basic-modals
v1.2.0
Published
A basic and ultra lightweight set of promise based HTML modals (prompt, alert, confirm, veil).
Downloads
10
Maintainers
Readme
Basic-Modals
An ultra lightweight set of promise based HTML modals: prompt, alert, confirm and veil.
Install
npm install basic-modalsUsage
Alert
Parameter list
This is the parameter list accepted by alert. All of them are optional.
message: Text content. The default value is "Default Message".button_ok_content: Text for the "ok button". Default value is "Ok".title: A title on the top of the modal. By default alert modals don't have any title.className: A class attribute applied to the alert's root element.id: An id attribute applied to the alert's root element.
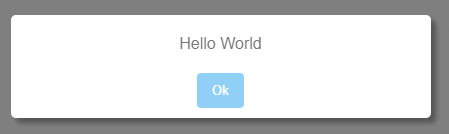
Use 1: Invoking it with a message without parameters
const { alert } = require('basic-modals')
alert('hello world')Use 2: Invoking it using parameters
alert( { message: 'hello world', button_ok_content: 'close' } )Use 3: Using it with a promise
alert( 'Accept this' )
.then( _ => console.log('The alert modal has been closed') )Use 4: Using the BasicModals global object in a browser's scope
<script>
BasicModals.alert('hello world')
</script>Confirm
Parameter list
This is the parameter list accepted by confirm. All of them are optional.
question: Text content for the question. Default value is "Default Question".button_yes_content: Text for the "yes button". Default value is "Yes".button_no_content: Text for the "no button". Default value is "No".button_cancel_content: Text for the "cancel button". Default value is null. By default confirm modals don't have a cancel button.title: A title on the top of the modal. By default confirm modals don't have any title.className: A class attribute applied to the confirm's root element.id: An id attribute applied to the confirm's root element.
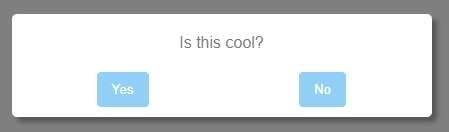
Use 1: Invoking it with a question without parameters
const { confirm } = require('basic-modals')
confirm('is this cool?')
.then( response => console.log(`The user said ${ response ? 'yes' : 'no' }`) )Use 2: Customizing button texts
confirm( { question: 'like notifications?', button_yes_content: 'always', button_no_content:'never' } )
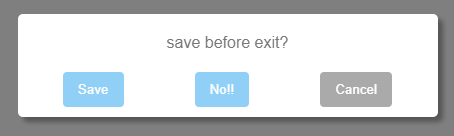
.then( response => { /* ... */ } )Use 3: Adding a Cancel button
For adding a cancel button, just add a button_cancel_content parameter with the button text content.
confirm({
question: 'save changes?',
button_yes_content: 'Of course',
button_no_content:'Never',
button_cancel_content:'Cancel'
})
.then( saved => { /* saved = true if button_yes was clicked, false if button_no was clicked */ } )
.catch( _ => { /* catch section is executed when button_cancel is clicked */ })Use 4: Using the BasicModals global object in a browser's scope
<script>
BasicModals.confirm('do you want some pizza?')
.then( response => { /* ... */ })
</script>Prompt
Parameter list
This is the parameter list accepted by prompt. All of them are optional.
question: Text content for the question. Default value is "Default Question".value: Default value in place for the input text box. Default value is '' (empty string).placeholder: Placeholder value for the input text box. Default value is '' (empty string).button_accept_content: Text for the "yes button". Default value is "Accept".button_cancel_content: Text for the "cancel button". Default value is "Cancel".title: A title on the top of the modal. Ny default prompt modals don't have any title.validate: A function to validate the input with each key press. This function will receive the value of the input field as first parameter, if the function returns...- An empty string: The input will be considered as valid, the modal will allow to the user clicks on the accept button.
- A non empty string: The input won't be considered as valid, an error message will be displayed and the accept button will be disabled.
className: A class attribute applied to the prompt's root element.id: An id attribute applied to the prompt's root element.
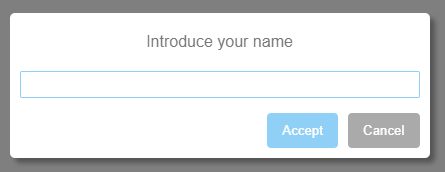
Use 1: Invoking it with a question without parameters
const { prompt } = require('basic-modals')
prompt("what's your name?")
