focal-app-tracking
v0.0.41
Published
Focal Analytics tracking for node apps
Downloads
6
Readme
Version: 21.01.2020
1) Initializing the Tracking
Focal.init(APP_ID, APP_TOKEN,READ_FUNC, WRITE_FUNC, FETCH_FUNC);- Call this function before you use any other tracking method
- You find the
APP_IDand theAPP_TOKENin the Focal login area ->Settingssection - For
WRITE_FUNCandREAD_FUNC, provide asynchronous functions to read and write any kind of persistent storage, e.g.- LocalStorage for a simple web application
- AsyncStorage for React Native (https://docs.expo.io/versions/latest/sdk/async-storage/)
- Make sure that your
READ_FUNCreturns an empty object{}if the storage key does not yet exist (see example) - For
FETCH_FUNC, provide your usual fetch function. Note that for web applications, it might be necessary to providewindow.fetch.bind(window)and for node-based applications, you have to use a library such asnode-fetch
Example integration: React native application
import { AsyncStorage } from 'react-native';
const APP_ID=27;
const APP_TOKEN="TESTTOKEN";
const FocalWriteFunction = async (key, jsonObj) => {
try {
await AsyncStorage.setItem(
key,
JSON.stringify(jsonObj)
);
} catch (error) {
// Handle errors for write function
}
}
const FocalReadFunction = async (key) => {
try {
const value = await AsyncStorage.getItem(key);
if (value !== null) {
return JSON.parse(value);
}
return {}
} catch (error) {
// Handle errors for read function
}
}
Focal.init (APP_ID,APP_TOKEN, FocalReadFunction, FocalWriteFunction, fetch)2) Register a new user / device
- After initializing the Focal tracking using
Focal.init, you need to register the new user or device - You should run this whenever the app is started in case a user has cleared the persistent storage (e.g. local storage). It will not do anything if the device has already been registered.
- If you want, for any reason, to reset and register a device again, you have to call
Focal.resetDevice()first, which will clean the configuration and event storage. If you only want to obtain a new Focal ID, you can also set theFORCE_NEW_FOCAL_IDflag (this is NOT the unique device id!). - In order to register a device, you will need to have the following information:
- Screen resolution of the device as integers
- User-Agent
- Optional: a
UNIQUE_DEVICE_ID. If you set a unique device id, make sure that a custom variable with the labelunique_device_idexists in the Focal login area underSettings.
Focal.registerDevice(RESOLUTION_X, RESOLUTION_Y, USER_AGENT, UNIQUE_DEVICE_ID, FORCE_NEW_FOCAL_ID)- you can set
FORCE_NEW_IDtotrueif you want to acquire a new Focal ID and/or disable the Focal device recognition (which uses the User-Agent string to recognize previously registered devices). Defaults to false.
Example integration: React native application
- For react native applications, we suggest to use the
react-native-device-infopackage (https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-native-device-info) to get both a user agent string and a unique device id - For
expo, you can useConstants.getWebViewUserAgentAsync()(https://docs.expo.io/versions/latest/sdk/constants/) to get the user agent andConstants.deviceIdto get a device id - An example of the device registration can look likt this
import { Dimensions } from 'react-native';
import { getUniqueId, getUserAgent } from 'react-native-device-info';
// Call this function when your app starts, e.g. in your App() function
async function initFocal() {
const {width, height} = Dimensions.get("window");
await Focal.init(APP_ID,APP_TOKEN, TestReadFunction, TestWriteFunction, window.fetch.bind(window));
const userAgent = await getUserAgent();
const uniqueDeviceId = await getUniqueId();
await Focal.registerDevice(width, height, userAgent, uniqueDeviceId);
await Focal.trackView("Initial View Name");
}3) Tracking views
- Views are different screens that your users open, such as a
Homeview or aLoginview - Whenever a user opens your app, you want to track the initial view and all changes, so make sure to implement the tracking of all view changes
- Note that before you can track any other event such as clicks or scrolls, you need to track a view. Doing so, our tracking knows where other events happen without proving the context to every event.
