domwires
v0.9.129
Published
Flexible and extensible MVC framework
Downloads
412
Readme
DomWires (beta) 
Flexible and extensible MVC framework for projects written in TypeScript.
npm install domwires
Actual examples can be seen in tests.
Features
- Splitting logic from visual part
- Immutable interfaces are separated from mutable, for safe usage of read-only models (for example in mediators)
- Possibility to use many implementations for interface easily
- Fast communication among components using IMessageDispatcher
- Object instantiation with dependencies injections using IFactory which is based on InversifyJS
- Possibility to specify dependencies in config and pass it to IFactory
- Easy object pooling management
- Custom message bus (event bus) for easy and strict communication among objects
1. Hierarchy and components communication
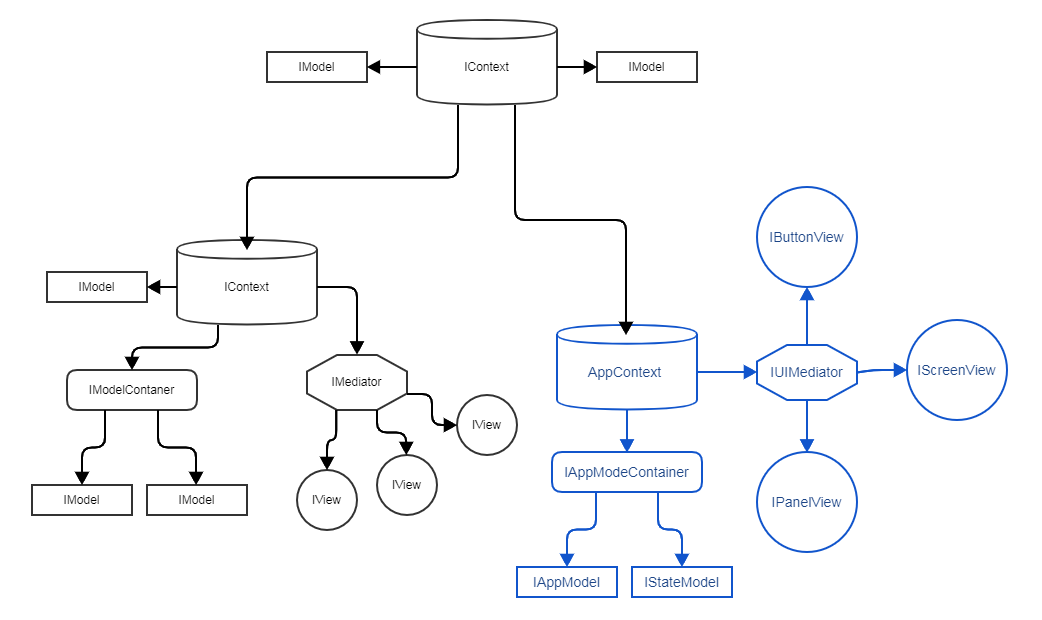
On diagram we have main IContext in the center with 2 child contexts.
Let's take a look at right IContext.
Right IContext is mapped to AppContext implementation. You can see its hierarchy on the screen: IModelContainer with 3 views.
IContext and its children all extend IMessageDispatcher and can listen or dispatch IMessage .
All messages in model hierarchy and from mediators bubble up to IContext. Also bubbled-up messages can be forwarded to parent contexts (by default forwarding message from child context to parent is disabled).
Also in default IContext configuration messages from models will be forwarded to mediators, messages from mediators will be forwarded to models and mediators.
IContext extends ICommandMapper and can map received messages (from model and mediators) to commands.
