blobby
v0.25.1
Published
An HTTP Proxy for Blob storage systems (such as S3) that automatically shards and replicates your data
Downloads
398
Readme
blobby
No, not that Mr. Blobby.
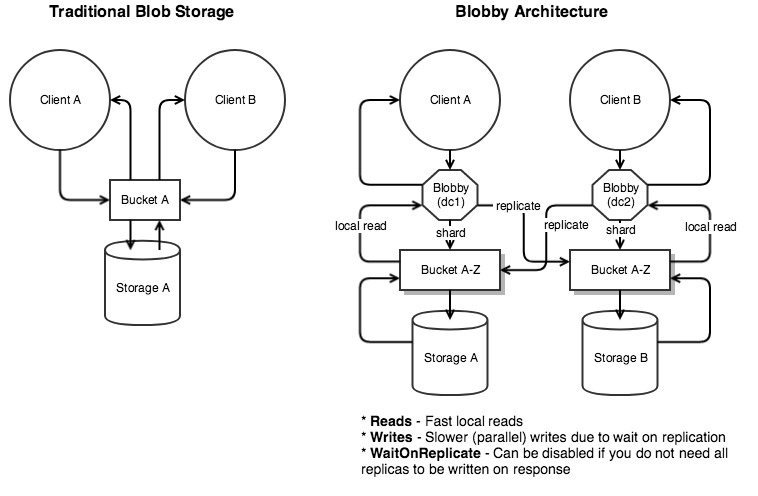
Blobby is an HTTP Proxy for Blob storage systems (such as S3) that automatically shards and replicates your data. Useful for single and multi datacenter architectures, blobby scales your storage and throughput requirements by way of sharding, as well as enables fast local reads in multi datacenter replication setups. Additionally blobby provides a simple CLI for analyzing your complex data architectures by way of storage comparisons, repairs, stats, and more.
Installation
Blobby can be installed as a local dependency of your app:
npm i blobby --save
./node_modules/.bin/blobbyOr installed globally:
npm i blobby -g
blobbyBasic Usage
Start the HTTP Proxy Server:
blobby serverCopy between storage systems:
blobby copy myOldStorage myNewStorageSee help for a full list of commands:
blobby helpOptions
A number of configuration formats are supported, including JSON, JSON5, CommonJS, and Secure Configurations.
| Option | Type | Default | Desc |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| config | arrayOf(string) | [] | One or more configuration files. If none are provided config-env will be used |
| config-dir | string | "config" | Directory of configuration files |
| config-env | string | "NODE_ENV" | Environment variable used to detect configuration |
| config-default | string | "local" | Default configuration to use if environment is not available |
| config-base | string | none | If specified will use this configuration as the base (defaults) config that will be deep merged |
| config-exts | arrayOf(string) | ['.json', '.json5', '.js'] | Supported extensions to detect for with configuration files |
| secure-config | string | none | Directory of secure configuration files |
| secure-secret | string | none | The secret required to decrypt secure configuration files |
| secure-file | string | none | File to load that holds the secret required to decrypt secure configuration files |
| mode | string | "headers" | Used when comparing files. For usage see Compare Modes |
| recursive | boolean | true | Enable deep query (recursive subdirectories) for operations that support it |
| removeGhosts | boolean | false | For repair's if true, will remove missing file instances instead of copying to missing storage |
| resume-key | string | none | If a previous command was stopped you can resume from where you left off with this option |
| date-min | string | none | Minimum date required when processing records, all others are ignored |
| date-max | string | none | Maximum date required when processing records, all others are ignored |
| retry-min | number | 1000 | Minimum timeout (in ms) for first retry, where retries are applicable |
| retry-factor | number | 2 | Multiple in time applied to retry attempts, where retries are applicable |
| retry-attempts | number | 3 | Maximum retry attempts before failure is reported, where retries are applicable |
Example using the default NODE_ENV environment variable to load config data:
blobby server --config-dir lib/configConfiguration
| Name | Type | Default | Desc |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| http | HttpBindings | { "default": { "port": 80 } } | Collection (hash for ease of merging) of HTTP bindings |
| http.{id} | HttpBinding | (required) | HTTP Binding Object |
| http.{id}.port | number | 80 | Port to bind to |
| http.{id}.host | string | undefined | Host to bind to, or nothing to use Node.js default |
| http.{id}.ssl | Object | (required if enabling SSL) | See Node.js TLS Options | http.{id}.ssl.pfx | Buffer or string | none | If string will attempt to load pfx from disk |
| http.{id}.ssl.key | Buffer or string | none | If string will attempt to load private key from disk |
| http.{id}.ssl.cert | Buffer or string | none | If string will attempt to load certificate from disk |
| httpAgent | Object|Boolean | Defaults | Initialize global http(s) agents with these options. Defaults are optimized for most scenarios. |
| httpHandler | string | undefined | If path is provided to a module (Function(req, res)) will allow parent app to peek into incoming requests. If handler returns false Blobby will ignore the request altogether and assume parent is handling the response |
| storage | StorageBindings | (required) | Collection of storage bindings |
| storage.{id} | StorageBinding| (required) | Storage Binding Object |
| storage.{id}.driver | string | (required) | Module name/path to use as storage client |
| storage.{id}.maxUploadSize | number | none | Size in bytes allowed by uploads |