Focal.trackView(VIEW_NAME);- a
VIEW_NAMEcan be any string that describes the view such as "Home" or "Login". View names that include special chars or spaces will be transformed to friendly names, e.g. "Welcome Screen" will become "Welcome_Screen"
4) Update viewport dimensions
- Focal supports different dimension parameters that you can set using the
setDimensionParametersmethod, e.g. the following call sets the screen width to 1024 (px)
Focal.setDimensionParameters( {
[DimensionParameters.SCREEN_WIDTH]: 1024
});
Focal.trackDimensionUpdate();- Note:
SCREEN_WIDTHandSCREEN_HEIGHTdefault to the values you have set in theregisterDevice()call - Note that to actually track the changes, you need to additionally call
Focal.trackDimensionUpdate()after setting a dimension parameter. Focal automatically tracks the dimensions you have set after everytrackView()call - The following different dimension parameters exist (defined in the
DimensionParametersenum)
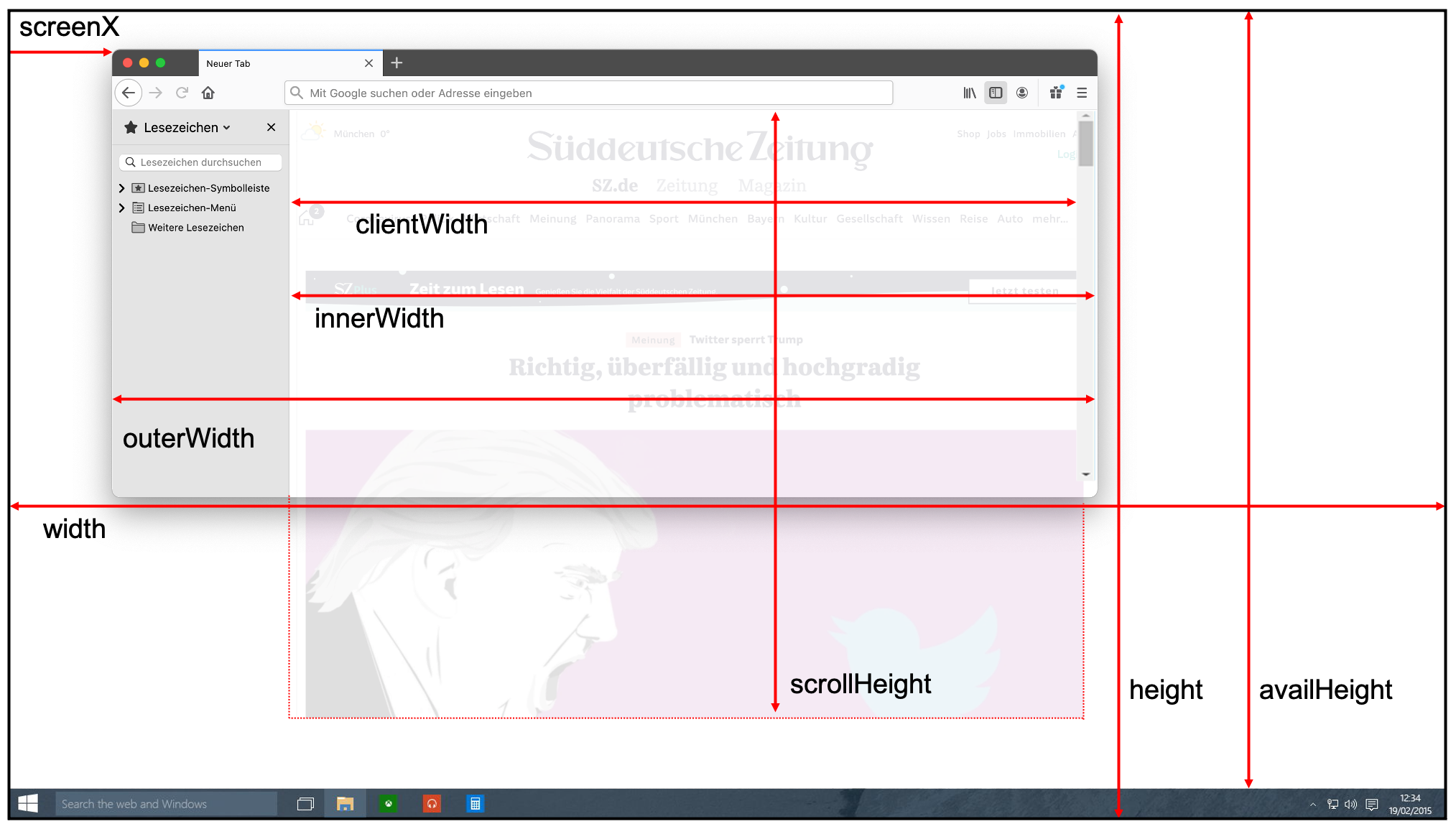
| ENUM | Description | JavaScript Reference | |------|-------------|----------------------| |DimensionParameters.SCREEN_WIDTH | Screen width (px)|screen.width| |DimensionParameters.SCREEN_HEIGHT | Screen height (px)|screen.height| |DimensionParameters.ORIENTATION_ANGLE | Orientation angle|screen.orientation.angle| |DimensionParameters.AVAILABLE_WIDTH | Screen available width (e.g. without bookmark panel, etc.)|screen.availWidth| |DimensionParameters.AVAILABLE_HEIGHT | Screen available height (e.g. without bookmark panel, etc.)|screen.availHeight| |DimensionParameters.SCROLL_WIDTH | Page wideness / scroll width (px)|document.documentElement.scrollHeight| |DimensionParameters.SCROLL_HEIGHT | Page length / scroll height (px)|document.documentElement.scrollHeight| |DimensionParameters.INNER_WIDTH | inner width: viewport including scrollbar|window.innerWidth| |DimensionParameters.INNER_HEIGHT | inner height: viewport including scrollbar|window.innerHeight| |DimensionParameters.CLIENT_WIDTH | client width: viewport without scrollbar|document.documentElement.clientWidth| |DimensionParameters.CLIENT_HEIGHT | client height: viewport without scrollbar|document.documentElement.clientHeight| |DimensionParameters.OUTER_WIDTH | outer width: window size (e.g. of the browser)|window.outerWidth| |DimensionParameters.OUTER_HEIGHT | outer height: window size (e.g. of the browser)|window.outerHeight| |DimensionParameters.SCREEN_X | Window position x |window.screenX| |DimensionParameters.SCREEN_Y | Window position y |window.screenY| |DimensionParameters.DEVICE_PIXEL_RATIO | The dpr parameter provides a means to multiply image dimensions in order to translate logical pixels (also 'CSS pixels') into physical pixels. The device pixel ratio is therefore the ratio between physical pixels and logical pixels. |window.devicePixelRatio|
5) Tracking orientation changes (usually necessary for mobile devices)
- Orientation change (e.g. from landscape to portrait) is a separate event that tracks the orientation angle. If you do not get angles/numbers from your function, use the values
0for portrait and90for landscape.