Creating context with default configuration
const factory: IFactory = new Factory();
const context: MockContext1 = factory.getInstance(MockContext1);Creating context with default configuration and mapping IContext interface to implementation
const factory: IFactory = new Factory();
factory.mapToType("IContext", MockContext1);
const context: IContext = factory.getInstance("IContext");Creating context with custom configuration
const factory: IFactory = new Factory();
factory.mapToType("IContext", MockContext1);
const config: ContextConfig = {
forwardMessageFromMediatorsToMediators: true,
forwardMessageFromMediatorsToModels: true,
forwardMessageFromModelsToMediators: true,
forwardMessageFromModelsToModels: false
};
factory.mapToValue("ContextConfig", config);
const context: IContext = factory.getInstance("IContext");Dispatching message from model
export class MockModel extends AbstractHierarchyObject
{
@postConstruct()
private init(): void
{
this.dispatchMessage(MockMessageType.HELLO, "hi!");
}
}
export class MockMessageType extends MessageType
{
public static readonly HELLO: MockMessageType = new MockMessageType();
}Listening message of model in mediator without having reference to model
export class UIMediator extends AbstractMediator implements IUIMediator
{
@postConstruct()
private init(): void
{
this.addMessageListener(AppModelMessage.NOTIFY, this.handleAppModelNotify);
}
private handleAppModelNotify(message: IMessage): void
{
console.log("Message received: " + message.type);
}
}Listening model message in mediator with hard reference to model
export class UIMediator extends AbstractMediator implements IUIMediator
{
@inject("IAppModelImmutable")
private appModel: IAppModelImmutable;
@postConstruct()
private init(): void
{
this.appModel.addMessageListener(AppModelMessage.NOTIFY, this.handleAppModelNotify);
}
public override dispose(): void
{
this.appModel.removeMessageListener(AppModelMessage.NOTIFY, this.handleAppModelNotify);
super.dispose();
}
private handleAppModelNotify(message: IMessage): void
{
console.log("Message received: " + message.type);
}
}Listening model message in mediator with hard reference to model
export class UIMediator extends AbstractMediator implements IUIMediator
{
@inject("IAppModelImmutable")
private appModel: IAppModelImmutable;
@postConstruct()
private init(): void
{
this.appModel.addMessageListener(AppModelMessage.NOTIFY, this.handleAppModelNotify);
}
public override dispose(): void
{
this.appModel.removeMessageListener(AppModelMessage.NOTIFY, this.handleAppModelNotify);
super.dispose();
}
private handleAppModelNotify(message: IMessage): void
{
console.log("Message received: " + message.type);
}
}2. Types mapping
Map 1 type to another
const factory: IFactory = new Factory();
factory.mapToType("IMyObj", MyObj);
//Will return new instance of MyObj
const obj: IMyObj = factory.getInstance("IMyObj");Map type to value
const factory: IFactory = new Factory();
factory.mapToType("IMyObj", MyObj);
//Will return new instance of MyObj
const obj: IMyObj = factory.getInstance("IMyObj");
factory.mapToValue("IMyObj", obj);
//obj2 will equal obj1
const obj2: IMyObj = factory.getInstance("IMyObj");Apply mapping at runtime via configuration
{
"IDefault$def": {
"implementation": "Default",
"newInstance": true
},
"ISuperCoolModel": {
"implementation": "SuperCoolModel"
},
"number$coolValue": {
"value": 7
},
"boolean$myboolean": {
"value": false
},
"any$obj": {
"value": {
"firstName": "nikita",
"lastName": "dzigurda"
}
},
"string[]": {
"value": [
"botan",
"sjava"
]
}
}const config: MappingConfigDictionary = new MappingConfigDictionary(json);
factory.appendMappingConfig(config.map);
const m: ISuperCoolModel = factory.getInstance("ISuperCoolModel");
expect(m.getCoolValue).equals(5);
expect(m.getMyboolean).equals(false);
expect(m.def.result).equals(123);
expect(m.object.firstName).equals("nikita");
expect(m.object.lastName).equals("dzigurda");
expect(m.array[1]).equals("sjava");Default value of interface
If no mapping is specified, IFactory will try to find default implementation on the interface.
Default implementation should be defined via setDefaultImplementation method in global scope.
