} />
}Custom Layout
A custom layout begins with replacing one or many of the top level layout components (Header | Body | Footer) with your own component. This custom component can be a Layout Component with a custom layout prop, or any other React Component.
Even if you just want to add or remove one control from the player, you must replace one of the top level layout components.
Example: Remove the Title control
import {Player, Header, ControlGroup} from 'forma-video-player'
const customLayout = {
Header: <Header layout={{
Left: <ControlGroup layout={[<Back />]} />,
Center: <ControlGroup layout={[]} />,
Right: <ControlGroup layout={[]} />
}} />
}
...
render() {
return <Player layout={customLayout} ... />
}In the above example, we override the Header section of the default layout and exclude the Title component. Notice we still have to define the Back component since we are replacing that section as well. Because we did not define a Body or Footer, those sections will still use the default layout.
null
Passing null for any of the layout sections will exclude that section
Example: Exclude Header section
const customLayout = {
Header: null
}makeHeader, makeBody, makeFooter
In order to make control customization a little bit easier, we expose some convenience methods for creating a new Header, Body, and Footer. Instead of defining the entire component tree like we did in the example above, you could just do the following:
Example: Remove the Title control with makeHeader
import {makeHeader} from 'forma-video-player'
const customLayout = {
Header: makeHeader([<Back />], [], [])
}
The arrays passed in represent the Left, Middle, and Right sections.
makeHeader(Left, Middle, Right)
Arguments
Left(array): The left section of the HeaderMiddle(array): The middle section of the HeaderRight(array): The right section of the Header
makeBody(Left, Middle, Right)
Arguments
Left(array): The left section of the BodyMiddle(array): The middle section of the BodyRight(array): The right section of the Body
makeFooter(Left, Middle, Right)
Arguments
Left(array): The left section of the FooterMiddle(array): The middle section of the FooterRight(array): The right section of the Footer
Styles
Most components accept a set of styles that can be used to customize their look. These styles should be passed to the Player component with the styles prop. The styles prop accepts an object containing styles grouped by component name.
Example: Custom styles object
{
Mute: {
iconColor: 'red',
size: 30
},
Title: {
textColor: 'blue'
}
}See each component for more details about the styles it accepts.
Themes
Themes provide a convenient way to change multiple styles at once. The player comes packaged with a default theme, but you can change this by passing your own theme to the Player.
Default Theme
{
control: {
size: 25,
iconColor: '#ffffff',
fontSize: 14,
textColor: '#ffffff',
underlayColor: '#ffffff',
backgroundColor: 'transparent'
}
}Custom Themes
Custom themes should use the same structure as the default theme. Your custom theme will be deep merged with the default theme, overriding any common properties.
In the following example, the custom theme will make all controls smaller, but the other default theme styles will still be used.
Example: Reduce the size of all controls
const customTheme = {
control: {
size: 20
}
}
...
render() {
return <Player theme={customTheme} ... />
}Theme styles will only be applied once when the player is created. Updating the theme prop that is passed to the player will have no effect.
Layout Components
Layout components are intended to affect the positioning of controls within the player.
Header
Defines the top row of the player layout
import {Header} from 'forma-video-player'
<Header
layout=object
/>Props
layout (object): Must include a Left, Middle, and Right section
Body
Defines the middle row of the player layout
import {Body} from 'forma-video-player'
<Body
layout=object
/>Props
layout (object): Must include a Left, Middle, and Right section
Footer
Defines the bottom row of the player layout
import {Footer} from 'forma-video-player'
<Footer
layout=object
/>Props
layout (object): Must include a Left, Middle, and Right section
ControlGroup
A control group renders an array of Controls, in their array order
import {ControlGroup} from 'forma-video-player'
<ControlGroup
layout=object
/>Props
layout (array): An array of components. Each will be rendered in their array order, in a row.
Control Components
Back
Back button with a left arrow icon. When pressed, this calls the back function passed into the Player.
import {Back} from 'forma-video-player'
<Back />Styles
Name | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- buttonColor | string | button fill color | 'transparent' backgroundColor | string | container background color | theme control.backgroundColor underlayColor | string | button color on press | theme control.underlayColor size | number | size of the control | theme control.size iconColor | string | color of the button icon | theme control.iconColor
Mute
Toggles the player volume on and off
import {Mute} from 'forma-video-player'
<Mute />Styles
Name | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- buttonColor | string | button fill color | 'transparent' backgroundColor | string | container background color | theme control.backgroundColor underlayColor | string | button color on press | theme control.underlayColor size | number | size of the control | theme control.size iconColor | string | color of the button icon | theme control.iconColor
Play
Toggles play/pause
import {Play} from 'forma-video-player'
<Play />Styles
Name | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- buttonColor | string | button fill color | 'transparent' backgroundColor | string | container background color | theme control.backgroundColor underlayColor | string | button color on press | theme control.underlayColor size | number | size of the control | theme control.size iconColor | string | color of the button icon | theme control.iconColor
PlayerTime
Displays the currentTime and video duration, ie 0:00 / 2:00
import {PlayerTime} from 'forma-video-player'
<PlayerTime />Styles
Name | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- backgroundColor | string | container background color | theme control.backgroundColor fontSize | number | size of the font | theme control.fontSize textColor | string | color of the text | theme control.textColor
ProgressBar
Tracks the current time in video. Drag to seek. This component wraps Slider from react-native-slider
import {ProgressBar} from 'forma-video-player'
<ProgressBar />Styles
Name | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- thumbStyle | object | style of the thumb circle | {width: 10, height: 10, borderWidth: 1, borderColor: 'red'}, thumbTintColor | string | fill color of the thumb circle | '#f00' trackStyle | object | styling for the progress track | {backgroundColor: '#666677ff', borderRadius: 0} minimumTrackTintColor | string | color of the track where time has elapsed | '#f00'
Title
Displays the video title
import {Title} from 'forma-video-player'
<Title />Styles
Name | Type | Description | Default --- | --- | --- | --- backgroundColor | string | container background color | theme control.backgroundColor fontSize | number | size of the font | theme control.fontSize textColor | string | color of the text | theme control.textColor
Custom Controls
Player state is maintained by a redux store. This makes it easier to pass specific pieces of player state to controls without having to worry about unwanted renders. It also makes it pretty easy to implement your own controls.
