fluid-chains
v0.5.10
Published
A simple way to organize asynchronous Javascript functions.
Downloads
42
Maintainers
Readme
Fluid-chains
A simple way to organize asynchronous Javascript functions that looks like this:
And turn it into something like this: (ES6)
Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Installation
- Creating your first chain
- Starting the chain
- Creating chain sequence
- Reusing Chains
- Error handling
- Using decorator
- Adding specifications and validation
- Strict mode
- Caching
- Middlewares
- How it works
- Examples
- Documentation
- Authors
- License
Getting Started
Installing fluid-chains is easy. We want to make it light and simple.
Installation
npm install --save fluid-chains- Javascript (ES6)
import {Chain} from 'fluid-chains';- Javascript
var FluidChains = require('fluid-chains');
var Chain = FluidChains.Chain;Creating your first chain
new Chain('FindPeople', function(context, param, next) {
var people = ['john','jane','sam'];
context.set('people', people.filter(
function(person) {
person === param.filterBy()
}));
next();
});
Starting the chain
- ES6
import {ExecuteChain} from 'fluid-chains';- Javascript
var FluidChains = require('fluid-chains');
var ExecuteChain = FluidChains.ExecuteChain;ExecuteChain('FindPeople', {filterBy: 'jane'},
function(result) {
var people = result.people();;
console.log('people', people);
});Creating chain sequence
new Chain('firstChain', function(context, param, next) {
/*
context.set(key, value) will set
param value of the next chain.
*/
if (param.name) {
context.set('remarksTo', param.name());
} else {
context.set('remarksTo','everyone');
}
next();
/* call to proceed to the next chain.
Good for asynchronous callbacks */
}, 'secondChain' /* name of the next chain */);
new Chain('secondChain', function(context, param, next) {
/*
the context value of the previous chain can
be accessed with param.{field}() and it's always
a Function.
*/
context.set('remarks','Hello, '+param.remarksTo()+'!');
next();
/* not calling next() will break the chain
and will not trigger the callback below.*/
});
ExecuteChain('firstChain', function(result) {
/*
This will run because you call next()
from the last chain.
*/
console.log(result.remarks());
});Note: You cannot put Function as a value in context.set(key, value). You can put value and object.
Reusing Chains
ExecuteChains(Array, Parameter, Done);
new Chain('first', function(context,param, next){
// param.host() can be accessed here
next()},'second');
new Chain('second', function(context,param,next) {
next()},'third');
new Chain('third', function(context,param,next {
// param.host() can be accessed here
next()},'fourth');
new Chain('fourth', function(context,param,next) {
next()});
ExecuteChain(['first','third'],{host: 'http://localhost'}, function(result) {
// last chain processed was "third"
});
Note: Executing chains like the sample above will ignore the chain's predefined sequence and it will follow the chain sequence in the array. The sample above will run the "first" chain then "third" as long as you satify their parameter and it will complete the sequence even if there is a sequence defined in the "third" chain (which is the "fourth") thus make the chains reuseable.
Additional note: Parameters can be used throughout the chains.
Error handling
You can also use a chain as an error handler. Basically you're just creating another chain.
new Chain('firstChain', function(context, param, next) {
/*
context.set(key, value) will set param value of the
next chain.
*/
if (param.name) {
context.set('remarksTo', param.name());
} else {
throw new Error('Name is required.');
}
next();
}, 'secondChain', 'firstErrorHandler'
/*error handler is on the fourth argument*/);
new Chain('firstErrorHandler', function(context, param, next) {
/*
param.$error and param.$errorMessage functions
are created.
*/
console.log('error', param.$error());
// Error('Name is required.');
console.log('errorMessage', param.$errorMessage());
// 'Name is required.'
next();
/*
You can call next() to finish the chain or
just ignore it and break the chain.
You can even start a new chain of actions.
*/
});Note: You can place an error handler for each chain otherwise it will be thrown to the nearest error handler of its previous chain.
new Chain('firstChain', function(context, param, next) {
if (param.name){
context.set('remarksTo', param.name());
} else {
context.set('remarksTo','everyone');
}
next();
}, 'secondChain', 'firstErrorHandler');
new Chain('secondChain', function(context, param, next) {
context.set('remarks','Hello, '+param.remarksTo()+'!');
next();
}, 'thirdChain', 'anotherErrorHandler');
new Chain('thirdChain', function(context, param, next) {
if (param.name){
context.set('remarksTo', param.name());
} else {
throw new Error('Name is required.');
}
next();
});
new Chain('firstErrorHandler', function(context, param, next) {
console.log('error', param.$error());
// Error('Name is required.');
console.log('errorMessage', param.$errorMessage());
// 'Name is required.'
next();
});
new Chain('anotherErrorHandler', function(context, param, next) {
//thirdChain error will also be handled here.
next();
});Note: For asynchronous callback errors you may do "next(Error)".