// this can be done only once for each key
setDefaultImplementation("IMyObj", MyObj);
const factory: IFactory = new Factory();
//Will try to return instance of MyObj class
const obj: IMyObj = factory.getInstance("IMyObj");3. Message bubbling
By default, when message is dispatched it will be bubbled-up to top of the hierarchy. But you can dispatch message without bubbling.
Dispatch message without bubbling it up
//set the 3-rd parameter "bubbles" to false
this.dispatchMessage(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, {state: AppState.ENABLED}, false);It is also possible to stop bubbling up received message from bottom of hierarchy
Stop message propagation
public override onMessageBubbled(message: IMessage): boolean
{
super.onMessageBubbled(message);
//message won't propagate to higher level of hierarchy
return false;
}To stop forwarding redirected message from context (for ex. mediator dispatcher bubbling message, context receives it and forwards to models), you can do that way:
public override dispatchMessageToChildren(message: IMessage): void
{
/*
* Do not forward received messages to children.
* Just don't call super.dispatchMessageToChildren(message);
*/
}4. Mapping messages to commands in IContext
IContext extends ICommandMapper and can map any received message to command.
Mapping message to command
export class AppContext extends AbstractContext implements IContext
{
protected override init(): void
{
super.init();
this.map(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, UpdateAppStateCommand);
}
}In code screen above, when context receive message with UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE type, it will
execute UpdateAppStateCommand. Everything that is mapped
to IContext
factory will be injected to command.
inject model to command
export class AppContext extends AbstractContext implements IContext
{
private appModel: IAppModel;
protected override init(): void
{
super.init();
this.appModel = this.factory.getInstance("IAppModel");
this.addModel(appModel);
this.factory.mapToValue("IAppModel", this.appModel)
this.map(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, UpdateAppStateCommand);
}
}
export class UpdateAppStateCommand extends AbstractCommand
{
@lazyInject("IAppModel")
private appModel: IAppModel;
public override execute(): void
{
super.execute();
//TODO: do something
}
}Also IMessage can deliver data, that will be also injected to command.
injecting IMessage data to command
export class UIMediator extends AbstractMediator implements IUIMediator
{
@postConstruct()
private init(): void
{
this.dispatchMessage(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, {state: AppState.ENABLED});
}
}
export class UpdateAppStateCommand extends AbstractCommand
{
@lazyInject("IAppModel")
private appModel: IAppModel;
@lazyInjectNamed(AppState, "state")
private state: AppState;
public override execute(): void
{
super.execute();
this.appModel.setCurrentState(this.state);
}
}5. Command guards
It is possible to add “guards“, when mapping commands. Guards allow doesn’t allow to execute command at current application state.
Adding guards to command mapping
export class AppContext extends AbstractContext implements IContext
{
private appModel: IAppModel;
protected override init(): void
{
super.init();
this.appModel = this.factory.getInstance("IAppModel");
this.addModel(this.appModel);
this.factory.mapToValue("IAppModel", this.appModel)
this.map(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, UpdateAppStateCommand)
.addGuards(CurrentStateIsDisabledGuards);
}
}
export class CurrentStateIsDisabledGuards extends AbstractGuards
{
@lazyInject("IAppModel")
private appModel: IAppModel;
public override get allows(): boolean
{
super.allows;
return this.appModel.currentState === AppState.DISABLED;
}
}In above example command won’t be executed, if this.appModel.currentState !== AppState.DISABLED.
6. Object pooling
IFactory has API to work with object pools.
Register pool
export class AppContext extends AbstractContext implements IContext
{
protected override init(): void
{
super.init();
//Registering pool of MyObj with capacity 5 and instantiate them immediately
this.factory.registerPool(MyObj, 5, true);
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
//Will return one of objects in pool
this.factory.getInstance(MyObj);
}
}
}There are other helpful methods to work with pool in IFactory
7. Handling multiple implementations of one interface
It is possible to dynamically map different implementations to one interface.