Focal.trackOrientationChange(90);6) Tracking scrolls
- Scrolling can either relate to the complete viewport (e.g. on a website) or relate to an element (e.g. a
ScrollViewor atextareaelement)
Track scrolling related to an element (e.g. ScrollView in react native or textarea on a website)
- Track the current scroll position by using
Focal.trackScrolling(Y_POSITION, X_POSITION, ELEMENT_NAME, ELEMENT_WIDTH, ELEMENT_HEIGHT, CONTENT_WIDTH, CONTENT_HEIGHT)Y_POSITION/X_POSITIONmeans the scroll positionELEMENT_NAMEcan be any string, e.g. the CSS-ID of an elementELEMENT_WIDTH/ELEMENT_HEIGHTis the dimension of the element that we are scrolling (comparable toINNER_WIDTH/INNER_HEIGHT, see viewport dimensions)CONTENT_WIDTH/CONTENT_HEIGHTis the dimension of the element that we are scrolling (comparable toSCROLL_WIDTH/SCROLL_HEIGHT, see viewport dimensions)
Example integration: React native application
<ScrollView
onScroll={(event) => {
const {contentOffset, contentSize, layoutMeasurement} = event.nativeEvent
Focal.trackScrolling(contentOffset.y, contentOffset.x,
"yourScrollElement",
layoutMeasurement.width, layoutMeasurement.height,
contentSize.width, contentSize.height);
}}
scrollEventThrottle={100}>
/* Your very long content */
</ScrollView>Track scrolling related to the complete viewport (e.g. on a website)
- Track the current scroll position by using
Focal.trackScrolling(Y_POSITION, X_POSITION)X_POSITIONis optional
Focal.trackScrolling(300);- Note that you should set the
SCROLL_WIDTH/SCROLL_HEIGHTand theINNER_WIDTH/INNER_HEIGHTdimension parameter before tracking a scroll, so that we are able to internally calculate and automatically track the visible percentage of the page length (percentage visible)
6) Tracking clicks
- use the function
Focal.trackClick(X_POSITION, Y_POSITION, ELEMENT_NAME)ELEMENT_NAMEcan be any string, e.g. the CSS-ID of an element
Example integration: React native application
<Button title="Press me" onPress={(e) => {
Focal.track([
createFocalClickEvent("PressMeButton",e.nativeEvent.pageX,e.nativeEvent.pageY)
])
}} />7) Tracking custom variables and events
- Besides existing events such as views, scrolls or clicks, you can track custom events or variables, e.g. an additional user id, a login status or cart values.
- To do so, create a new custom variable in the Focal login area under
Settingsand specify a label for your variable. - After that, call
Focal.trackCustomVariable(LABEL, CONTENT) - you can send any content that can be stringified as a JSON, e.g. a string or an object
Example integration
Focal.trackCustomVariable("cart", {value:15, items: [900, 313]});8) Tracking app states
- Focal currently supports to track the app states
ACTIVE(1) andBACKGROUND(0) - On a website this maps to the window's
focusandblurevents
Example integration: React native application
import { AppState } from 'react-native';
AppState.addEventListener('change', (nextAppState) => {
if(nextAppState == "active"){
Focal.trackAppState(1)
}else{
Focal.trackAppState(0);
}
});More examples
Initialize the tracking on a simple web aplication
const APP_ID=27;
const APP_TOKEN="TESTTOKEN";
const FocalWriteFunction = async (key, jsonObj) => {
localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(jsonObj) );
}
const FocalReadFunction = async (key) => {
const tmpObj = localStorage.getItem(key);
if(tmpObj === null){
return {}
}else{
return JSON.parse(tmpObj);
}
}
Focal.init (APP_ID,APP_TOKEN, FocalReadFunction, FocalWriteFunction, window.fetch.bind(window))Using node-localstorage to replace local storage in node apps
- If you develop your app in node, you can use
node-localstorageto replace the local storage functions:
Initialize the tracking on a simple web aplication
import { LocalStorage } from "node-localstorage";
import fetch from "node-fetch";
global.localStorage = new LocalStorage('./_scratch'); // LocalStorage constructor requires a folder for your storage
const FocalWriteFunction = async (key, jsonObj) => {
localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(jsonObj) );
}
// ... 