new Chain('firstChain', function(context, param, next) {
setTimeout(function() {
next(new Error('sample'));
});
}, 'secondChain', 'firstErrorHandler'); Using decorator
You can create a chain by using decorator @ChainAction.
import {ChainAction, ExecuteChain} from 'fluid-chains';
class Student {
@ChainAction
createStudent(context, param, next) {
//param.name();
//context.set('studentId',####);
}
@ChainAction
findAll(context, param, next) {
}
}
const student = new Student();
ExecuteChain(student.CHAIN_CREATESTUDENT, {
name:'John Doe'
}, result =>{
//result.studentId
})
// student.CHAIN_FINDALL
// student.CHAIN_CREATESTUDENTChainAction can only be used in a function inside a class. It will initialize a chain based on the function name and will set a string constant CHAIN_{Name of the function in upper case} in the current class.
Adding specifications and validation
For each chain we can specify required fields and custom validations
var FindPeopleChain = new Chain('FindPeople', function(context, param, next) {
param.name() // should not be null or empty
param.type() // should not be null or empty and must be "quick"
next();
});
/*
@param field: string,
@param required: boolean
@param customerValidation (Optional) : Function(callback) => callback(valid, message)
*/
FindPeopleChain.addSpec('name', true);
FindPeopleChain.addSpec('type',true, function(done) {
done(type ==='quick', 'Type should be "quick"'); });
// or
FindPeopleChain.addSpec('email').require('custom message').validator((currentValue, valid)=>{
valid(currentValue.match('email regex here'));
});
Strict mode
You can turn on strict mode by invoking "ChainStrictModeEnabled" function.
- ES6
import {ChainStrictModeEnabled} from 'fluid-chains';
ChainStrictModeEnabled();- Javascript
var FluidChains = require('fluid-chains');
var ChainStrictModeEnabled = FluidChains.ChainStrictModeEnabled;
ChainStrictModeEnabled();With strict mode "on", chains can will only accept parameter that is specified in addSpec.
new Chain('StrictModeChain01', function(context, param, next) {
context.set('name', 'John');
context.set('surname', 'Wick');
context.set('age', 'unknown');
next();
}, 'StrictModeChain02');
var strictChain = new Chain('StrictModeChain02', function(context, param, next) {
param.name() // is available
param.surname() // is available
param.age() // is not available
next();
}, null, null);
strictChain.addSpec('name', true);
strictChain.addSpec('surname', true)
Caching
Since the chain output can be based on the value of its parameter making it possible to cache the output of a chain.
To enable caching you must have strict mode enabled.
- ES6
import {ChainStrictModeEnabled, ChainCacheEnabled} from 'fluid-chains';
ChainStrictModeEnabled();
ChainCacheEnabled();- Javascript
var FluidChains = require('fluid-chains');
var ChainStrictModeEnabled = FluidChains.ChainStrictModeEnabled;
var ChainCacheEnabled = FluidChains.ChainCacheEnabled;
ChainStrictModeEnabled();
ChainCacheEnabled();Note: Only the fields specified in Chain.addSpec() will be used as identifier of the chain cache. If Chain.addSpec() are not used it will cache the chain using its name.
Running with Middlewares
- ES6
import { ChainMiddleware } from 'fluid-chains';- Javascript
var FluidChains = require('fluid-chains');
var ChainMiddleware = FluidChains.ChainMiddleware;/*
* Will only get here before chain 'FindPeople' is executed
*/
new ChainMiddleware('FindPeople', function(param, context, next) {
next();
});
/*
* Will only get here before chain name that starts with "Find" is executed
*/
new ChainMiddleware(\^Find\g, function(param, context, next) {
if(context.$next() === 'CreatePeopleChain' && param.sessionKey){
//validates
} else {
throw new Error('Chain authentication failed.');
}
next();
});
/*
* Will run before every chains
*/