Mapping specific implementation according platform
export class AppContext extends AbstractContext implements IContext
{
protected override init(): void
{
super.init();
/* use-tcp */
this.factory.mapToType(INetworkConnector, TcpNetworkConnector);
/* end-use-tcp */
/* use-udp */
this.factory.mapToType(INetworkConnector, UdpNetworkConnector);
/* end-use-udp */
}
}There are even possibilities to remap commands.
Remapping command
this.factory.mapToType(BaseUpdateModelsCommand, ProjectUpdateModelsCommand);
/*
* Will execute com.mycompany.coolgame.commands.UpdateModelsCommand instead of
* com.crazyflasher.app.commands.UpdateModelsCommand
*/
this.commandMapper.executeCommand(BaseUpdateModelsCommand);Also you can map extended class to base
Map extended class to base
// GameSingleWinVo extends SingleWinVo
this.factory.mapToType(SingleWinVo, GameSingleWinVo);
// Will return new instance of GameSingleWinVo
this.factory.getInstance(SingleWinVo);8. Immutability
DomWires recommends to follow immutability paradigm. So mediators have access only to immutable interfaces of hierarchy components. But feel free to mutate them via commands. To handle this way, it’s better to have separate factories for different types of components. At least to have separate factory for context components (do not use internal context factory, that is used for injecting stuff to commands and guards).
Mapping mutable and immutable interfaces of model
export class AppContext extends AbstractContext implements IContext
{
protected override init(): void
{
super.init();
const appModel: IAppModel = factory.getInstance("IAppModel");
this.addModel(appModel);
this.map(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, UpdateAppStateCommand)
.addGuards(CurrentStateIsDisabledGuards);
const mediatorFactory: IFactory = new Factory();
// mutable interface will be available in commands
this.factory.mapToValue("IAppModel", appModel);
// immutable interface will be available in mediators
mediatorFactory.mapToValue("IAppModelImmutable", appModel);
const uiMediator: IUIMediator = mediatorFactory.getInstance("IUIMediator");
this.addMediator(uiMediator);
}
}
export class AppModel extends AbstractHierarchyObject implements IAppModel
{
private _currentState: Enum;
public setCurrentState(value: Enum): IAppModel
{
this._currentState = value;
this.dispatchMessage(AppModelMessage.STATE_UPDATED);
}
public get currentState(): Enum
{
return this._currentState;
}
}
export interface IAppModel extends IAppModelImmutable, IModel
{
setCurrentState(value: Enum): IAppModel;
}
export interface IAppModelImmutable extends IModelImmutable
{
get currentState(): Enum;
}
export class AppModelMessage extends MessageType
{
public static readonly STATE_UPDATED: AppModelMessage = new AppModelMessage("STATE_UPDATED");
}
class UIMediator extends AbstractMediator implements IUIMediator
{
@inject("IAppModelImmutable")
private appModel: IAppModelImmutable;
@postConstruct()
private init(): void
{
this.addMessageListener(AppModelMessage.STATE_UPDATED, this.appModelStateUpdated);
this.dispatchMessage(UIMediatorMessage.UPDATE_APP_STATE, {state: AppState.ENABLED});
}
private appModelStateUpdated(message: IMessage): void
{
//possibility to access read-only field
console.log(this.appModel.currentState);
}
}
export class UIMediatorMessage extends MessageType
{
public static readonly UPDATE_APP_STATE: UIMediatorMessage = new UIMediatorMessage("UPDATE_APP_STATE");
}
export class UpdateAppStateCommand extends AbstractCommand
{
@lazyInject("IAppModel")
private appModel: IAppModel;
@lazyInjectNamed(AppState, "state")
private state: AppState;
public override execute(): void
{
super.execute();
this.appModel.setCurrentState(this.state);
}
}
export class CurrentStateIsDisabledGuards extends AbstractGuards
{
@inject("IAppModel")
private appModel: IAppModel;
public override get allows(): boolean
{
super.allows;
return this.appModel.currentState === AppState.DISABLED;
}
}Requirements
- TypeScript 4.4.3+