| storage.{id}.cacheControl | string | "public,max-age=31536000" | Default cache control headers to apply for GET's and PUT's if file does not provide it |
| storage.{id}.accessControl | string | "public-read" | Default to publically readable. Full ACL List |
| storage.{id}.driver | string | (required) | Module name/path to use as storage client |
| storage.{id}.dirSplit | number | false | (future) If Number, auto-split paths every N characters to make listing of directories much faster |
| storage.{id}.auth | string | none | Required to support Uploads and Deletes, see Secure API Operations |
| storage.{id}.replicas | arrayOf(string) | [] | Required to support Replication, see File Replication |
| storage.{id}.options | Object | {} | Options provided to storage driver |
| retry | RetryOptions | (optional) | Retry options used by some HTTP Server operations |
| retry.min | number | 500 | Minimum timeout (in ms) for first retry |
| retry.factor | number | 2 | Multiple in time applied to retry attempts |
| retry.retries | number | 3 | Maximum retry attempts before failure is reported |
| cors | CorsOptions | (optional) | CORS access is enabled by default, for GET's only |
| cors.access-control-allow-credentials | string | true | Allow credentials |
| cors.access-control-allow-headers | string | * | Allow headers |
| cors.access-control-allow-methods | string | GET | Allow methods |
| cors.access-control-allow-origin | string | * | Allow origins |
| cors.access-control-max-age | string | 86400 | Cache duration of CORS headers |
| auth | AuthOptions | (optional) | Collection of named auth groups |
| auth.{id}.driver | string | (required) | Path of the driver to load, ala blobby-auth-header |
| auth.{id}.options | Object | (optional) | Any options to pass to the auth driver |
| auth.{id}.publicReads | Boolean | true | Set to false if GET's also require auth |
| log | LogOptions | (optional) | Options based on EventEmitter |
| log.warnings | bool | true | Log warnings to console.warn automatically. You can subscribe to client.on('warn') if you prefer |
| log.errors | bool | true | Log warnings to console.error automatically. You can subscribe to client.on('error') if you prefer |
Storage Drivers
- blobby-s3 - An S3 storage client for Blobby, powered by Knox.
- blobby-fs - A File System storage client for Blobby.
- blobby-gcp-storage - An Google Cloud storage client for Blobby.
Secure Configuration
An optional feature for sensitive credentials is to leverage the
included Config Shield
support. Any secure configuration objects will be merged into the
parent configuration object. If secure-config option is provided,
it's expected that for every configuration file, there will be a
corresponding secure configuration file using the same file name, but
under the secure-config directory.
blobby server --secure-config config/secure --secure-file config/secure/secret.txtExample for creating a secure configuration:
npm i config-shield -g
cshield config/secure/local.json config/secure/secret.txt
set storage { app1: { options: { password: 'super secret!' } } }
save
exitSee Config Shield for more advanced usage.
Server
Start HTTP Server using the provided Configuration.
blobby serverREST API
| Method | Route | Auth | Info |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| GET | /{storageId}/{filePath} | Public | Get a file from storage |
| HEAD | /{storageId}/{filePath} | Public | Get info for file from storage |
| PUT | /{storageId}/{filePath} | Secure | Create or overwrite file in storage. |
| PUT (copy) | /{storageId}/{filePath} | Secure | Copy file via experimental header x-amz-copy-source: [optional-bucket:]/source/path. |
| DELETE | /{storageId}/{filePath} | Secure | Delete file from storage |
| GET | /{storageId}/{directoryPath}/ | Secure | Get directory contents by postfixing the path with / |
| DELETE | /{storageId}/{filePath}/ | Secure | Delete directory (recursively) from storage |
Example Usage:
curl -XPUT -H "Authorization: ApiKey shhMySecret" --data-binary "@./some-file.jpg" http://localhost/myStorage/some/file.jpg
curl -XHEAD http://localhost/myStorage/some/file.jpg
curl http://localhost/myStorage/some/file.jpg
curl -H "Authorization: ApiKey shhMySecret" http://localhost/myStorage/some/
curl -XDELETE -H "Authorization: ApiKey shhMySecret" http://localhost/myStorage/some/file.jpgDefault permissions will be applied via storage.{id}.accessControl, but can be overridden via the x-amz-acl header, like so:
curl -XPUT -H "x-amz-acl: private" -H "Authorization: ApiKey shhMySecret" --data-binary "@./some-file.jpg" http://localhost/myStorage/some/file.jpgThe above examples is a perfect segway into Secure API Operations.
