cst
v0.4.10
Published
JavaScript CST Implementation
Downloads
139,747
Readme
JavaScript CST implementation
CST
Check out code samples and rest of the wiki for more.
CST means Concrete Syntax Tree. Unlike an AST (Abstract Syntax Tree), a CST contains all the information
from the JavaScript source file: whitespace, punctuators, comments. This information is extremely useful for
code style checkers and other code linters. CST is also useful for cases when you need to apply modifications
to existing JavaScript files while preserving the initial file formatting.
This CST implementation is designed to be 100% compatible with JS AST (https://github.com/estree/estree).
Main principles:
- CST contains all the information from a parsed file (including whitespace and comments).
- Compatible with AST (https://github.com/estree/estree).
- Requires tokens to modify CST structure.
- The tree is always valid (it protects itself against breaking changes).
- CST can be rendered to valid JS at any time.
Let's see an example:
x = 0;
if (x) x++;The CST for this example:
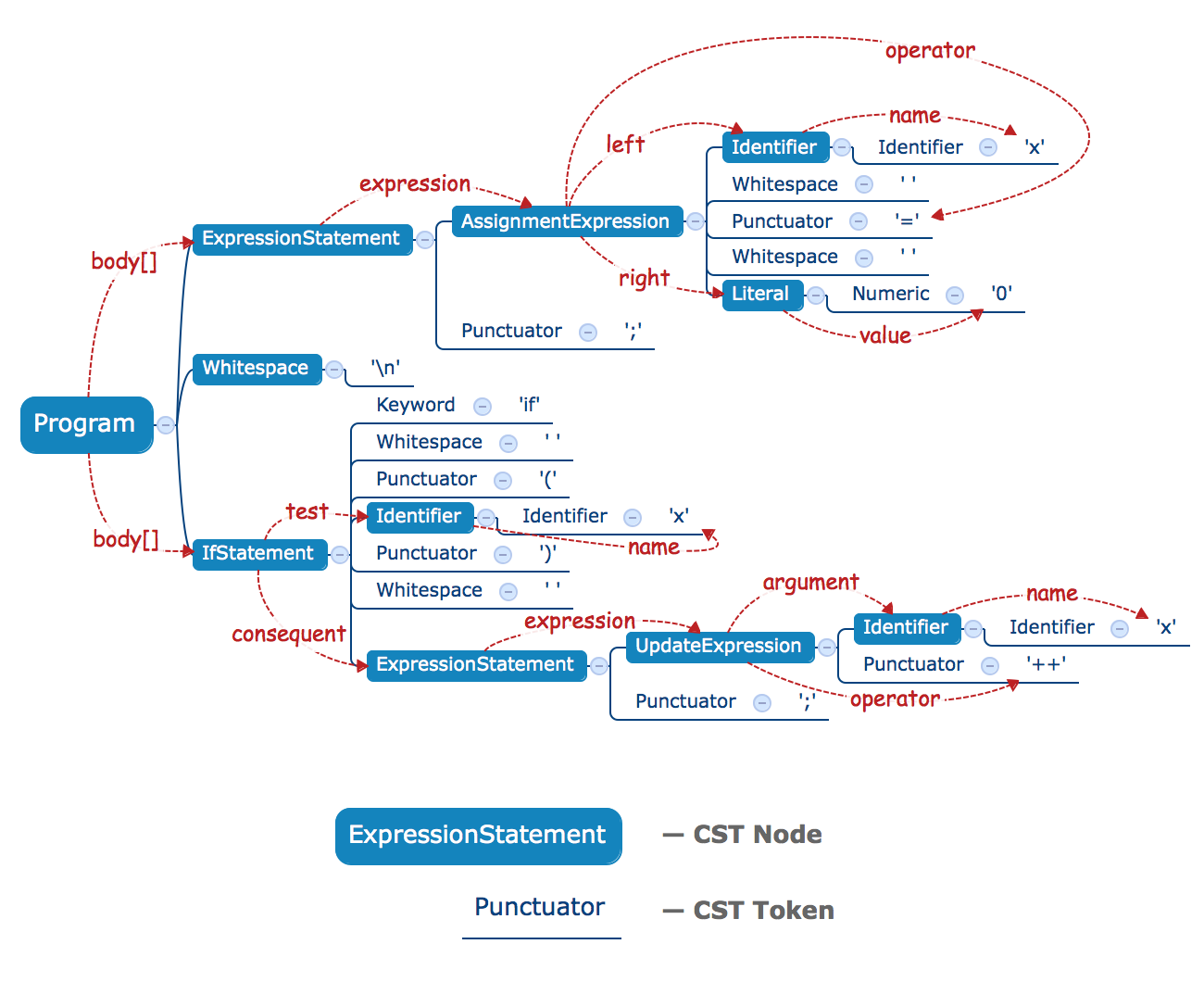
- Blue text — CST Tokens.
- White text in blue blocks — CST Nodes (their structure is equal to an AST).
- Blue lines — CST Structure.
- Red lined — AST Links.
Classes
Element
Element is the base class for Node and Token.
declare class Element {
// traversal for children
childElements: Array<Element>;
firstChild: ?Element;
lastChild: ?Element;
// traversal for parent
parentElement: ?Element;
// traversing between siblings
nextSibling: ?Element;
previousSibling: ?Element;
// traversing to first/last tokens (not only direct tokens)
getFirstToken(): ?Token;
getLastToken(): ?Token;
// traversing to next/previous tokens (not only siblings)
getNextToken(): ?Token;
getPreviousToken(): ?Token;
// Code properties
type: string;
isToken: boolean;
isNode: boolean;
isExpression: boolean;
isStatement: boolean;
isWhitespace: boolean;
isFragment: boolean;
isModuleDeclaration: boolean;
isModuleSpecifier: boolean;
// Code methods
getSourceCode(): string;
getSourceCodeLength(): number;
// Mutation methods
// appends child to the end of the `Element`
appendChild(newElement: Element): void;
// prepends child to the end of the `Element`
prependChild(newElement: Element): void;
// inserts child before `referenceChild`
insertChildBefore(newElement: Element, referenceChild: Element): void;
// replaces specified child interval (from `firstChildRef` to lastChildRef`) with specified child.
replaceChildren(newElement: Element, firstRefChild: Element, lastRefChild: Element): void;
// Location methods
getRange(): Range;
getLoc(): Location;
}
declare class Token extends Element {
// token value
value: string;
}
type Range = [
start: number;
end: number;
];
type Position = {
line: number,
column: number
};
type Location = {
start: Position,
end: Position
};Node
Node extends Element. The Nodes are the "AST part of a CST". If you drop everything but Nodes from a CST, you will
get a pure AST from the Node structure. So it is fair to say that Nodes provide the AST logic for a CST. Currently
only Nodes can contain children.
The Node property isNode always returns true.
Token
Token extends Element. The purpose of a CST is to have tokens in the tree. By only manipulating tokens,
we can change code formatting without any effect on the behaviour.
The Token property isToken always returns true.