State
The store contains all props that can be passed to react-native-video's Video component, plus a few more:
Name | Initial Value --- | --- source | null buffering | false error | null ignoreSilentSwitch | 'ignore' loaded | false loading | false metadata | null muted | false paused | true playInBackground | false playWhenInactive | false progress | null progressUpdateInterval | 250 rate | 1.0 repeat | false resizeMode | 'contain' volume | 1.0 duration | null ref | null ended | false name | null back | null styles | {} theme | defaultTheme currentTime | null
Actions
We also expose a setter action for each of the above that has the same name as the state it sets. See the connectVideo example below.
connectVideo([state], [actions], [mergeProps], [options])
A wrapper around redux's connect method with a syntax tailored to the player's state. When a component is wrapped in connectVideo, player state will be exposed in props.player and redux actions will be exposed in props.actions.
Arguments
state(array): An array of string, each of which is a piece of stateactions(object): Keys are the action name in props and values are the action methods
Example: Connect to player state and actions
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import {TouchableHighlight, Text} from 'react-native'
import {connectVideo, actions} from 'forma-video-player'
class Repeat extends Component {
toggleRepeat = () => {
const {player, actions} = this.props
actions.repeat(!player.repeat)
}
render() {
const {player} = this.props
return (
<TouchableHighlight onPress={this.toggleRepeat}>
<Text style={{color: 'blue'}}>{player.repeat ? 'repeat' : 'do not repeat'}</Text>
</TouchableHighlight>
)
}
}
export default connectVideo(['repeat'], {
repeat: actions.repeat
})(Repeat)styles(styleFn)
Internally, this is used to connect player components to custom state and themes. You can use if for your custom controls as well.
Arguments
styleFn(function): a function that accepts state and theme arguments and returns an object of styles. The 'state' argument will be the styles you pass into the Player props. The theme argument will be set to the configured theme.
(state, theme) => ({
styleName: 'styleValue',
groupStyles: {
anotherStyle: state.ControlName.anotherStyle,
defaultToTheme: state.ControlName.undefined || theme.defaultValue
}
})Example: Connect to styles
Let's use the Repeat control again
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import {TouchableHighlight, Text} from 'react-native'
import {connectVideo, actions, styles} from 'forma-video-player'
class Repeat extends Component {
toggleRepeat = () => {
const {player, actions} = this.props
console.log(this.props)
actions.repeat(!player.repeat)
}
render() {
const {player, styles} = this.props
return (
<TouchableHighlight onPress={this.toggleRepeat} underlayColor={styles.underlayColor}>
<Text style={{color: styles.text.color, fontSize: styles.text.size}}>{player.repeat ? 'repeat' : 'do not repeat'}</Text>
</TouchableHighlight>
)
}
}
const connected = connectVideo(['repeat'], {
repeat: actions.repeat
})(Repeat)
export default styles((state, theme) => ({
underlayColor: state.Repeat.underlayColor || theme.underlayColor, // pull from user styles or theme
text: {
color: state.Repeat.textColor || 'blue', // hardcode a default
size: 25 // hardcode style
}
}))(connected)Redux Integration
By default, the player will manage its state internally with redux by creating its own store and Provider. This is not ideal.
If you are using redux in your application, you can integrate the Player state into your store by integrating the Player reducer with createReducer() and setting integrateRedux={true} on the Player component.
Important The key in your root reducer must be
playerfor the Player reducer. This is a limitation we hope to work around in the future.
Example: Integrate Redux
import {Player, createReducer} from 'forma-video-player'
import {createStore, combineReducers} from 'redux'
import {Provider} from 'react-redux'
const store = createStore(combineReducers({
player: createReducer()
}))
const videoProps = {
name: 'Big Buck Bunny',
source: {
uri: 'https://archive.org/download/BigBuckBunny_328/BigBuckBunny_512kb.mp4'
}
}
...
render() {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<View style={{flex: 1}}>
<Player integrateRedux={true} videoProps={videoProps} />
</View>
</Provider>
)
}Roadmap
- Add more style / theme options
- Support for multiple mounted players
