ai-stream-multi
v0.2.2
Published
Allows you to stream multiple chunks of text and tool calls using Vercel AI SDK
Downloads
9
Readme
streamMulti Vercel AI SDK extension
The Vercel AI SDK has several useful functions like streamUI and streamText, but currently it does not have one that allows you to stream text along with one or more tools. streamMulti enables this, introducing the notion of a Segment, which is either a tool segment or a text segment.
When function-calling capable LLMs like the newer OpenAI ChatGPT versions are executed and decide to run tools, they often return text as well. Any given response from the LLM could consist of any number of text blocks, and any number of tool invocations, in any order (though typically the returned text occurs before the tool calls).
In streamMulti, blocks of text and tools are called Segments. If the LLM just returns text, there will be just one Segment generated. If the LLM returns text plus 2 tool invocations, streamMulti will create 3 segments - one for the text and one each for the tools.
Demo
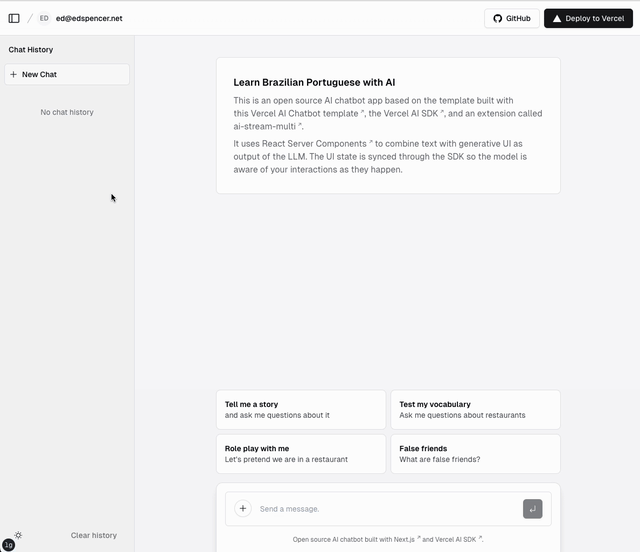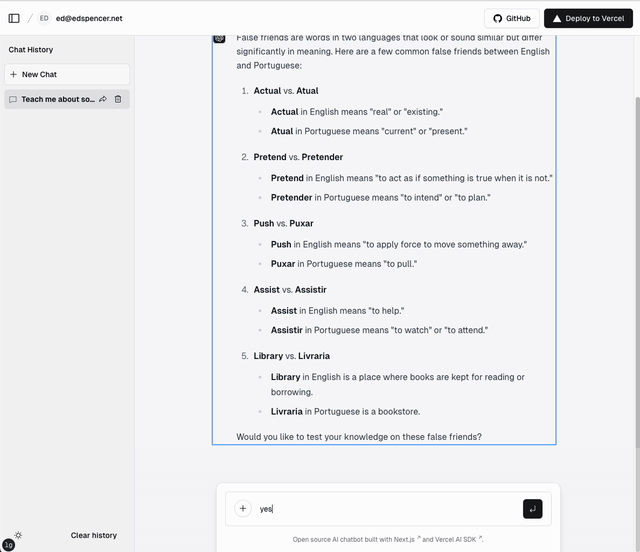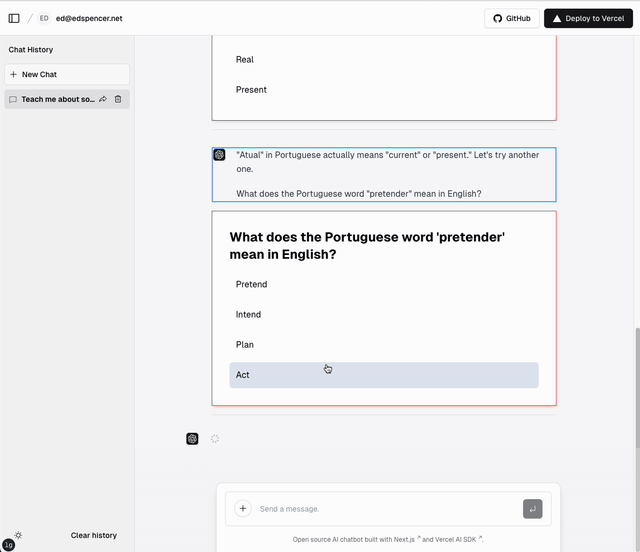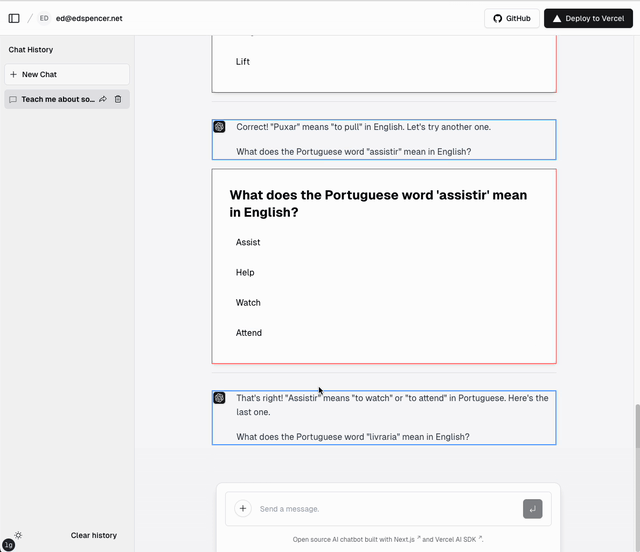
This video shows the LLM responding with both streaming text and tool calls. The streaming text elements are shown with a blue border; the tool calls are shown with a red border. The LLM is able to send both types back in the same response. The LLM may send back any number of text and/or tool blocks using ai-stream-multi.