new ChainMiddleware(function(param, context, next) {
console.log('param',param.$owner());
next();
});
How it works
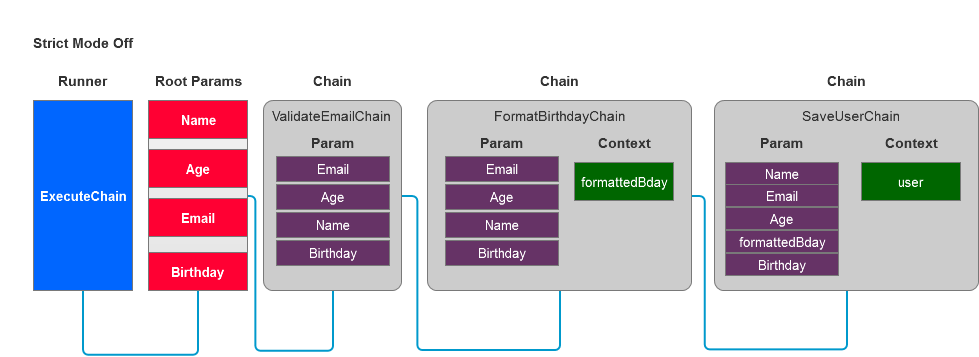
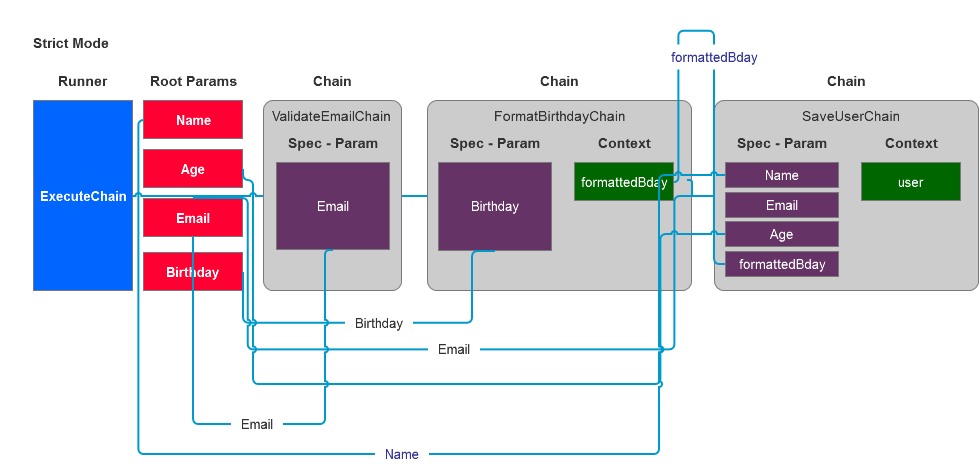
Examples
Documentation
Chain
The star of this package.
var chainSample = new Chain('ChainSample', function(context, param) {
// do something
})constructor(name:String, action:Function, next:String, errorHandler:String)
- name: defines the name of the chain
- action: function(context:ChainContext, param: ChainContext, [next:Function])
- context: context of the current chain
- param: consist of root parameters and context or the previous chain
- next (optional): triggers the callback of the chain
- next: defines the next chain in sequence
- errorHandler: defines the name of the error handler chain
Note: chain will run synchronously if next is not defined in action parameters
field | description | usage -------------|--------------------------------------------|-------- addSpec() | sets the chain parameter spec | chain.addSpec(ChainSpec) info() | returns the name, status & response time | chain.info() status() | returns thes current status of chain | chain.status() terminate() | stops the running chain | chain.terminate() execute() | executes the chain | chain.execute(callback, ChainContext, NextChain, disableNext)
ChainSpec
Defines the input of the chain.
var chainSample = new Chain('ChainSample', function(context, param) {
param.name() // this is required for this chain
param.email() // this is required for this email and validated before going here
});
chainSample.addSpec('name', true);
chainSample.addSpec('user')
.transform(function(currentValue, newForm){
if(currentValue){
findUser(currentValue, function(userData) {
newForm(userData);
});
}
});
chainSample.addSpec('email')
.require()
.validator(function(currentValue, valid) {
valid(currentValue.match(/email-regex/g));
});
chainSample.addSpec('fullname')
.translate(function(currentValue, context) {
const names = currentValue.split(',');
context.set('lastname', names[0]);
context.set('firstname', names[1]);
});
field | description | usage -------------|---------------------------------------------|-------- require() | mark the field as a required input in chain | chain.addSpec(field:String).require(customMessage:String) default() | defines the default value | chain.addSpec(field:String).default(value:String) validator() | defines the validator | chain.addSpec(field:String).validator(validate:Function) transform() | defines the transformer | chain.addSpec(field:String).transform(transformer:Function) translate() | defines the translator | chain.addSpec(field:String).translate(translator:Function)
ChainMiddleware
constructor(target:String, action:Function(param:ChainContext, context:ChainContext, next:Function(err:Error)));
new ChainMiddleware('{targetChainName}', function(param, context, next) {
next();
});
- target: defines the name of the target chain
- action: function(param:ChainContext, context: ChainContext, [next:Function])
- param: consist of root parameters and context of the previous chain
- context: context of the target chain
- next (optional): triggers the callback of the chain
ExecuteChain
Executes and composes sequence of chains.
- function([name:String|Array], parameters, callback);
ExecuteChain('ChainSample', {
hello: 'hello'
}, function(result) {
});
ExecuteChain(['ChainSample','ChainSample_2'], {
hello: 'hello'
}, function(result) {
});
ChainExists
Availability checker of chain in the current instance.
ChainExists = function(name:String):Boolean
ChainList
Returns an array of all the available chains in the current instance
Authors
- Jerico de Guzman - LinkedIn
See also the list of contributors who participated in this project.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details



