es-check
v8.0.2
Published
Checks the ECMAScript version of .js glob against a specified version of ECMAScript with a shell command
Downloads
348,682
Maintainers
Readme
ES Check ✔️
ES Check checks JavaScript files against a specified version of ECMAScript (ES) with a shell command. If a specified file's ES version doesn't match the ES version argument passed in the ES Check command, ES Check will throw an error and log the files that didn't match the check.
Ensuring that JavaScript files can pass ES Check is important in a modular and bundled world. Read more about why.
Version 8 🎉
ES Check version 8 is a major release update that can enforce actual ES version specific features checks; no longer just that a files are syntatically correct to the es version. To enable this feature, just pass the --checkFeatures flag. This feature will become default in version 9. Besides this, there are minor feature updates based on user feedback—glob matching updates and some optional fixes. This should not break any existing scripts. Please report any issues!
es-check es6 './dist/**/*.js' --checkFeaturesGet Started
Install
npm i es-check --save-dev # locally
npm i es-check -g # or globally
Check if an array or glob of files matches a specified ES version.
- Note: adds quotation around globs. Globs are patterns like so,
<something>/*.js.
es-check es5 './vendor/js/*.js' './dist/**/*.js'
- The ES Check script (above) checks
/dist/*.jsfiles to see if they're ES5. It throws an error and logs files are that do not pass the check.
Why ES Check?
In modern JavaScript builds, files are bundled up so they can be served in an optimized manner in the browsers. It is assumed by developers that future JavaScript—like ES8 will be transpiled (changed from future JavaScript to current JavaScript) appropriately by a tool like Babel. Sometimes there is an issue where files are not transpiled. There was no efficient way to test for files that weren't transpiled—until now. That's what ES Check does.
What features does ES Check check for?
ES Check checks syntax out of the box—to protect against breaking errors going to production. Additionally, by adding the --checkFeatures flag, ES Check will check for actual ES version specific features. This ensures that your code is syntactically correct and only using features that are available in the specified ES version. Look here to view/add features that ES Check checks for with the --checkFeatures flag!
Walk through
The images below demonstrate command line scripts and their corresponding logged results.
Pass

Fail
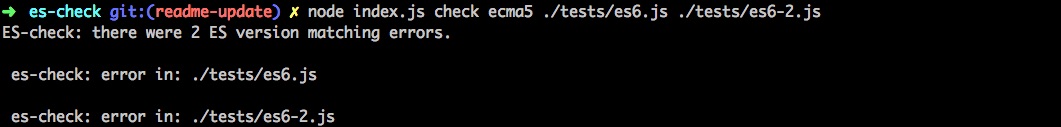
ES Check is run above with node commands. It can also be run within npm scripts, ci tools, or testing suites.
API
ES Check provides the necessities. It accepts its place as a JavaScript matcher/tester.
General Information
# USAGE
es-check <ecmaVersion> [files...]
Arguments
Usage: index [options] [ecmaVersion] [files...]
Arguments:
ecmaVersion ecmaVersion to check files against. Can be: es3, es4, es5, es6/es2015, es7/es2016, es8/es2017, es9/es2018, es10/es2019, es11/es2020, es12/es2021,
es13/es2022, es14/es2023
files a glob of files to to test the EcmaScript version against
Options
Modules Flag
--module use ES modules, default false
Allow Hash Bang
--allowHashBang supports files that start with hash bang, default false
Not
--not=target1,target2 An array of file/folder names or globs that you would like to ignore. Defaults to `[]`.
Files
--files=target1,target2 An array of file/folder names or globs to test the ECMAScript version against. Alias of [...files] argument.
Loose Glob Matching
--looseGlobMatch allows for loose glob matching, default false
⚠️ NOTE: This is primarily intended as a way to override the files setting in the .escheckrc file for specific invocations. Setting both the [...files] argument and --files flag is an error.
Check Features
es-check es6 './dist/**/*.js' --checkFeaturesGlobal Options
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
--module use ES modules
--allowHashBang if the code starts with #! treat it as a comment (default: false)
--files <files> a glob of files to to test the EcmaScript version against (alias for [files...])
--not <files> folder or file names to skip
--noColor disable use of colors in output (default: false)
-v, --verbose verbose mode: will also output debug messages (default: false)
--quiet quiet mode: only displays warn and error messages (default: false)
--looseGlobMatching doesn't fail if no files are found in some globs/files (default: false)
--silent silent mode: does not output anything, giving no indication of success or failure other than the exit code (default: false)
--checkFeatures check for actual ES version specific features (default: false)
-h, --help display help for command
Usage
ES Check is a shell command CLI. It is run in shell tool like Terminal, ITerm, or Hyper. It takes in two arguments: an ECMAScript version (<ECMAScript version>) and files ([files]) in globs.
Here are some example of es check scripts that could be run:
# globs
es-check ./js/*.js
# array of arguments
es-check ./js/*.js ./dist/*.jsConfiguration
If you're using a consistent configuration, you can create a .escheckrc file in JSON format with the ecmaVersion and files arguments so you can conveniently run es-check standalone from the command line.
Here's an example of what an .escheckrc file will look like:
{
"ecmaVersion": "es6",
"module": false,
"files": "./dist/**/*.js",
"not": ["./dist/skip/*.js"]
}⚠️ NOTE: Using command line arguments while there is an .escheckrc file in the project directory will override the configuration values in .escheckrc.
Debugging
As of ES-Check version 2.0.2, a better debugging interface is provided. When a file errors, An error object will be logged with:
- the erroring file
- the error
- the error stack
⚠️ NOTE: Error logs are from the Acorn parser while parsing JavaScript related to specific versions of ECMAScript. This means error messaging is not specific to ECMAScript version. It still offers context into parsing issues!
Acknowledgements
ES Check is a small utility using powerful tools that Isaac Z. Schlueter, Marijn Haverbeke, and Matthias Etienne built. ES Checker by Ruan YiFeng checks the JavaScript version supported within a browser at run time. ES Check offers similar feedback to ES Checker but at build time and is specific to the product that is using it. ES Check was started after reading this post about [deploying es2015 code to production today] by Philip Walton.
Contributing
ES Check has 6 dependencies: acorn and acorn-walk, fast-glob, supports-color, winston, and commander. To contribute, file an issue or submit a pull request.
To update es versions, check out these lines of code here and here (in acorn.js).
To update es feature detection, update these files here and here as enabled feature testing using acorn walk.
tests to go with new version and/or feature detection updates are great to have!