Secure API Operations
As indicated in Configuration, storage.{id}.auth is required to support uploads and deletes.
Example Config:
auth: {
mainAuth: {
driver: './lib/my-jwt-handler',
options: { /* options only my auth driver will understand */ }
}
},
storage: {
store1: {
driver: '...',
auth: 'mainAuth' // uploads to store1 require mainAuth
}
}If you're creating your own Authorization handler, you can export a module with the following format:
module.exports = function(req, storageId, fileKey, authConfig, cb) {
doSomethingAsync(function (err) => {
if (err) return void cb(err); // fail authorization
cb(); // authorization check passed, let them through
});
}Your handler can be synchronous or asynchronous, but cb must be invoked in either case.
Authorization Drivers
- Authorization Header - An HTTP Authorization client.
File Replication
As indicated in Configuration, storage.{id}.replicas is required to enabled
replication. An array of one or more replicas can be provided, consisting of the storage identifier
and optionally the configuration if the desired storage exists in a different environment (such
as replication across data centers).
Format is [ConfigId::]StorageId, where ConfigId only needs to be specified if from a different
environment.
Example of two replicas, one from same environment, other from a different environment:
replicas: ['myOtherStorage', 'otherConfig::AnotherStorage']Important: Successful uploads (PUT's) and deletes (DELETE's) are only confirmed if all replica's
have been written to. This is to avoid data inconsistencies and race conditions (i.e. performing an
action on an asset before it's been written in all locations). In cases where speed is more important
than consistency, querystring param waitForReplicas=0 can be set. There is no way to turn off
replication without removing from configuration, so this option will only return success once the
local storage is successful. The downside of this approach is that high availability is expected
for every replica, and uploads (or deletes) will fail if one of the replica's cannot be written to.
Full Command List
Commands:
checkdir <dir> <storage..> One-Way shallow directory compare between storage
bindings and/or environments
check <storage..> One-Way compare files between storage bindings
and/or environments
compare <storage..> Compare files between storage bindings and/or
environments
copydir <dir> <storage..> One-way shallow directory copy between storage
bindings and/or environments
copy <storage..> One-way copy of files between storage bindings
and/or environments
shard <storage> <dir> Look up the given shard for a given storage and
path
initialize <storage..> Perform any initialization tasks required by the
given storage (ex: pre-creating bucket shards in
S3)
repair <storage..> Repair files between storage bindings and/or
environments
rmdir <dir> <storage..> Delete files for the given directory and storage
bindings and/or environments
server Start HTTP API Server
acl <dir> <storage..> Set ACL's for a given directory for the given
storage bindings and/or environments
stats <storage..> Compute stats for storage bindings and/or
environmentsCompare
For comparing the difference between storage bindings
and/or environments. This is a two-way comparison. Use check
instead if you only want to do a one-way comparison.
blobby compare <storage..>Example of comparing two bindings:
blobby compare old newExample of comparing one binding across 2 datacenters:
blobby compare app --config dc1 dc2Example of comparing two bindings across 2 datacenters:
blobby compare old new --config dc1 dc2Compare Modes
blobby compare old new --mode deepAvailable modes:
fast- A simple check of file existence. Only recommended when you're comparing stores configured for immutable data.Sizecheck will also be performed, if the storage driver provides it.headers(recommended) - Similar in speed tofast, but requiresETagorLastModifiedheaders or comparison will fail. Should only be used between storage drivers that support at least one of these headers. NOTE: S3 should only be compared against other S3 storages in this mode due to their inability to overwrite these headers.deep- Performs anETagcheck if available, otherwise falls back to loading files and performing hash checks. This option can range from a little slower, to much slower, depending onETagavailability. Recommended for mutable storage comparisons where caching headers are not available (ex: comparing a file system with S3 or vice versa).force- If you want to skip comparison for any reason, this will force the comparison to fail, resulting in update of the destination for all source files. Also has the benefit of being the fastest option since destination does not need queried.
Repair
For repairing the difference between storage bindings
and/or environments. This is a two-way repair. Use copy
instead if you only want to do a one-way repair.

blobby repair <storage..>Example of syncing data between old and new storage:
blobby repair old newExample of syncing one storage across 2 datacenters:
blobby repair app --config dc1 dc2Example of syncing two storage across 2 datacenters:
blobby repair old new --config dc1 dc2For usage of mode, see Compare Modes.
Stats
Query statistics against your storage(s).
blobby stats <storage..>Example of querying stats for a single storage:
blobby stats oldInitialize
Useful one-time initialization required by some storage drivers, such as pre-creating shard buckets in S3.
blobby initialize <storage..>Example of initializing a single storage:
blobby initialize newShard
Useful for identifying the location of a given directory for storage drivers that support sharding.
blobby shard <storage> <dir>Example:
blobby shard new 'some/path'