.then( name => console.log(`The user's name is ${name}`) )Use 2: Catching when the user closes the modal
prompt("what's your name?")
.then( name => console.log(`The user's name is ${name}`) )
.catch( _ => console.warning('The user closed the modal') )Use 3: Customizing button texts, add a default response and placeholder
prompt( {
question: "what's your name?",
value: 'Eric',
placeholder: 'Your name here',
button_accept_content: 'Next',
button_cancel_content:'Quit',
})
.then( response => { /* ... */ } )Use 4: Adding validation
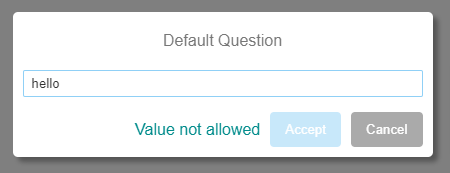
const validate = value => {
const forbidden_values = ['hello', 'world']
return forbidden_values.includes(value) ? 'Value not allowed' : ''
}
prompt( { validate }).then( response => { /* ... */ } )Use 5: Using the BasicModals global object in a browser's scope
<script>
BasicModals.prompt("what's your name?").then( response => { /* ... */ })
</script>Veil
An empty veil to block the viewport. It returns a function which will remove the veil when called.
Parameter list
This is the parameter list accepted by veil. All of them are optional.
text: Text content. The default value is '' (empty string).className: A class attribute applied to the veil's root element.id: An id attribute applied to the veil's root element.
Use 1: Invoking it and closing it after 3 seconds
const { veil } = require('basic-modals')
// render the veil
const close = veil()
// remove the veil after 3 seconds
setTimeout( close, 3000)Use 2: Adding some text to the veil
const close = veil('some text here')
setTimeout( close, 3000)or
const close = veil({ text : 'some text here' })
setTimeout( close, 3000)Use 3: The "close method" returns a promise
When calling close the veil won't be removed immediately, it will be removed asynchronously once a fade out transition ends. If you need to know when the veil is removed from the DOM you can use the promise returned by the close method.
const close = veil()
close().then( _ => do_something() )Use 4: Using the BasicModals global object in a browser's scope
<script>
const close = BasicModals.veil( { text: 'loading... please wait' } )
</script>Adding custom styles
This package will add a style tag with the modal's CSS in your head section. The classes are prefixed by .BasicModals and they should be self-explanatory, so you can add your own CSS selectors for those classes in your CSS and override / expand the default style.
Example:
/* This will turn the Ok button red for all the modals */
.BasicModalsButtonOk:hover: {
background: red
}Every modal is a children of a "veil" div with one of the following classes: BasicModalsVeilAlert, BasicModalsVeilConfirm and BasicModalsVeilPrompt. You can use this to customize the style of the different modals separately.
/* this will affect only confirm modals */
.BasicModalsVeilConfirm .BasicModalsButtonOk:hover: {
background: red
}TIP: If you need to increase the specificity of your selectors to override the default ones, just use a body tag before your selector:
body .BasicModalsButtonOk:hover: {
background: red
}or any redundant selector fragment to increase the specificity.
Adding default values
You can add default values for any parameter, so you don't need to set them again and again.
Getting access to the defaults object
const { defaults } = require('basic-modals')or, in a browser's scope:
const defaults = BasicModals.defaultsChanging the default value for the alert button
defaults.alert.button_ok_content = 'Agree'Then, for the scenario below:
alert('hello')
alert( { message: 'world' } )in both cases the "button ok" will have the text 'Agree' instead of the default 'Ok'.
More examples
The defaults object schema is:
defaults[modal_type][parameter_name]So, the defaults are available for every parameter of every modal, a few examples below:
// setting a default for the ok button in alert modals
defaults.alert.button_ok_content = 'Agree'
// setting a default for "yes" and "no" buttons in confirm modals
defaults.confirm.button_yes_content = 'Yep!'
defaults.confirm.button_no_content = 'Nope'
/* setting a default for the question and the cancel button in a
single line, overriding the original default objects */
defaults.prompt = { question:'¿?', button_cancel_content: 'Back' }
// setting a default for the veil text
defaults.veil.text = 'loading'
// setting a default for the validate function
defaults.prompt.validate = value => global_validator( value )