Usage
The call to streamMulti accepts all of the same arguments as streamText does, plus onSegment, initial, textComponent and toolComponent:
- onSegment: Called each time a Segment is completed. For text segments, this is called as soon as the LLM transitions from sending text to sending tool calls.
- initial: React component (usually a spinner) that will be rendered until the LLM sends its first results back
- textComponent: Optional, allows you to pass your own React component for the streaming text response to be rendered into. Should accept a
contentprop, which will be a Vercel AI StreamableValue that can be consumed using readStreamableValue. - toolComponent: Optional, allows you to pass your own React component to wrap whatever your tool's
generatefunction outputs.
streamMulti will hopefully go away once this is natively supported inside the Vercel AI SDK. I have kept its API as close as possible to the existing streamText and streamUI functions, so that it should be easy to migrate your code back to vanilla Vercel AI SDK by swapping out streamMulti for whichever function(s) start to support this in Vercel AI SDK.
Aside from the 3 new props listed above, steamMulti also supports a generate function on each tool definition (see example). This functions exactly the same way as it does in Vercel AI SDK's streamUI function, again easing future migration.
Installation
npm install ai-stream-multiExample
90% of this code example is creating the Vercel AI setup. This example exports a function called submitUserMessage, which takes a new message from the user and passes it along with the prior conversation and other configuration to streamMulti.
The main thing to look at here is the onSegment call - this updates the Vercel AI SDK AIState with the messages from the LLM, whether they be text or tool calls. We need to also define the onFinish call (which is a streamText function) to tell AIState that we're done updating it. An initial component is passed in (a spinner) that will be rendered until the LLM has started responding.
"use server";
import { createAI, getMutableAIState } from "ai/rsc";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { Spinner } from "@/components/spinner";
import { MyComponent } from "@/components/MyComponent";
import { z } from "zod";
import { CoreMessage, generateId } from "ai";
import { streamMulti } from "ai-stream-multi";
export async function submitUserMessage(message: ClientMessage) {
"use server";
const aiState = getMutableAIState<typeof AI>();
//add the new message to the AI State
aiState.update({
...aiState.get(),
messages: [...aiState.get().messages, message],
});
//streamMulti is a thin wrapper around streamText, so its API is identical except tools can have a `generate` function
//and you can pass in an onSegment callback
const result = await streamMulti({
model: openai("gpt-4o-2024-08-06"),
initial: <Spinner />,
system: `\
You are a helpful assistant who can answer questions about a user's network and show them information
about their network.`,
messages: [
...aiState.get().messages.map((message: any) => ({
role: message.role,
content: message.content,
name: message.name,
})),
],
//called every time a new segment is completed
onSegment: (segment: any) => {
if (segment.type === "tool-call") {
const { args, toolName } = segment.toolCall;
const toolCallId = generateId();
const toolCall = {
id: generateId(),
role: "assistant",
content: [
{
type: "tool-call",
toolName,
toolCallId,
args,
},
],
} as ClientMessage;
const toolResult = {
id: generateId(),
role: "tool",
content: [
{
type: "tool-result",
toolName,
toolCallId,
result: args,
},
],
} as ClientMessage;
aiState.update({
...aiState.get(),
messages: [...aiState.get().messages, toolCall, toolResult],
});
} else if (segment.type === "text") {
const text = segment.text;
const textMessage = {
id: generateId(),
role: "assistant",
content: text,
} as ClientMessage;
aiState.update({
...aiState.get(),
messages: [...aiState.get().messages, textMessage],
});
}
},
onFinish: () => {
aiState.done(aiState.get());
},
tools: {
//let the LLM render a table for Firewalls for a given filter configuration
firewallTable: {
description: `Display a table of firewall devices, with optional filtering and display configuration.
The data will be fetched by the component, you just need to provide the configuration per the user's request.`,
parameters: z.object({
location: z.string().optional().describe("The location to fetch the firewall devices from"),
name: z.string().describe("A meaningful name for the table."),
}),
generate: async function* (config: any) {
console.log("generating firewall table");
//render your component here with whatever params the LLM passed, plus whatever you want
return <MyComponent {...config} />;
},
},
},
});
return {
id: generateId(),
content: result.ui.value,
};
}
export type ClientMessage = CoreMessage & {
id: string;
};
export type AIState = {
chatId: string;
messages: ClientMessage[];
};
export type UIState = {
id: string;
role?: string;
content: React.ReactNode;
}[];
export const AI = createAI<AIState, UIState>({
actions: {
submitUserMessage,
},
initialUIState: [] as UIState,
initialAIState: { chatId: generateId(), messages: [] } as AIState,
});