elrpc
v0.1.0
Published
EPC (RPC Stack for Emacs Lisp) for NodeJS
Downloads
6
Readme
elrpc : EPC (RPC Stack for Emacs Lisp) for Node.js
EPC is an RPC stack for Emacs Lisp and elrpc is an implementation of EPC in Node.js.
Using elrpc, you can develop an emacs extension in JavaScript.
Sample Code
JavaScript code (server process)
This code is started by the client process, such as Emacs Lisp.
echo.js
var epc = require("elrpc");
epc.startServer().then(function(server) {
server.defineMethod("echo", function(args) {
return args;
});
server.wait();
});Emacs Lisp code (client process)
This elisp code calls the server process.
The package epc is required.
echo-client.el
(require 'epc)
(let (epc)
;; start a server process (using bundle exec)
(setq epc (epc:start-epc "bundle" '("node" "echo.js")))
(deferred:$
(epc:call-deferred epc 'echo '("hello"))
(deferred:nextc it
(lambda (x) (message "Return : %S" x))))
(message "%S" (epc:call-sync epc 'echo '(world)))
) ; just `eval-last-sexp' here
(epc:stop-epc epc) ; dispose EPC stack and peer processJavaScript code (client process)
You can also write the client process code in JavaScript.
echo-client.js
var elrpc = require("elrpc");
elrpc.startProcess(["node", "echo.js"]).then(function(client) {
client.callMethod("echo", "3 hello OK").then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
client.stop();
});
console.log("2 call hello");
});
console.log("1 start");Here is the result.
$ node echo-client.js
1 start
2 call hello
3 hello OKInstallation
Add this line to your application's package.json:
"dependencies": {
"elrpc": "*"
}And then execute:
$ npm installOr install it yourself as:
$ npm install elrpcAPI Document
EPC Overview
The EPC uses a peer-to-peer-architecture. After the connection is established, both peers can define remote methods and call the methods at the other side.
Let we define the words server and client. Server is a process which opens a TCP port and waiting for the connection. Client is a process which connects to the server. In most cases, a client process starts a server process. Then, the server process provides some services to the client process.
This diagram shows the API usage and the relation of processes.
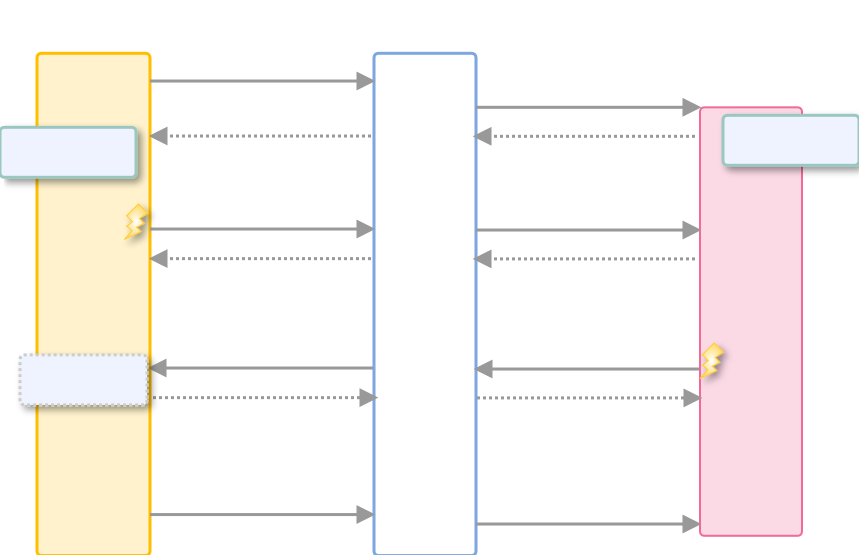
Please see the EPC document for the overview of EPC stack and protocol details.
Please see the elparser document for object serialization.
Building Server-Process
- Module method :
startServer(methods = [], port = 0)- Arguments
methods: Array ofMethodinstances.port: TCP Port number. 0 means that the OS decides the port number.
- Return
- A promise object for
RPCServer
- A promise object for
- Arguments
Sample Code
elrpc.startServer().then(function(server){
server.callMethod("remote_method", argument).then(function(ret){
console.log(ret);
server.stop();
});
});Defining Remote Method
RPCServer#defineMethod(name, bodyFunc, argdoc, docstring)- Arguments
name: String. Method name which is referred by the peer process.bodyFunc: Function. Code block which is called by the peer process. The return value is serialized and sent to the peer.argdoc: String[optional]. Argument information for human.docstring: String[optional]. Method information for human.
