de-formed-validations
v2.0.7
Published
Function-based modular validations
Downloads
36
Maintainers
Readme
De-Formed Validations
This package has been deprecated - please use @de-formed/react-validations for the latest version
De-Formed Validations is a robust and unopinionated API to manage form and data validations in JavaScript and React. With only a handful of properties to learn, de-formed maintains its own internal state with simple function calls so that you can design your architecture the way you want to.
Why Use De-Formed?
- Modular and Composable
- Unopinionated
- Easy to use and test.
- Works for Client or Server.
Install
yarn add de-formed-validationsnpm install de-formed-validationsReact Usage
Step 1: Create a file to define your validations.
// PersonValidation.ts
import { useValidation } from 'de-formed-validations';
export const PersonValidation = () => {
return useValidation<Person>({
firstName: [
{
errorMessage: 'First Name is required.',
validation: (val: string) => val.length > 0,
},
{
errorMessage: 'First Name cannot be longer than 20 characters.',
validation: (val: string) => val.length <= 20,
},
],
lastName: [
{
errorMessage: 'Last Name is required.',
validation: (val: string) => val.length > 0,
},
{
errorMessage: 'Last Name cannot be longer than 20 characters.',
validation: (val: string) => val.length <= 20,
},
{
errorMessage: 'Must be Ross if fist name is Bob.',
validation: (val: string, state: Person) => {
return state.firstName === 'Bob' ? val === 'Ross' : true;
},
},
],
});
};Step 2: Plug into React Component
// PersonForm.component.tsx
import React from 'react';
import { PersonValidation } from './PersonValidation';
export const PersonForm = ({ person, onChange }) => {
const v = PersonValidation();
const handleChange = v.validateOnChange(onChange, person);
const handleBlur = v.validateOnBlur(person);
const handleSubmit = (e: any) => {
e.preventDefault();
const canSubmit = v.validateAll(person);
if (canSubmit) {
// submit logic
}
};
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<div>
<label>First Name</label>
<input
name="firstName"
onBlur={handleBlur}
onChange={handleChange}
value={person.firstName}
/>
{v.getError('firstName') && <p>{v.getError('firstName')}</p>}
</div>
<div>
<label>Last Name</label>
<input
name="lastName"
onBlur={handleBlur}
onChange={handleChange}
value={person.lastName}
/>
{v.getError('lastName') && <p>{v.getError('lastName')}</p>}
</div>
<button>Submit</button>
</form>
);
};Node/Express or Vanilla JavaScript Usage
Step 1: Create a file to define your validations.
// PersonValidation.js
import { Validation } from 'de-formed-validations';
export const PersonValidation = () => {
return new Validation({
firstName: [
{
errorMessage: 'First Name is required.',
validation: val => val.length > 0,
},
{
errorMessage: 'First Name cannot be longer than 20 characters.',
validation: val => val.length <= 20,
},
],
lastName: [
{
errorMessage: 'Last Name is required.',
validation: val => val.length > 0,
},
{
errorMessage: 'Last Name cannot be longer than 20 characters.',
validation: val => val.length <= 20,
},
{
errorMessage: 'Must be Ross if fist name is Bob.',
validation: (val, person) => {
return person.firstName === 'Bob' ? val === 'Ross' : true;
},
},
],
});
};Step 2: Import as needed
// controller.js
const PersonValidation = require('./PersonValidation');
app.use("/", (req, res) => {
const v = PersonValidation();
return v.validateAll(req.body)
? res.json('success')
: res.json(v.validationState);
});Double-Trouble
If you are using a Node server, you can send the validationState back to the Client with the response and the UI can then call forceValidationState to automatically render any server validation errors back to the user.
A Different Approach
De-formed generates validations by calling an array of functions that define the exact requirements for a given property. There are no special properties to define (e.g. type, length, max, min, etc). We avoided this because it requires de-formed to make assumptions about the data it is recieving which can be a common runtime error. It also forces redundant error messages because if there is only one error message a user will be shown, then just write one function that handles the validation and you're done. Ultimately, you know your data and de-formed does not, and our goal is make validations that are as unopinionated as possible; therefore, each function returns either true or false, and if it fails, it generates the error message associated with that function. In this way, de-formed allows you to write validations from the perspective of what error messages are users supposed to see and then write a function that does that thing.
Importantly, all validations are de-coupled from your form and controller architecture allowing them to be executed, reused, and composed together in any context necessary. Just define as many functions as you want in your schema and then execute them on whichever events you choose (client-side or server-side). This provides you with a function-based, modular approach to design validation patterns that meet your requirements without the hassle of managing the validation data yourself.
Documentation
Check out the documentation.
Examples
More examples and CodeSandboxes.
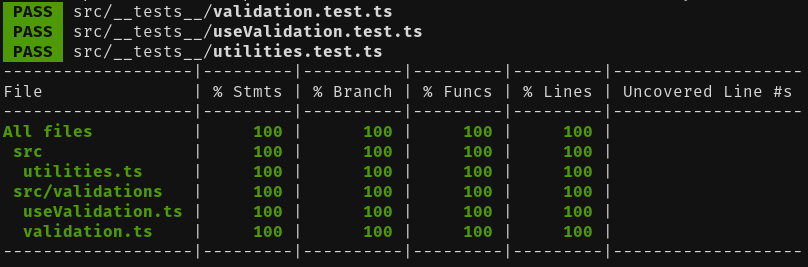
Coverage
License
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