- Arguments
The return value of the code block is serialized and sent to the peer process. If the code block returns a promise object, the EPC stack waits for the return object which is wrapped by promise and serializes it and sent to the peer process.
If the return value includes wrong values which can't be serialized by elparser, the runtime exception EPCStackException is thrown to the method calling of the peer process.
Sample Code
server.defineMethod("echo", function(args) {
return args;
});
server.defineMethod("add", function(a, b) {
return a + b;
});
server.defineMethod("reduce", function(init, body, list) {
var f = new Function("a", "b", body);
return list.reduce(f, init);
}, "init(initial value), \"js expression\", list", "Apply Array#reduce method.");Calling Remote Method
If the peer process defines some methods, the instance of RPCServer can call the peer's method, regardless of the server process or the client one. (See the EPC document.)
RPCServer#callMethod(name, arg1, arg2, ...)- Synchronous method calling. The current thread is blocked until the calling result is returned.
- Arguments
name: String. Method name to call.arg1..: Argument value.
- Return (Promise)
- The promise object for a value which is returned by the peer process.
- Exception (Promise)
EPCRuntimeException: An exception which is thrown by the peer's method.EPCStackException: An exception which is thrown by the EPC protocol stack.
Sample Code
// server : RPCServer
server.callMethod("add", 1, 2).then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
return server.callMethod("add", "A", "B");
}).then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
return server.callMethod("reduce", 0, "return a+b;", [1,2,3,4]);
}).then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
return server.callMethod("reduce", "","return a+b;", ["A","B","C","D"]);
}).then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
});
// => 3
// => AB
// => 10
// => ABCDUtilities
RPCServer#queryMethods- Return
- Array of method specs of the peer process.
- Return
Sample Code
server.queryMethods().then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
});
// => [[:echo, null, null], [:add, null, null], [:reduce, "init(initial value), \"js expression\", list", "Apply Array#reduce method."]]EPC Process
elrpc can implement the client process which starts a server process. The server process can be implemented in JavaScript and the other language, such as Perl, Python and Emacs Lisp.
- Module method
startProcess(cmd)- Argument
cmd: Array. Command line elements for the server process.
- Return
- A promise object for the instance of
PeerProcess. (PeerProcess)
- A promise object for the instance of
- Argument
Sample Code
elrpc.startProcess(["node", "echo.js"]).then(function(client) {
client.callMethod("echo", "hello").then(function(ret) {
console.log(ret);
client.stop();
});
});Development
In most cases, the client process is Emacs and the server one is implemented by elrpc to extend Emacs functions in JavaScript.
However, it may be difficult to develop the programs which belong to the different environment.
So, at first, it is better to implement both sides in JavaScript and write tests.
If you want to watch the STDOUT and STDERR of the server process, start the process from command line and connect to the process with interactive REPL of node, like following:
Starting server process
$ node echo.js
1234512345 is port number to connect from the client process. The number changes each time.
Then, start node repl in the another terminal.
Connecting to the process from node repl
$ node
> var cl, ret;
> elrpc = require("elrpc");
> elrpc.startClient(12345).then(function(c){ cl = c; });
> cl.callMethod("echo", "hello").then(function(r){ ret = r; });
> ret
=> 'hello'When you invoke callMethod, the first terminal in which the server process runs, may show some output.
Performance
EPC is designed for fast communication between Emacs and other processes. Employing S-exp serialization and keeping TCP connection, EPC is faster than the conventional HTTP-based RPC stacks, such as JSON-RPC.
Executing the benchmark program test/echo-bench.js, You can check the performance in your environment. The program measures following aspects:
- round trip time of method invocation
- string transportation
- array/list serialization and transportation
- hash/alist serialization and transportation
Here is the result on Lenovo X240 with Intel Core i7-4600U CPU 2.10GHz, 8GB RAM, node v0.12.4 x86_64-linux.
$ node test/echo-bench.js
:
int: 109ms 9174.31 msg/sec
float: 117ms 8547.01 msg/sec
str: 774ms 1291.99 msg/sec
array: 2900ms 344.83 msg/sec
hash: 8991ms 111.22 msg/secIn the condition Node.js to Node.js, elrpc can perform around 9000 call/sec.
License
elrpc is licensed under MIT.
(C) 2015 SAKURAI Masashi. m.sakurai at kiwanami.net
